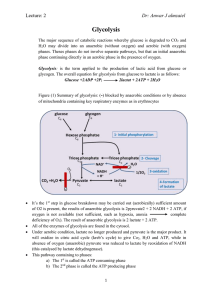
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... H2O may divide into an anaerobic (without oxygen) and aerobic (with oxygen) phases. Theses phases do not involve separate pathways, but that an initial anaerobic phase continuing directly in an aerobic phase in the presence of oxygen. Glycolysis: is the term applied to the production of lactic acid ...
... H2O may divide into an anaerobic (without oxygen) and aerobic (with oxygen) phases. Theses phases do not involve separate pathways, but that an initial anaerobic phase continuing directly in an aerobic phase in the presence of oxygen. Glycolysis: is the term applied to the production of lactic acid ...
EXAM 2 Lecture 15 1. What are cofactors? A: They are small organic
... A: Hyaluronic acid 9. What allows sequences to have specific recognition functions? A: Multiple sulfation 10. GAGs attach to core proteins to form what? A: Proteoglycan 11. GAGs are linked to serine or threonine residues how? A: Glycosidic linkage (O-linked) 12. Proteoglycans are predominantly…prote ...
... A: Hyaluronic acid 9. What allows sequences to have specific recognition functions? A: Multiple sulfation 10. GAGs attach to core proteins to form what? A: Proteoglycan 11. GAGs are linked to serine or threonine residues how? A: Glycosidic linkage (O-linked) 12. Proteoglycans are predominantly…prote ...
Plant Physiology, Fifth Edition
... Plant cells are surrounded by rigid cell walls 2 New cells are produced by dividing tissues called meristems 2 Three major tissue systems make up the plant body 4 Plant Cell Organelles 4 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers that contain proteins 4 The Endomembrane System 8 The nucleus cont ...
... Plant cells are surrounded by rigid cell walls 2 New cells are produced by dividing tissues called meristems 2 Three major tissue systems make up the plant body 4 Plant Cell Organelles 4 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers that contain proteins 4 The Endomembrane System 8 The nucleus cont ...
Flagellin perception: a paradigm for innate immunity
... respectively, leading to autophosphorylation of the kinases. Through poorly characterized steps involving the TRAF proteins, this activates the DmIKK (Drosophila homolog of Iκ B kinase) and IKK (cytokine-activated Iκ B kinase) kinases, which in turn phosphorylate Cactus and IκB, respectively. When p ...
... respectively, leading to autophosphorylation of the kinases. Through poorly characterized steps involving the TRAF proteins, this activates the DmIKK (Drosophila homolog of Iκ B kinase) and IKK (cytokine-activated Iκ B kinase) kinases, which in turn phosphorylate Cactus and IκB, respectively. When p ...
MCB Lecture 3 – ER and Golgi
... the ER and degraded in the proteasome. Recent studies have shown that if the protein could make it to the plasma membrane, it could still function properly (even though it is misfolded) Familial Hypercholesterolemia can be caused by mutations in LDL-R. Answer the following questions regarding this c ...
... the ER and degraded in the proteasome. Recent studies have shown that if the protein could make it to the plasma membrane, it could still function properly (even though it is misfolded) Familial Hypercholesterolemia can be caused by mutations in LDL-R. Answer the following questions regarding this c ...
NF-κB
... caspase 8-dependent pathways, resulting in the activation of caspase 3 . So, LUBAC plays crucial roles in the activation of the canonical NF-κB pathway. ...
... caspase 8-dependent pathways, resulting in the activation of caspase 3 . So, LUBAC plays crucial roles in the activation of the canonical NF-κB pathway. ...
Supplemental Data
... Gal80p-Gal80p interaction. Gal80p-Gal80p interactions were analyzed by complex formation with a Gal80p derivative with altered gel mobility. A fusion between Gal80p and the negatively charged activation domain of Herpes simplex VP16 (Gal80pVP16) migrates faster on native gels than Gal80p by itself. ...
... Gal80p-Gal80p interaction. Gal80p-Gal80p interactions were analyzed by complex formation with a Gal80p derivative with altered gel mobility. A fusion between Gal80p and the negatively charged activation domain of Herpes simplex VP16 (Gal80pVP16) migrates faster on native gels than Gal80p by itself. ...
Cells and Energy Cellular Respiration Chapter 2 Lesson 4 Part 1
... • How does a cell obtain energy? • How do some cells make food molecules? ...
... • How does a cell obtain energy? • How do some cells make food molecules? ...
Chapter 3: Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... 13-29 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase may be used more than once. Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that occurs in the __________________ of mitochondria ...
... 13-29 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase may be used more than once. Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that occurs in the __________________ of mitochondria ...
Click to the presentation
... ij entries denote the bond order between atoms i and j ii entries designate the number of nonbonded electrons associated with atom i ...
... ij entries denote the bond order between atoms i and j ii entries designate the number of nonbonded electrons associated with atom i ...
ap10 biology scoring guidelines - AP Central
... Transcription from the genes is affected: o Releases HDACs and recruits HATs — histone acetylases — to end chromosome repression. o Complex acts as a transcription factor that binds to a promoter (including HRE, hormone response element). Actions are slow but sustained. ...
... Transcription from the genes is affected: o Releases HDACs and recruits HATs — histone acetylases — to end chromosome repression. o Complex acts as a transcription factor that binds to a promoter (including HRE, hormone response element). Actions are slow but sustained. ...
Enzymes Notes - The Lesson Locker
... Energy is the capacity to do work. i. Energy exists in various forms, and cells transform energy from one type into another. ii. Organisms absorb energyClight or chemical energy in the form of organic moleculesCand release heat and metabolic waste products such as CO2 to their surroundings. b. Durin ...
... Energy is the capacity to do work. i. Energy exists in various forms, and cells transform energy from one type into another. ii. Organisms absorb energyClight or chemical energy in the form of organic moleculesCand release heat and metabolic waste products such as CO2 to their surroundings. b. Durin ...
VOCAB - Cellular Respiration
... The Citric Acid Cycle Also called the Krebs Cycle Takes place within the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotic cells or the cytosol of prokaryotes Second major phase of cellular respiration Back to contents ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle Also called the Krebs Cycle Takes place within the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotic cells or the cytosol of prokaryotes Second major phase of cellular respiration Back to contents ...
Cellular activity - Our eclass community
... physical barrier: separates the cell from the extracellular fluid The regulation of the passage of materials: the membrane controls the movement of materials into/out of cells Sensitivity: the cell membrane is the first part of the cell affected by any changes in the extracellular fluid Suppor ...
... physical barrier: separates the cell from the extracellular fluid The regulation of the passage of materials: the membrane controls the movement of materials into/out of cells Sensitivity: the cell membrane is the first part of the cell affected by any changes in the extracellular fluid Suppor ...
Meaning of Life Packet
... to synthesize (see description of synthesis on last page of this packet) new materials and structures. Questions 8. Two other life functions are required to carry out the life function of repair and growth: a) The materials for repair and growth are obtained by _________________ and, b) they are com ...
... to synthesize (see description of synthesis on last page of this packet) new materials and structures. Questions 8. Two other life functions are required to carry out the life function of repair and growth: a) The materials for repair and growth are obtained by _________________ and, b) they are com ...
Thyrostimulin beta subunit (Glycoprotein hormone beta 5) Human E
... distinct beta-subunits giving rise to four biologically active hormones in human: FSH, LH, TSH, and CG. FSH, LH, and TSH, mainly expressed in the anterior pituitary, are essential for coordinated endocrine regulation in the hypothalamus- pituitary axis and show to activate specific G protein-coupled ...
... distinct beta-subunits giving rise to four biologically active hormones in human: FSH, LH, TSH, and CG. FSH, LH, and TSH, mainly expressed in the anterior pituitary, are essential for coordinated endocrine regulation in the hypothalamus- pituitary axis and show to activate specific G protein-coupled ...
Genit 7
... -These disorders depend on the metabolic activity of the chemicals we ingest. -Generally, they are autosomal recessive, others are x-linked or autosomal dominant. -single gene inheritance. -Clinical pic of these diseases: they are v. much influenced by the environment and other epigenetic characteri ...
... -These disorders depend on the metabolic activity of the chemicals we ingest. -Generally, they are autosomal recessive, others are x-linked or autosomal dominant. -single gene inheritance. -Clinical pic of these diseases: they are v. much influenced by the environment and other epigenetic characteri ...
UNIT 3 – CELLULAR ENERGETICS Chapter 9
... Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. Identify where substrate-level phosphorylation and the reduction of NAD+ occur in glycolysis. Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl CoA, what molecules are produced, and how this process links glycolysis to the citric acid ...
... Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. Identify where substrate-level phosphorylation and the reduction of NAD+ occur in glycolysis. Describe where pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl CoA, what molecules are produced, and how this process links glycolysis to the citric acid ...
An abundant TIP expressed in mature highly vacuolated cells
... using ultrathin sections of leaves, petioles and roots. Antibody labelling of So-dTIP was visualized by electron and light microscopy using gold-conjugated secondary antibodies followed by silver enhancement. High density of gold particles could be observed in the vacuolar membrane with virtually no ...
... using ultrathin sections of leaves, petioles and roots. Antibody labelling of So-dTIP was visualized by electron and light microscopy using gold-conjugated secondary antibodies followed by silver enhancement. High density of gold particles could be observed in the vacuolar membrane with virtually no ...























