
Examination in Bi3016 Molecular Cell Biology
... humans and mediate signals from various extracellular stimuli. a. Describe how G-protein coupled receptors can mediate signals via phospholipids localized in the plasma membrane. b. Explain how changes in Ca2+ concentration inside a cell contribute to regulation of enzyme activity and protein functi ...
... humans and mediate signals from various extracellular stimuli. a. Describe how G-protein coupled receptors can mediate signals via phospholipids localized in the plasma membrane. b. Explain how changes in Ca2+ concentration inside a cell contribute to regulation of enzyme activity and protein functi ...
Lesson
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
bio4751Ch15-Part2W
... F. Signaling over short or long distances G. Autocrine signaling H. Cells respond to specific combinations of factors I. Signaling through gap junctions J. Different cells respond differently to the same signal molecules K. Nuclear receptors are ligand-activated gene regulatory proteins L. Three cla ...
... F. Signaling over short or long distances G. Autocrine signaling H. Cells respond to specific combinations of factors I. Signaling through gap junctions J. Different cells respond differently to the same signal molecules K. Nuclear receptors are ligand-activated gene regulatory proteins L. Three cla ...
Neoplasia lecture 7
... • APC is an important component of these destruction complexes • Loss of APC .. B catenin not degraded and WNT pathway activated without the WNT • This leads to transcription of growth promoting genes cyclin D1 ,MYC and transcription regulators: TWIST AND SLUG that repress e cadherin and thus reduce ...
... • APC is an important component of these destruction complexes • Loss of APC .. B catenin not degraded and WNT pathway activated without the WNT • This leads to transcription of growth promoting genes cyclin D1 ,MYC and transcription regulators: TWIST AND SLUG that repress e cadherin and thus reduce ...
Neurotrophin Signaling
... death in numerous cells, including injured neurons, but promotes migration, growth and survival in other cells. In the next development (2008), NGF was found to exist in both unprocessed ('pro') and mature forms. On some cells the mature NGF preferentially activates TrkA, whereas proNGF only activat ...
... death in numerous cells, including injured neurons, but promotes migration, growth and survival in other cells. In the next development (2008), NGF was found to exist in both unprocessed ('pro') and mature forms. On some cells the mature NGF preferentially activates TrkA, whereas proNGF only activat ...
Introduction to Hormone Signalling Receptors and signals theme
... FITC [E[E-BSABSA-FITC] (nM) 100 nM ...
... FITC [E[E-BSABSA-FITC] (nM) 100 nM ...
functional screening of human genes in zebrafish animal model
... embryos display variable phenotypes from developmental defects to neuronal cell death in injected embryos. Many of these genes were involved in not only developmental process but also diseases, such as cancer. After these phenotypebased screening, homologous zebrafish genes were cloned and further f ...
... embryos display variable phenotypes from developmental defects to neuronal cell death in injected embryos. Many of these genes were involved in not only developmental process but also diseases, such as cancer. After these phenotypebased screening, homologous zebrafish genes were cloned and further f ...
Structural Basis of Wnt Recognition by Frizzled
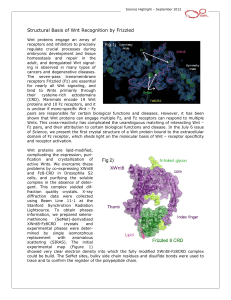
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
Powerpoint
... Cell Signaling by Oxidants: Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPK) and Activator Protein – 1 (AP-1) Brooke T. Mossman* and Maria Stern ...
... Cell Signaling by Oxidants: Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPK) and Activator Protein – 1 (AP-1) Brooke T. Mossman* and Maria Stern ...
Fundamentals of Cell Biology
... Figure 11.02: Signaling pathways use linear, convergent, divergent, and branched signaling pathways to generate complex responses to external signals. ...
... Figure 11.02: Signaling pathways use linear, convergent, divergent, and branched signaling pathways to generate complex responses to external signals. ...
3. Activator, gene-specific transcription facotr
... Affinity column with protein A-VP16 activation domain HeLa cell extract eluate In vitro transcription VP16-bound factor recovers transcription; TFIID ...
... Affinity column with protein A-VP16 activation domain HeLa cell extract eluate In vitro transcription VP16-bound factor recovers transcription; TFIID ...
Cancer and Genome Evolution
... Genes Associated with Cancer • Oncogenes – cancer-causing genes in certain retroviruses – Mutated versions of proto-oncogenes – genes that code for proteins that stimulate normal cell growth and division – Caused by the following • Movement of DNA within the genome • Amplification of a proto-oncoge ...
... Genes Associated with Cancer • Oncogenes – cancer-causing genes in certain retroviruses – Mutated versions of proto-oncogenes – genes that code for proteins that stimulate normal cell growth and division – Caused by the following • Movement of DNA within the genome • Amplification of a proto-oncoge ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... The nine vertebrate PAX transcription factors (PAX1-PAX9) play essential roles during early development and organogenesis. Pax genes were identified in vertebrates using their homology with the Drosophila melanogaster paired gene DNA-binding domain. PAX1-9 functions are largely conserved throughout v ...
... The nine vertebrate PAX transcription factors (PAX1-PAX9) play essential roles during early development and organogenesis. Pax genes were identified in vertebrates using their homology with the Drosophila melanogaster paired gene DNA-binding domain. PAX1-9 functions are largely conserved throughout v ...
Plant Response to Signals
... 1. Light signal is detected by the phytochrome receptor, which then activates at least 2 signal 2. One pathway uses cGMP as a 2nd transduction pathways messenger to activate 3. Both pathways leada protein kinase. to expression of genes The pathway forother proteins that involves increases Ca2+ that ...
... 1. Light signal is detected by the phytochrome receptor, which then activates at least 2 signal 2. One pathway uses cGMP as a 2nd transduction pathways messenger to activate 3. Both pathways leada protein kinase. to expression of genes The pathway forother proteins that involves increases Ca2+ that ...
Signal Receptors 4 types
... signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually by turning genes on or off in the nucleus ...
... signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually by turning genes on or off in the nucleus ...
[Science] 31 MAY 2013 VOL 340, ISSUE 6136, PAGES 1005-1132
... Canonical Wnt signaling plays a rate-limiting role in regulating self-renewal and differentiation in mouse embryonic ste m cells (ESCs). We have previously shown that mutation in the Apc (adenomatous polyposis coli) tumor suppressor gen e constitutively activates Wnt signaling in ESCs and inhibits t ...
... Canonical Wnt signaling plays a rate-limiting role in regulating self-renewal and differentiation in mouse embryonic ste m cells (ESCs). We have previously shown that mutation in the Apc (adenomatous polyposis coli) tumor suppressor gen e constitutively activates Wnt signaling in ESCs and inhibits t ...
Ch 11 PP - medmood.com
... IV. Changes in signal transduction pathways can alter cellular response. A. Conditions where signal transduction is blocked or defective can be deleterious, preventative or prophylactic. ...
... IV. Changes in signal transduction pathways can alter cellular response. A. Conditions where signal transduction is blocked or defective can be deleterious, preventative or prophylactic. ...
Classical pathway
... Over 30 circulating and membrane-bound proteins (synthesized in liver and other cells- immune and epithelial) Acts as a cascade (one event must occur before another takes place) ...
... Over 30 circulating and membrane-bound proteins (synthesized in liver and other cells- immune and epithelial) Acts as a cascade (one event must occur before another takes place) ...
A new blueprint for plant pathogen resistance
... the interior of the cell and the transcriptional response in the nucleus. In their Nature paper, Sheen and colleagues confirm previous studies in various plant systems, including both monocot6 ...
... the interior of the cell and the transcriptional response in the nucleus. In their Nature paper, Sheen and colleagues confirm previous studies in various plant systems, including both monocot6 ...
AP Biology - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... (4) The changes in the enzyme and G protein are only temporary because the G pr otein also functions as a enzyme – in other words, it then hydrolyzes its bound GTP to GDP. Now inactive again, the G protein protein allows the pathway to is no longer present. ...
... (4) The changes in the enzyme and G protein are only temporary because the G pr otein also functions as a enzyme – in other words, it then hydrolyzes its bound GTP to GDP. Now inactive again, the G protein protein allows the pathway to is no longer present. ...
Cell Signaling
... A) They are seen in "primitive" cells such as yeast. B) Yeast cells signal each other for mating. C) Signal transduction molecules found in distantly related organisms are similar. D) Signals can be sent long distances by cells. E) Most signals are received by cell surface receptors. ...
... A) They are seen in "primitive" cells such as yeast. B) Yeast cells signal each other for mating. C) Signal transduction molecules found in distantly related organisms are similar. D) Signals can be sent long distances by cells. E) Most signals are received by cell surface receptors. ...
Cross-species Extrapolation of an Adverse Outcome Pathway for Ecdysteroid Receptor Activation
... for Ecdysteroid Receptor Activation Carlie A. LaLone University of Minnesota Water Resources Center ...
... for Ecdysteroid Receptor Activation Carlie A. LaLone University of Minnesota Water Resources Center ...
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4
... component of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein MST1/MST2, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylate ...
... component of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein MST1/MST2, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylate ...
Abstract
... (Nox) isozymes can be activated by toll-like receptors (TLRs), which are key regulators of innate immunity. TLRs recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on the surface of pathogens as well as altered host proteins and lipoproteins and stimulate inflammatory signaling pathways. We sh ...
... (Nox) isozymes can be activated by toll-like receptors (TLRs), which are key regulators of innate immunity. TLRs recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on the surface of pathogens as well as altered host proteins and lipoproteins and stimulate inflammatory signaling pathways. We sh ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.












![[Science] 31 MAY 2013 VOL 340, ISSUE 6136, PAGES 1005-1132](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004177342_1-c0251bf41a2d53b02343ec7da5e25607-300x300.png)







