Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
... Apoptosis pathway. Two distinct, but not mutually exclusive, pathways of apoptotic cell death have been well desribed: extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. In the extrinsic pathway, soluble or cell surface death ligands, such as TNF-α and Fas ligand, bind to the corresponding death receptors inducing a ...
... Apoptosis pathway. Two distinct, but not mutually exclusive, pathways of apoptotic cell death have been well desribed: extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. In the extrinsic pathway, soluble or cell surface death ligands, such as TNF-α and Fas ligand, bind to the corresponding death receptors inducing a ...
Ass4_ans - The University of Sydney
... An influx of Ca2+ through activation of a ligand-gated ion channel Displacement of GDP by GTP on a G protein bound to the receptor Dissociation of the receptor from a dimer to a monomer form Inhibition of intra-cellular adenyl cyclase ...
... An influx of Ca2+ through activation of a ligand-gated ion channel Displacement of GDP by GTP on a G protein bound to the receptor Dissociation of the receptor from a dimer to a monomer form Inhibition of intra-cellular adenyl cyclase ...
Cancer:19.3 A. - Oncogenes – cancer causing genes found in some
... - Tumor suppressor gene products normally inhibit cell division. - Any decrease in normal activity can lead to uncontrolled cell growth. - Some TS genes repair damaged DNA so that cancer-causing mutations don’t build up. - Some TS genes control adhesion of cells to each other or ECM. - Some TS genes ...
... - Tumor suppressor gene products normally inhibit cell division. - Any decrease in normal activity can lead to uncontrolled cell growth. - Some TS genes repair damaged DNA so that cancer-causing mutations don’t build up. - Some TS genes control adhesion of cells to each other or ECM. - Some TS genes ...
lecture notes
... with SoxB1 to activate Msx in the neural tube, but not in any of the other tissues receiving BMP signals. 7. There are many other examples of signaling pathways working in concert with localized TFs to obtain tissue-specific patterns of gene expression. We previously discussed localized expression o ...
... with SoxB1 to activate Msx in the neural tube, but not in any of the other tissues receiving BMP signals. 7. There are many other examples of signaling pathways working in concert with localized TFs to obtain tissue-specific patterns of gene expression. We previously discussed localized expression o ...
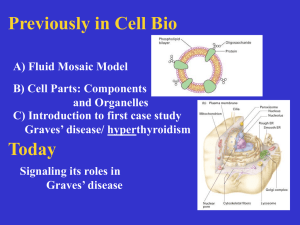
Chapter 5 Chemical Messengers
... • Signal transduction is the process of producing a response afer a messenger binds to a receptor in the target • Receptor Properties o Specificity: One messenger may bind to many receptor types o One target may have many types of receptors o The number of receptors per cell varies and is dynamic • ...
... • Signal transduction is the process of producing a response afer a messenger binds to a receptor in the target • Receptor Properties o Specificity: One messenger may bind to many receptor types o One target may have many types of receptors o The number of receptors per cell varies and is dynamic • ...
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors
... • Stopped by protein phosphatases that continually remove phosphate groups from target proteins • Stopped by endocytosis of receptors and their bound extracellular signals ...
... • Stopped by protein phosphatases that continually remove phosphate groups from target proteins • Stopped by endocytosis of receptors and their bound extracellular signals ...
RICHARD STANLEY, Ph.D. Positions: Research interests:
... We have defined the biological roles of colony stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and its receptor (CSF-1R) using biochemical, cell biological and mouse genetic approaches. We have elucidated the developmental and physiological roles of CSF-1 and CSF-1R, showing that they regulate the production of macrop ...
... We have defined the biological roles of colony stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and its receptor (CSF-1R) using biochemical, cell biological and mouse genetic approaches. We have elucidated the developmental and physiological roles of CSF-1 and CSF-1R, showing that they regulate the production of macrop ...
Cell Communication
... • Caffeine has many effects on the body, but the most noticeable is that it keeps us awake. • The caffeine molecule is large and polar, so it doesn’t diffuse easily across the cell membrane. • Instead it binds to receptors on the surfaces of nerve cells in the brain. ...
... • Caffeine has many effects on the body, but the most noticeable is that it keeps us awake. • The caffeine molecule is large and polar, so it doesn’t diffuse easily across the cell membrane. • Instead it binds to receptors on the surfaces of nerve cells in the brain. ...
Outline 4.2 (M)
... One of the most important membrane pumps in animal cells is a carrier protein called the sodiumpotassium pump. In a complete cycle, the sodium-potassium pump transports three sodium ions, Na+, out of a cell and two potassium ions, K+, into the cell. The sodium-potassium pump has four steps: 1. Three ...
... One of the most important membrane pumps in animal cells is a carrier protein called the sodiumpotassium pump. In a complete cycle, the sodium-potassium pump transports three sodium ions, Na+, out of a cell and two potassium ions, K+, into the cell. The sodium-potassium pump has four steps: 1. Three ...
European Respiratory Society Annual Congress 2013
... (Wingless/integrase-1) signaling pathway has been implicated in various proliferative diseases, including lung cancer. In addition, the phosphorylation of GSK-3β, a key regulator of the WNT pathway, correlates with ASM hypertrophy. The WNT pathway may therefore be of particular significance in under ...
... (Wingless/integrase-1) signaling pathway has been implicated in various proliferative diseases, including lung cancer. In addition, the phosphorylation of GSK-3β, a key regulator of the WNT pathway, correlates with ASM hypertrophy. The WNT pathway may therefore be of particular significance in under ...
CELL SIGNALLING
... • There are four major classes of eicosanoids • prostaglandins, prostacyclins, thromboxanes,and leukotrienes • Are continuously synthesized in the plasma membrane and released to the cell exterior • Where they are degraded by enzymes Involved in various biological activities • Contraction of smooth ...
... • There are four major classes of eicosanoids • prostaglandins, prostacyclins, thromboxanes,and leukotrienes • Are continuously synthesized in the plasma membrane and released to the cell exterior • Where they are degraded by enzymes Involved in various biological activities • Contraction of smooth ...
Activation of protein kinase A and protein kinase C via intracellular
... behavior could contribute to uncontrolled cell growth. You’re looking for those proteins which are part of a growth factor-initiated Receptor Protein Tyrosine Kinase-mediated intracellular signaling pathway IRS-1 (required for insulin-induced signaling) Janus kinases (JAKs) (part of the Tyr kinase a ...
... behavior could contribute to uncontrolled cell growth. You’re looking for those proteins which are part of a growth factor-initiated Receptor Protein Tyrosine Kinase-mediated intracellular signaling pathway IRS-1 (required for insulin-induced signaling) Janus kinases (JAKs) (part of the Tyr kinase a ...
Protein Synthesis Is a Major Function of Cells
... • Free ribosomes are found in the cell’s cytoplasm • Produces proteins for use within the cell • Attached ribosomes are found on the endoplasmic reticulum • Produces proteins for use in the cell membrane or is exported outside of the cell ...
... • Free ribosomes are found in the cell’s cytoplasm • Produces proteins for use within the cell • Attached ribosomes are found on the endoplasmic reticulum • Produces proteins for use in the cell membrane or is exported outside of the cell ...
Gene Section CRTC1 (CREB regulated transcription coactivator 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Abnormal Protein MECT1-MAML2; in the fusion protein the first 171 aa including the basic domain of MAML2 are replaced by 42 aa of MECT1; there are no sequence similarities in the N-terminal domains of MAML2 and MECT1; the fusion protein activates transcription of the Notch target gene HES1 independe ...
... Abnormal Protein MECT1-MAML2; in the fusion protein the first 171 aa including the basic domain of MAML2 are replaced by 42 aa of MECT1; there are no sequence similarities in the N-terminal domains of MAML2 and MECT1; the fusion protein activates transcription of the Notch target gene HES1 independe ...
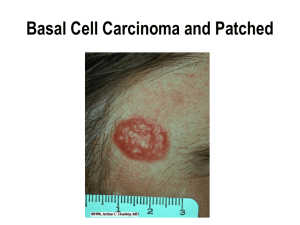
The Sonic Hedgehog
... • Like most skin cancers, BCC is primarily caused by sun exposure, specifically UVB rays • These rays cause mutations in DNA including deletions and substitutions ...
... • Like most skin cancers, BCC is primarily caused by sun exposure, specifically UVB rays • These rays cause mutations in DNA including deletions and substitutions ...
ppt
... Yeast aging and CR Regulation of Yeast Replicative Life Span by TOR and Sch9 in Response to Nutrients. (Kaeberlein et al., 2005) HST2 Mediates SIR2-Independent LifeSpan Extension by Calorie Restriction. (Lamming et al., 2005) ...
... Yeast aging and CR Regulation of Yeast Replicative Life Span by TOR and Sch9 in Response to Nutrients. (Kaeberlein et al., 2005) HST2 Mediates SIR2-Independent LifeSpan Extension by Calorie Restriction. (Lamming et al., 2005) ...
Endocrine System 1 - Napa Valley College
... - bind to intracellular (cytoplasmic) receptors 2. Lipophobic (water-soluble) e.g., epinephrine, insulin, antidiuretic hormone - do not cross plasma membrane - bind to receptors on the PM C. Cellular Mechanisms of Hormone Action 1. Lipophilic Hormones - hormone binds to cytoplasmic receptor intracel ...
... - bind to intracellular (cytoplasmic) receptors 2. Lipophobic (water-soluble) e.g., epinephrine, insulin, antidiuretic hormone - do not cross plasma membrane - bind to receptors on the PM C. Cellular Mechanisms of Hormone Action 1. Lipophilic Hormones - hormone binds to cytoplasmic receptor intracel ...
In This Issue
... migration correlated with 3D motility and found that the extent to which cells formed membrane protrusions in response to different growth factors was a reliable predictor of their 3D migratory behavior. Strengthening the connection, cytoskeletal inhibitors that preferentially block 3D migration als ...
... migration correlated with 3D motility and found that the extent to which cells formed membrane protrusions in response to different growth factors was a reliable predictor of their 3D migratory behavior. Strengthening the connection, cytoskeletal inhibitors that preferentially block 3D migration als ...
In This Issue
... migration correlated with 3D motility and found that the extent to which cells formed membrane protrusions in response to different growth factors was a reliable predictor of their 3D migratory behavior. Strengthening the connection, cytoskeletal inhibitors that preferentially block 3D migration als ...
... migration correlated with 3D motility and found that the extent to which cells formed membrane protrusions in response to different growth factors was a reliable predictor of their 3D migratory behavior. Strengthening the connection, cytoskeletal inhibitors that preferentially block 3D migration als ...
Outline
... binding of the ligand ? • Introducing fluorophores at residues that exhibit changes in fluorescence emission • due to changes in conformation (open vs close) ...
... binding of the ligand ? • Introducing fluorophores at residues that exhibit changes in fluorescence emission • due to changes in conformation (open vs close) ...
Wnt signaling
... phosphorylation of three domains of Dishevelled (Dvl), a family of cytosolic signal transducer molecules. • Activation of Dvl ultimately leads to phosphorylation and consequently inhibition of GSK-3 • Inhibition of GSK-3 results in stabilisation and consequent cytosolic accumulation of -catenin, ...
... phosphorylation of three domains of Dishevelled (Dvl), a family of cytosolic signal transducer molecules. • Activation of Dvl ultimately leads to phosphorylation and consequently inhibition of GSK-3 • Inhibition of GSK-3 results in stabilisation and consequent cytosolic accumulation of -catenin, ...
Presentation
... hormone that prevents brain cells from dying could protect cells through a previously unknown pathway. We also aimed to develop a method to determine the concentration of a certain protein in cell samples using results of a normally qualitative analysis technique. ...
... hormone that prevents brain cells from dying could protect cells through a previously unknown pathway. We also aimed to develop a method to determine the concentration of a certain protein in cell samples using results of a normally qualitative analysis technique. ...
Slide 1 - ParklandNatSciWiki
... 1. Signal amplification – Binding of signal to single receptor can cause the synthesis of many cAMP that activate PKA, each PKA can phosphorylate many proteins ...
... 1. Signal amplification – Binding of signal to single receptor can cause the synthesis of many cAMP that activate PKA, each PKA can phosphorylate many proteins ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.