Cell - mrhubbardsci
... cross the cell membrane by net diffusion. H2O molecules are small enough that they also move into the cell by simple diffusion. facilitated diffusion – occurs with the help of proteins (protein channels & protein carrier molecules); is slower than simple diffusion, is important for large water-solub ...
... cross the cell membrane by net diffusion. H2O molecules are small enough that they also move into the cell by simple diffusion. facilitated diffusion – occurs with the help of proteins (protein channels & protein carrier molecules); is slower than simple diffusion, is important for large water-solub ...
Q01to05
... ATP can be produced in the mitochondria of liver cells and transported in the blood for use by the muscle ATP doesn’t move out of cells ...
... ATP can be produced in the mitochondria of liver cells and transported in the blood for use by the muscle ATP doesn’t move out of cells ...
BR22, a 26 kDa thyroid transcription factor-1 associated protein
... Institute and the James M. Collins Center for Biomedical Research to J.C. Weissler. ...
... Institute and the James M. Collins Center for Biomedical Research to J.C. Weissler. ...
Hemolytic Anemias due to Other Intracorpuscular Defects
... The condition is exacerbated during sleep when CO2 levels rise and the pH drops. It is believed to be caused by an abnormal clone of stem cells (idiopathic or due to marrow damage). All of the cell lines lack several anchored membrane proteins and this makes them abnormally sensitive to the co ...
... The condition is exacerbated during sleep when CO2 levels rise and the pH drops. It is believed to be caused by an abnormal clone of stem cells (idiopathic or due to marrow damage). All of the cell lines lack several anchored membrane proteins and this makes them abnormally sensitive to the co ...
significance of the putative upstream polybasic nuclear localisation
... Interferon-gamma (IFNγ) accomplishes its multiple biological effects by activating the STAT transcription factors, which are translocated to the nucleus through a specific nuclear localization sequence(s) (NLS) located in the IFNγ molecule. Two putative NLS have been pointed out in the human interfe ...
... Interferon-gamma (IFNγ) accomplishes its multiple biological effects by activating the STAT transcription factors, which are translocated to the nucleus through a specific nuclear localization sequence(s) (NLS) located in the IFNγ molecule. Two putative NLS have been pointed out in the human interfe ...
Revving up glycolysis
... enzyme present nearly universally across tumor types. Based on that research, activating the enzyme might be most effective in tumors with low levels of serine or oxygen.1–3 Pyruvate kinase occurs as two isoforms: pyruvate kinase M1 isozyme (PKM1) is expressed by most nonproliferative healthy tissue ...
... enzyme present nearly universally across tumor types. Based on that research, activating the enzyme might be most effective in tumors with low levels of serine or oxygen.1–3 Pyruvate kinase occurs as two isoforms: pyruvate kinase M1 isozyme (PKM1) is expressed by most nonproliferative healthy tissue ...
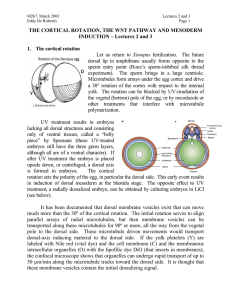
the cortical rotation, the wnt pathway
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
Adenovirus Overrides Cellular Checkpoints for Protein Translation
... or mutant E4-ORF4, to endogenous c-Src. These data suggest that the ability of E4-ORF4 to activate mTOR is most likely through its binding and modulation of the regulatory B subunit of PP2A. Thus, E4-ORF4 may reveal a novel role for PP2A in the mTOR signaling pathway. Previously, in both yeast mutan ...
... or mutant E4-ORF4, to endogenous c-Src. These data suggest that the ability of E4-ORF4 to activate mTOR is most likely through its binding and modulation of the regulatory B subunit of PP2A. Thus, E4-ORF4 may reveal a novel role for PP2A in the mTOR signaling pathway. Previously, in both yeast mutan ...
Chemistry-Biology Interface Symposium Frontiers at the
... Biochemistry, Newark, DE 19716. Organophosphorus compounds (OPs) such as sarin (GB) and soman (GD) are the most toxic chemicals created. They exert toxic effects by inactivating acetylcholinesterase and binding to secondary targets. OP inhibitors are hemi-substrates for enzymes of the serine hydrola ...
... Biochemistry, Newark, DE 19716. Organophosphorus compounds (OPs) such as sarin (GB) and soman (GD) are the most toxic chemicals created. They exert toxic effects by inactivating acetylcholinesterase and binding to secondary targets. OP inhibitors are hemi-substrates for enzymes of the serine hydrola ...
Part 1 - ISpatula
... - Natural products, especially those derived from plants, have been used for medicinal purposes since ancient times - Clay tablets of the Babylonian, Assyrian, and Sumerian eras dated 2600 - 4000 BC are thought to be the earliest recordings of plant usage as herbal remedies - Egyptians also had many ...
... - Natural products, especially those derived from plants, have been used for medicinal purposes since ancient times - Clay tablets of the Babylonian, Assyrian, and Sumerian eras dated 2600 - 4000 BC are thought to be the earliest recordings of plant usage as herbal remedies - Egyptians also had many ...
Endocrine System PPT
... 1. Steroid (lipid-based) hormones – steroid hormones are lipidbased, so they can easily pass through the phospholipid bilayer. Once in the cell, they target receptors deep in the cytoplasm or the nucleus. Ex. Testosterone, estrogen, aldosterone 2. Peptide (protein-based) hormones – peptide hormones ...
... 1. Steroid (lipid-based) hormones – steroid hormones are lipidbased, so they can easily pass through the phospholipid bilayer. Once in the cell, they target receptors deep in the cytoplasm or the nucleus. Ex. Testosterone, estrogen, aldosterone 2. Peptide (protein-based) hormones – peptide hormones ...
Insight into Metabolic Reprogramming in Tumor Cells
... some of the most frequently altered gene products/signaling pathways observed in tumor cells. It is now clear that oncogenes and tumor suppressors can directly regulate metabolic pathways. More importantly, we now know that measuring the resulting metabolite changes can yield a better understanding ...
... some of the most frequently altered gene products/signaling pathways observed in tumor cells. It is now clear that oncogenes and tumor suppressors can directly regulate metabolic pathways. More importantly, we now know that measuring the resulting metabolite changes can yield a better understanding ...
TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE
... oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are negative and positive controls for the TCA ...
... oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are negative and positive controls for the TCA ...
Welcome to Our Microbial Genetics Class
... A controlling factor can either inhibit or activate transcription. Although the responses to the presence of metabolites are different, both induction and repression are forms of negative control: mRNA synthesis proceeds more rapidly in the absence of the active controlling factor. The rate of mRNA ...
... A controlling factor can either inhibit or activate transcription. Although the responses to the presence of metabolites are different, both induction and repression are forms of negative control: mRNA synthesis proceeds more rapidly in the absence of the active controlling factor. The rate of mRNA ...
The relationship between amino acid sequences and protein folds.
... site and and intracellular recognition site for a GTP-binding protein. •! Single-transmembrane (1-TMS) catalytic receptors- contain a single transmembrane segment, an extracellular ligand domain and intracellular catalytic domain (tyrosine kinase or guanylyl cyclase) •! Oligomeric ion channels- cont ...
... site and and intracellular recognition site for a GTP-binding protein. •! Single-transmembrane (1-TMS) catalytic receptors- contain a single transmembrane segment, an extracellular ligand domain and intracellular catalytic domain (tyrosine kinase or guanylyl cyclase) •! Oligomeric ion channels- cont ...
3. Biological membranes and cell compartments
... Biological membranes are two-dimensional fluids Biological membranes are dynamic, molecules can cross it thanks to specific proteins Biological membranes are often associated to the cell cytoskeletons The plasma membrane is anchored to the extracellular matrix by adhesion proteins ...
... Biological membranes are two-dimensional fluids Biological membranes are dynamic, molecules can cross it thanks to specific proteins Biological membranes are often associated to the cell cytoskeletons The plasma membrane is anchored to the extracellular matrix by adhesion proteins ...
Identification and characterization of heavy metal induced
... and heavy metal homeostasis and how they subsequently trigger signals to activate physiological responses is rather incomplete (Hung et al., 2005). In the next chapter (4.2) some factors known to be related to these processes are discussed. ...
... and heavy metal homeostasis and how they subsequently trigger signals to activate physiological responses is rather incomplete (Hung et al., 2005). In the next chapter (4.2) some factors known to be related to these processes are discussed. ...
GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS – I: Brief Review of: AEROBIC
... • In the presence of O2 cancer cells convert Glucose to Lactate, which is then released in blood, picked up by the Liver for conversion to Glucose via Gluconeogenesis; • Conversion of Lactate to Glucose in Liver requires 6 ATP; • Cancer cells produce net of 2 ATP per molecule of Glucose converted in ...
... • In the presence of O2 cancer cells convert Glucose to Lactate, which is then released in blood, picked up by the Liver for conversion to Glucose via Gluconeogenesis; • Conversion of Lactate to Glucose in Liver requires 6 ATP; • Cancer cells produce net of 2 ATP per molecule of Glucose converted in ...