Apoptosis Oncogenes
... • Products of tumor supresssor genes suppress the cell division cycle or promote apoptosis • Tumor suppressor gene must lose activity to contribute to cancer • Both alleles of a tumor suppressor gene must be inactivated or lost in order to eliminate their tumor suppression activity from a cell • Ret ...
... • Products of tumor supresssor genes suppress the cell division cycle or promote apoptosis • Tumor suppressor gene must lose activity to contribute to cancer • Both alleles of a tumor suppressor gene must be inactivated or lost in order to eliminate their tumor suppression activity from a cell • Ret ...
@ tin Scruppsfusrencu Iusrnurs
... According to Tainer, "Defectsin cell cycle control is a commontrait of all cancers. Understandingthe structureand function of this protein could be a first step in leading us to the developmentof more effective anti-cancertherapiesand/or an enhancementof those currently utilized." ...
... According to Tainer, "Defectsin cell cycle control is a commontrait of all cancers. Understandingthe structureand function of this protein could be a first step in leading us to the developmentof more effective anti-cancertherapiesand/or an enhancementof those currently utilized." ...
Concept 11.2 Reception: A signaling molecule binds to a receptor
... -Intracellular receptor proteins are found in the cytoplasm or nucleus of target cells. -Signaling molecules, a.k.a. chemical messengers can permeate through the membrane to reach these receptors Signaling molecules are hydrophobic or small enough to cross the ...
... -Intracellular receptor proteins are found in the cytoplasm or nucleus of target cells. -Signaling molecules, a.k.a. chemical messengers can permeate through the membrane to reach these receptors Signaling molecules are hydrophobic or small enough to cross the ...
M001 Signalling to the translation initiation machinery Nahum
... activity is also controlled by phosphorylation of 4E-BPs (eIF4Ebinding proteins). 4E-BPs repress cap-dependent translation by binding to eIF4E. Upon their phosphorylation, 4E-BPs dissociate from eIF4E. The signalling pathway that leads to phosphorylation of 4E-BPs is the PI3K pathway. The mammalian ...
... activity is also controlled by phosphorylation of 4E-BPs (eIF4Ebinding proteins). 4E-BPs repress cap-dependent translation by binding to eIF4E. Upon their phosphorylation, 4E-BPs dissociate from eIF4E. The signalling pathway that leads to phosphorylation of 4E-BPs is the PI3K pathway. The mammalian ...
Hic1
... - In presence of Wnt, it can interact with coactivator, β-catenin, Pygo, Bcl9, Chromatin remodeling complexes. ...
... - In presence of Wnt, it can interact with coactivator, β-catenin, Pygo, Bcl9, Chromatin remodeling complexes. ...
Cell Communication
... responds to its environment. Ex: Use of chemical messengers by microbes to communicate with nearby cells and to regulate specific pathways in response to population density. Question: Why would bacteria need to communicate with other ...
... responds to its environment. Ex: Use of chemical messengers by microbes to communicate with nearby cells and to regulate specific pathways in response to population density. Question: Why would bacteria need to communicate with other ...
Typical Signal Transduction Pathway
... • Enduring Understanding 3.D Cells communicate by generating, transmitting and receiving chemical signals. • EK 3D2: Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to ...
... • Enduring Understanding 3.D Cells communicate by generating, transmitting and receiving chemical signals. • EK 3D2: Cells communicate with each other through direct contact with other cells or from a distance via chemical signaling c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to ...
Cell Signalling Pathways
... Long term: In event of increased cytokine signalling, SOCS transcribed from STAT. They bind to phosphotyrosines in activated receptors or via SH2 domain + target them for ubiquitin mediated degradation. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) Function: cell growth + proliferation. Examples: EGF, insulin fi ...
... Long term: In event of increased cytokine signalling, SOCS transcribed from STAT. They bind to phosphotyrosines in activated receptors or via SH2 domain + target them for ubiquitin mediated degradation. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) Function: cell growth + proliferation. Examples: EGF, insulin fi ...
Types of Hormones
... nucleus of the target cells; 3. Together, they form a “hormone-receptor complex” 4. which serves as a transcription factor, promoting or inhibiting 5. transcription and 6. translation of genes. ...
... nucleus of the target cells; 3. Together, they form a “hormone-receptor complex” 4. which serves as a transcription factor, promoting or inhibiting 5. transcription and 6. translation of genes. ...
Cell Communication Word Document
... Chemicals that are used for this type of long-distance communication are called hormones. ...
... Chemicals that are used for this type of long-distance communication are called hormones. ...
Division of Morphogenesis
... of nectin-2, one of the nectin family members, from early embryos resulted in incomplete neural fold formation. Cellular analyses revealed less accumulation of F-actin at the apical surface, causing an aberrant apical constriction, a cellshape change that is required for neural tube folding. Further ...
... of nectin-2, one of the nectin family members, from early embryos resulted in incomplete neural fold formation. Cellular analyses revealed less accumulation of F-actin at the apical surface, causing an aberrant apical constriction, a cellshape change that is required for neural tube folding. Further ...
Problem Set 3 Answer Key, Spring 2003 1) The following
... A) You overexpress a B-catenin mutant that has a serine to alanine mutation thatprevents its phosphorylation by GSK3. The mutant B-catenin cannot be inhibited by GSK3 so it will always be active and induce the expression of the alkaline phosphatase gene. Thus the ratio of alkaline phosphatase mRNA ...
... A) You overexpress a B-catenin mutant that has a serine to alanine mutation thatprevents its phosphorylation by GSK3. The mutant B-catenin cannot be inhibited by GSK3 so it will always be active and induce the expression of the alkaline phosphatase gene. Thus the ratio of alkaline phosphatase mRNA ...
Meili, R and R.A. Firtel (2002). Leading the way. Nature Cell Biol. 4
... The ability to chemotax, that is, to sense and move in the direction of chemical signals, is a feature of a wide variety of eukaryotic cells. Chemotaxis is important for many biological responses, from the movement of leukocytes towards sites of infection or inflammation to the aggregation of Dictyo ...
... The ability to chemotax, that is, to sense and move in the direction of chemical signals, is a feature of a wide variety of eukaryotic cells. Chemotaxis is important for many biological responses, from the movement of leukocytes towards sites of infection or inflammation to the aggregation of Dictyo ...
Slide () - AccessEmergency Medicine
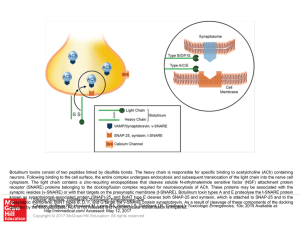
... neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the nerve cell cytoplasm. The light chain contains a zinc-requiring endopeptidase that cleaves soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor (NSF) attachment prot ...
... neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the nerve cell cytoplasm. The light chain contains a zinc-requiring endopeptidase that cleaves soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor (NSF) attachment prot ...
pathway_cell_models
... These have recently come to the forefront due to emergence of high-throughput technologies. ...
... These have recently come to the forefront due to emergence of high-throughput technologies. ...
Modification of the K-Ras Signaling Pathway
... • Uncontrolled cell proliferation • Cells acquire ability to sustain growth without external growth queues (IGF, PDGF, etc) • MAPK (Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK) Pathway • The gene encoding Ras isoforms is mutated in many human cancers ...
... • Uncontrolled cell proliferation • Cells acquire ability to sustain growth without external growth queues (IGF, PDGF, etc) • MAPK (Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK) Pathway • The gene encoding Ras isoforms is mutated in many human cancers ...
Cell to Cell Communication
... (WAS), is due to the absence of a single relay protein. – It leads to abnormal bleeding, eczema, and a predisposition to infections and leukemia. – The WAS protein interacts with the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton and several signaling pathways, including those that regulate immune cell prolifer ...
... (WAS), is due to the absence of a single relay protein. – It leads to abnormal bleeding, eczema, and a predisposition to infections and leukemia. – The WAS protein interacts with the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton and several signaling pathways, including those that regulate immune cell prolifer ...
ch_11 cell communication
... (WAS), is due to the absence of a single relay protein. – It leads to abnormal bleeding, eczema, and a predisposition to infections and leukemia. – The WAS protein interacts with the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton and several signaling pathways, including those that regulate immune cell prolifer ...
... (WAS), is due to the absence of a single relay protein. – It leads to abnormal bleeding, eczema, and a predisposition to infections and leukemia. – The WAS protein interacts with the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton and several signaling pathways, including those that regulate immune cell prolifer ...
Mid-semester examination Developmental Biology (BSE652
... fate to the ventral cells of the neural tube. A) Describe how you will demonstrate that the floor plate fate is imparted to cells of the neural tube by the notochord. Start by choosing the model organism in which you will demonstrate this and then describe the experiment(s) you will perform to show ...
... fate to the ventral cells of the neural tube. A) Describe how you will demonstrate that the floor plate fate is imparted to cells of the neural tube by the notochord. Start by choosing the model organism in which you will demonstrate this and then describe the experiment(s) you will perform to show ...
Feb 21 Bacteria, DNA Technology, and Cell Communication
... Local communication-gap junctions plasmodesmata, cell-cell recognistion Local signaling- paracrine, synaptic (secreting cell target cell) Long distance communication in the body hormonal signaling Signal transduction- reception, transduction, response Steroid hormones G-protein-linked plasma membr ...
... Local communication-gap junctions plasmodesmata, cell-cell recognistion Local signaling- paracrine, synaptic (secreting cell target cell) Long distance communication in the body hormonal signaling Signal transduction- reception, transduction, response Steroid hormones G-protein-linked plasma membr ...
11 Cell Communication
... Most signals never enter a cell. The signal is received at the membrane and passed on. Exception - intracellular receptors ...
... Most signals never enter a cell. The signal is received at the membrane and passed on. Exception - intracellular receptors ...
Principles of Biochemistry
... • The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways are typically comprised of a three-member protein kinase cascade. • Specificity of MAPK responses is achieved by activation of different three-kinase modules. • There are at least three sets of mammalian MAPK modules. – the extracellular-sig ...
... • The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways are typically comprised of a three-member protein kinase cascade. • Specificity of MAPK responses is achieved by activation of different three-kinase modules. • There are at least three sets of mammalian MAPK modules. – the extracellular-sig ...
New twists on embryonic patterning
... Another conserved protein is Twisted-gastrulation (Tsg), a small BMP-binding protein that has a pattern of expression similar to that of BMP-4/Dpp (reviewed in De Robertis et al., 2000). Tsg has limited sequence homology to the Chordin CR repeats and functions as a co-factor of Chordin in an intrica ...
... Another conserved protein is Twisted-gastrulation (Tsg), a small BMP-binding protein that has a pattern of expression similar to that of BMP-4/Dpp (reviewed in De Robertis et al., 2000). Tsg has limited sequence homology to the Chordin CR repeats and functions as a co-factor of Chordin in an intrica ...
ReliaTech GmbH Recombinant Human p16
... p16-INK4a is a nuclear protein that regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclin dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) and CDK6. p16-INK4a inhibits CDK activity by binding to the CDK molecules in a manner that interferes with their ability to interact with cyclin D. This activity has the effect of suppressing ...
... p16-INK4a is a nuclear protein that regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclin dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) and CDK6. p16-INK4a inhibits CDK activity by binding to the CDK molecules in a manner that interferes with their ability to interact with cyclin D. This activity has the effect of suppressing ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.