Gene Section RGS2 (regulator of G protein signaling 2, 24kDa) -
... G proteins. It is classified into the B/R4 subfamily. ...
... G proteins. It is classified into the B/R4 subfamily. ...
Classroom Cell Communication
... cytoplasm or within the nucleus. The signals can be sent over short distances (direct contact) or over long distances (via the blood stream). Some signals that are nonpolar may enter the cell without reception and act directly in the nucleus. There are three major signal transduction pathways: G-Pro ...
... cytoplasm or within the nucleus. The signals can be sent over short distances (direct contact) or over long distances (via the blood stream). Some signals that are nonpolar may enter the cell without reception and act directly in the nucleus. There are three major signal transduction pathways: G-Pro ...
Victor YU - National University of Singapore
... (7) B.T. Chua, C. Volbracht, K.O. Tan, R. Li, and V.C. Yu and P. Li Mitochondrial translocation to cofilin is an early step in apoptosis induction. Nature Cell Biology, 12: 1083-1089, 2003 (8) S. Baksh, S. Tommasi, S. Fenton, V.C. Yu, L.M. Martins, G.P. Pfeifer, F. Latiff, J. Downward and B.G. Neel ...
... (7) B.T. Chua, C. Volbracht, K.O. Tan, R. Li, and V.C. Yu and P. Li Mitochondrial translocation to cofilin is an early step in apoptosis induction. Nature Cell Biology, 12: 1083-1089, 2003 (8) S. Baksh, S. Tommasi, S. Fenton, V.C. Yu, L.M. Martins, G.P. Pfeifer, F. Latiff, J. Downward and B.G. Neel ...
Principles of cell signaling Lecture 2
... Ligands for receptor tyrosine kinases are called growth factors ...
... Ligands for receptor tyrosine kinases are called growth factors ...
Ch11-cell-communicat..
... This leads the G protein to substitute GTP for GDP. The G protein then binds with another membrane protein, often an enzyme, altering its activity and leading to a cellular response. The G protein can also act as a GTPase enzyme and hydrolyzes the GTP, which activated it, to GDP. This change ...
... This leads the G protein to substitute GTP for GDP. The G protein then binds with another membrane protein, often an enzyme, altering its activity and leading to a cellular response. The G protein can also act as a GTPase enzyme and hydrolyzes the GTP, which activated it, to GDP. This change ...
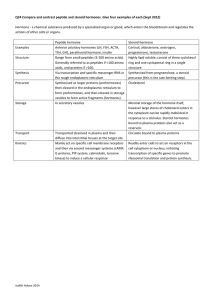
Q24 Compare and contrast peptide and steroid hormones. Give four
... however large stores of cholesterol esters in the cytoplasm can be rapidly mobilized in response to a stimulus. Steroid hormones bound to plasma proteins also act as a reservoir. Transport Transported ...
... however large stores of cholesterol esters in the cytoplasm can be rapidly mobilized in response to a stimulus. Steroid hormones bound to plasma proteins also act as a reservoir. Transport Transported ...
Microbial Metabolism
... allows for overproduction of a product, production of more than one product by the same organism, or synthesis of modified products ...
... allows for overproduction of a product, production of more than one product by the same organism, or synthesis of modified products ...
Recombinant human c-Kit (mutated V559 D) protein
... C family members. Phosphorylation at Tyr-568 is required for interaction with PTPN11/SHP-2, CRK (isoform Crk-II) and members of the SRC tyrosine-protein kinase family. Phosphorylation at Tyr-570 is required for interaction with PTPN6/SHP-1. Phosphorylation at Tyr-703, Tyr-823 and Tyr-936 is importan ...
... C family members. Phosphorylation at Tyr-568 is required for interaction with PTPN11/SHP-2, CRK (isoform Crk-II) and members of the SRC tyrosine-protein kinase family. Phosphorylation at Tyr-570 is required for interaction with PTPN6/SHP-1. Phosphorylation at Tyr-703, Tyr-823 and Tyr-936 is importan ...
lin-15
... 5 Key Signal transduction pathways Are critical for development and homeostasis All are involved in Cancer ...
... 5 Key Signal transduction pathways Are critical for development and homeostasis All are involved in Cancer ...
www.cmu.edu.cn
... Signaling molecules • Signaling molecules, which are released by signal-producing cells, reach and transfer biological signals to their target cells to initiate specific cellular responses. ...
... Signaling molecules • Signaling molecules, which are released by signal-producing cells, reach and transfer biological signals to their target cells to initiate specific cellular responses. ...
(2) G Protein-Coupled Receptors
... Signaling molecules • Signaling molecules, which are released by signal-producing cells, reach and transfer biological signals to their target cells to initiate specific cellular responses. ...
... Signaling molecules • Signaling molecules, which are released by signal-producing cells, reach and transfer biological signals to their target cells to initiate specific cellular responses. ...
Hao Nguyen
... If ras is always in the inactive form (ras-GDP), it cannot perform its function, which is to bind to raf-1 and allows it (raf-1) to associate with the plasma membrane. Normally, ras can do this through the hydrolysis of the GTP that is bound to it when it (ras) is in the active form (ras-GTP). Witho ...
... If ras is always in the inactive form (ras-GDP), it cannot perform its function, which is to bind to raf-1 and allows it (raf-1) to associate with the plasma membrane. Normally, ras can do this through the hydrolysis of the GTP that is bound to it when it (ras) is in the active form (ras-GTP). Witho ...
Proteins relevant for Stem Cell Research - Bio
... fibroblast genome. The reprogrammed cells thus obtained resemble ESC in morphology, gene expression, and in the capacity to form teratomas in immune-deficient mice. Recombinant human Sox2 is a 34.3 kDa protein containing 317 amino-acid residues. ...
... fibroblast genome. The reprogrammed cells thus obtained resemble ESC in morphology, gene expression, and in the capacity to form teratomas in immune-deficient mice. Recombinant human Sox2 is a 34.3 kDa protein containing 317 amino-acid residues. ...
Models and Theory in Molecular Cell Biology
... At present mathematical modelling in systems biology focusses to a large extent on supramolecular processes taking place within individual cells. These processes are generally organised in the form of reaction networks, such as metabolic pathways, signal transduction networks and gene regulatory net ...
... At present mathematical modelling in systems biology focusses to a large extent on supramolecular processes taking place within individual cells. These processes are generally organised in the form of reaction networks, such as metabolic pathways, signal transduction networks and gene regulatory net ...
Chapter 11: Cell Communication - Biology E
... 22. Explain what has happened with the binding of the ligand to the receptor. ! When the ligand binds to the receptor and the gate opens, specific ions can flow through the channel and rapidly change the concentration of that particular ion inside the cell. This change may directly affect the activ ...
... 22. Explain what has happened with the binding of the ligand to the receptor. ! When the ligand binds to the receptor and the gate opens, specific ions can flow through the channel and rapidly change the concentration of that particular ion inside the cell. This change may directly affect the activ ...
No Slide Title
... activity of the complex maintains the tight association between deacetylated histones and chromatin that results in repressed gene transcription. When 9-cis retinoic acid binds to the RAR-RXR heterodimeric complex the corepressor complex dissociates from the receptor complex with simultaneous recrui ...
... activity of the complex maintains the tight association between deacetylated histones and chromatin that results in repressed gene transcription. When 9-cis retinoic acid binds to the RAR-RXR heterodimeric complex the corepressor complex dissociates from the receptor complex with simultaneous recrui ...
ABSTRACT Mast cells are critical component of the immune system
... triggers signaling cascade leading to cell degranulation and cytokine production. The antigenmediated signaling through the FcεRI is critically dependent on interplay with intracellular proteintyrosine kinases that phosphorylate the ITAM motifs and many other components of the signaling pathway. Thi ...
... triggers signaling cascade leading to cell degranulation and cytokine production. The antigenmediated signaling through the FcεRI is critically dependent on interplay with intracellular proteintyrosine kinases that phosphorylate the ITAM motifs and many other components of the signaling pathway. Thi ...
Summary of Cell Communication Chapter 11
... At each step in a pathway, the signal is transduced into a different form, commonly a conformational change in a protein. 1. Protein phosphorylation The addition of a phosphate in order to activate an enzyme is a widespread mechanism in regulating protein activity. The general name of an enzyme that ...
... At each step in a pathway, the signal is transduced into a different form, commonly a conformational change in a protein. 1. Protein phosphorylation The addition of a phosphate in order to activate an enzyme is a widespread mechanism in regulating protein activity. The general name of an enzyme that ...
Types of signals and types of receptors and which occur in Thyroid
... Negative feedback loop: What is it and why is it important? ...
... Negative feedback loop: What is it and why is it important? ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.