An Introduction to Cells
... The Cellular Level of Organization An Introduction to Cells • Learning Outcomes • 3-1 List the functions of the plasma membrane and the structural features that enable it to perform those functions. • 3-2 Describe the organelles of a typical cell, and indicate the specific functions of each. • 3-3 E ...
... The Cellular Level of Organization An Introduction to Cells • Learning Outcomes • 3-1 List the functions of the plasma membrane and the structural features that enable it to perform those functions. • 3-2 Describe the organelles of a typical cell, and indicate the specific functions of each. • 3-3 E ...
Respiration Test Study Guide
... 31. Where in the mitochondria is the ETC located? _____________ _____________________ 32. In lactic acid fermentation, lactic acid (lactate) is produced from _________________. 33. ____________ and _____________ carry electrons to the electron transport chain. 34. The equation for aerobic cellular r ...
... 31. Where in the mitochondria is the ETC located? _____________ _____________________ 32. In lactic acid fermentation, lactic acid (lactate) is produced from _________________. 33. ____________ and _____________ carry electrons to the electron transport chain. 34. The equation for aerobic cellular r ...
InduciI)le Expression of Calcyclin, a Gene with
... different cell types have different surface antigens and biochem ical properties. It has been suggested that N, I. and S cells are multipotent cells able to differentiate one from the other. In any case, they are clearly different and may represent a different stage in which the transformation occur ...
... different cell types have different surface antigens and biochem ical properties. It has been suggested that N, I. and S cells are multipotent cells able to differentiate one from the other. In any case, they are clearly different and may represent a different stage in which the transformation occur ...
Midterm Exam Advanced Biochemistry II (Answer) 1. At equilibrium
... Answer Under anaerobic conditions, the phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase reactions are essential. The shortcut in the mutant yeast would bypass the formation of an acyl phosphate by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and therefore would not allow the formation of 1,3-bisphosphoglycer ...
... Answer Under anaerobic conditions, the phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase reactions are essential. The shortcut in the mutant yeast would bypass the formation of an acyl phosphate by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and therefore would not allow the formation of 1,3-bisphosphoglycer ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... elastin) • Produced by fibroblasts. • A group of three proteins, fibrillin-1, -2 and -3. • The main role - maintaining the structural integrity of tissues, the regulation of cytokines – TGF-b • In humans, defects in the fibrillin-1 and fibrillin-2 genes have been linked to diseases that affect the c ...
... elastin) • Produced by fibroblasts. • A group of three proteins, fibrillin-1, -2 and -3. • The main role - maintaining the structural integrity of tissues, the regulation of cytokines – TGF-b • In humans, defects in the fibrillin-1 and fibrillin-2 genes have been linked to diseases that affect the c ...
Chapter 5, part A
... • Entner-Doudoroff pathway: – Produces NADPH and ATP – Does not involve glycolysis – Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Agrobacterium ...
... • Entner-Doudoroff pathway: – Produces NADPH and ATP – Does not involve glycolysis – Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, Agrobacterium ...
投影片 1
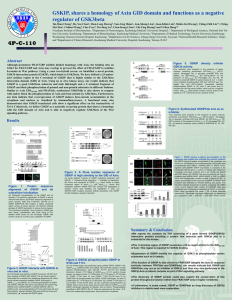
... vector control plasmid (right panel). (C) HEK293 cells were transfected with increasing concentration of GSKIP as indicated. Each value represents the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. Statistically significant differences as determined by a Student’s t test: * p<0.005, ** p<0.0005 versus con ...
... vector control plasmid (right panel). (C) HEK293 cells were transfected with increasing concentration of GSKIP as indicated. Each value represents the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. Statistically significant differences as determined by a Student’s t test: * p<0.005, ** p<0.0005 versus con ...
S4 Table.
... regulation; Binding site of tobacco TGA1a (a member of the bZip family of TFs; Abiotic and biotic stress differentially stimulate "as-1 element" activity "C-box" according to the nomenclature of ACGT elements by Foster et al. (1994); One of ACGT elements; Factors groups 2 and 3 have affinity for C-b ...
... regulation; Binding site of tobacco TGA1a (a member of the bZip family of TFs; Abiotic and biotic stress differentially stimulate "as-1 element" activity "C-box" according to the nomenclature of ACGT elements by Foster et al. (1994); One of ACGT elements; Factors groups 2 and 3 have affinity for C-b ...
EN-1-27-99
... Ex – signs and symptoms If the endocrine system operates normally, you don’t see any consequences If it doesn’t, you see consequences (signs and symptoms) Usually due to an abnormality in hormone concentration ...
... Ex – signs and symptoms If the endocrine system operates normally, you don’t see any consequences If it doesn’t, you see consequences (signs and symptoms) Usually due to an abnormality in hormone concentration ...
Unit 1 Notes
... Types of Enzyme Reactions The chemical reactions in a cell involve either breaking down (degrading) large molecules or building up (synthesising) large molecules. Breakdown reactions convert large molecules into small molecules. For example the carbohydrate starch is a very large molecule which can ...
... Types of Enzyme Reactions The chemical reactions in a cell involve either breaking down (degrading) large molecules or building up (synthesising) large molecules. Breakdown reactions convert large molecules into small molecules. For example the carbohydrate starch is a very large molecule which can ...
1 Food intake regulation
... peptide hormone produced in the small intestine in response to feeding. It causes the release of digestive enzymes from the (exocrine) pancreas, bile from the galbladder and release of H+ in parietal cells of the stomach. In the central nervous system it acts as an anorexigen (hunger suppressant). P ...
... peptide hormone produced in the small intestine in response to feeding. It causes the release of digestive enzymes from the (exocrine) pancreas, bile from the galbladder and release of H+ in parietal cells of the stomach. In the central nervous system it acts as an anorexigen (hunger suppressant). P ...
Supplemental Methods Statistical analysis. All NMR spectra were
... model (4). The classification accuracy of the O-PLS-DA model was established from the predicted samples in the 7-fold cross-validation cycle. Intermediates metabolites from β-oxidation, amino acid, NAD, SCFA, TCA and Urea metabolic pathways assigned in urine and stool 1H NMR spectra were relatively ...
... model (4). The classification accuracy of the O-PLS-DA model was established from the predicted samples in the 7-fold cross-validation cycle. Intermediates metabolites from β-oxidation, amino acid, NAD, SCFA, TCA and Urea metabolic pathways assigned in urine and stool 1H NMR spectra were relatively ...
Gene Section NCR2 (natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 2)
... viral entry into target cells (Vieillard et al., 2005). The 3S peptide of gp41 binds to its receptor gC1qR, a receptor for the globular domain of complement component 1q, on CD4+ T cells (Fausther-Bovendo et al., 2010). Binding of the 3S motif to this receptor activates a signaling cascade involving ...
... viral entry into target cells (Vieillard et al., 2005). The 3S peptide of gp41 binds to its receptor gC1qR, a receptor for the globular domain of complement component 1q, on CD4+ T cells (Fausther-Bovendo et al., 2010). Binding of the 3S motif to this receptor activates a signaling cascade involving ...
PowerPoint - Scranton Prep Biology
... modifications can affect gene expression Chemical modification of DNA bases or histone proteins can result in epigenetic inheritance. – Certain enzymes can add a methyl group to DNA bases, without changing the sequence of the bases. – Individual genes are usually more methylated in cells in which ...
... modifications can affect gene expression Chemical modification of DNA bases or histone proteins can result in epigenetic inheritance. – Certain enzymes can add a methyl group to DNA bases, without changing the sequence of the bases. – Individual genes are usually more methylated in cells in which ...
Signal Transduction I
... o Targeted therapies to growth factors, receptors o Intracellular signaling “downstream” of receptors - key pathways: Ras/MAPK, Src, PI3K o Intracellular signaling defects in cancer o Targeted therapies to intracellular signaling molecules o TNF and TRAIL ...
... o Targeted therapies to growth factors, receptors o Intracellular signaling “downstream” of receptors - key pathways: Ras/MAPK, Src, PI3K o Intracellular signaling defects in cancer o Targeted therapies to intracellular signaling molecules o TNF and TRAIL ...
T Cell Co-inhibitory Receptors-Functions and Signalling Mechanisms
... T cell activation is a central event in the adaptive immune response and essentially begins with the recognition of an antigenic peptide in the context of a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on an antigen-presenting cell by the T cell receptor (TCR). The process of T cell activation consists of ...
... T cell activation is a central event in the adaptive immune response and essentially begins with the recognition of an antigenic peptide in the context of a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on an antigen-presenting cell by the T cell receptor (TCR). The process of T cell activation consists of ...
Red Blood Cell Metabolism: Objectives
... 2. It can go back into the glycolysis pathway with the enzyme: 2,3diphosphoglycerate phosphatase ii. Increase in 2,3-DPG will inhibit Diphosphoglycerate mutase b. 2,3-DPG’s concentration during hypoxia (like high altitude, heart failure, anemia, obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis, congen ...
... 2. It can go back into the glycolysis pathway with the enzyme: 2,3diphosphoglycerate phosphatase ii. Increase in 2,3-DPG will inhibit Diphosphoglycerate mutase b. 2,3-DPG’s concentration during hypoxia (like high altitude, heart failure, anemia, obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis, congen ...
vocab - Cellular Respiration
... Catabolic pathway that consumes oxygen and organic molecules, producing ATP. This is the most efficient catabolic pathway and is carried out in most eukaryotic cells and many prokaryotic organisms ...
... Catabolic pathway that consumes oxygen and organic molecules, producing ATP. This is the most efficient catabolic pathway and is carried out in most eukaryotic cells and many prokaryotic organisms ...
Biology 202 Lecture Notes
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland See figure 15.6 The hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland by the infundibulum. Hypothalamic neurons go directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) and release oxytocin and ADH (antidiuretic hormone or vasopressin) Releasing and inhibiting h ...
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland See figure 15.6 The hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland by the infundibulum. Hypothalamic neurons go directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) and release oxytocin and ADH (antidiuretic hormone or vasopressin) Releasing and inhibiting h ...