HUMAN-CTNND1_isform 2ABC(Y174) Antibody
... Binds to and inhibits the transcriptional repressor ZBTB33, which may lead to activation of target genes of the Wnt signaling pathway (By similarity). Associates with and regulates the cell adhesion properties of both C-, E- and N-cadherins, being critical for their surface stability. Implicated bot ...
... Binds to and inhibits the transcriptional repressor ZBTB33, which may lead to activation of target genes of the Wnt signaling pathway (By similarity). Associates with and regulates the cell adhesion properties of both C-, E- and N-cadherins, being critical for their surface stability. Implicated bot ...
Special Guest Speaker Dr. Christopher Colbert
... a few, such as biphenyl 2,3-dioxygenase from Pandoraea pnomenusa B-356 (BPDO), can potently degrade a large variety of PCB congeners. We have elucidated the structural basis for the broad PCB oxidation properties of BPDO, based on information from our structural studies combined with activity assays ...
... a few, such as biphenyl 2,3-dioxygenase from Pandoraea pnomenusa B-356 (BPDO), can potently degrade a large variety of PCB congeners. We have elucidated the structural basis for the broad PCB oxidation properties of BPDO, based on information from our structural studies combined with activity assays ...
Signal Transduction II
... PROLIFERATION CELL SURVIVAL . Aaronson, Growth factor and receptor tyrosine kinases. Sci. STKE 2005, tr6 (2005). ...
... PROLIFERATION CELL SURVIVAL . Aaronson, Growth factor and receptor tyrosine kinases. Sci. STKE 2005, tr6 (2005). ...
G protein–coupled receptors
... Small G proteins are involved in many cellular functions. Members of the Rab family of these proteins regulate the rate of vesicle traffic between the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, endosomes, and the cell membrane . Another family of small GTP-binding proteins, the Rho/Rac f ...
... Small G proteins are involved in many cellular functions. Members of the Rab family of these proteins regulate the rate of vesicle traffic between the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, endosomes, and the cell membrane . Another family of small GTP-binding proteins, the Rho/Rac f ...
Signal networks and pathways
... • In liver or muscle cells in presence of the ligand epinephrine hormone (also called adernalin) increase in the cAMP concentration (in the cytoplasm) – activates protein kinase, – active protein kinases then converts inactive phosphorylase kinase to active form by ATP dependent phosphorylation, – a ...
... • In liver or muscle cells in presence of the ligand epinephrine hormone (also called adernalin) increase in the cAMP concentration (in the cytoplasm) – activates protein kinase, – active protein kinases then converts inactive phosphorylase kinase to active form by ATP dependent phosphorylation, – a ...
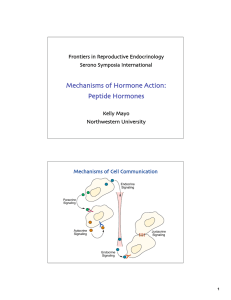
Mechanisms of Hormone Action: Peptide Hormones
... Receptor phosphorylation Effector proteins bind receptor - direct enzymatic function - STAT proteins STATs phosphorylated ...
... Receptor phosphorylation Effector proteins bind receptor - direct enzymatic function - STAT proteins STATs phosphorylated ...
AB205Abstract_proteomics_conference
... salinity stressand control cell lines. A large number of proteins were identified as pathogenesis related (PR) proteins belonging to class 10 and suggested that these differentially phosphorylated proteins play a crucial role in plant defense system against salinity stress. Full length PR10 was isol ...
... salinity stressand control cell lines. A large number of proteins were identified as pathogenesis related (PR) proteins belonging to class 10 and suggested that these differentially phosphorylated proteins play a crucial role in plant defense system against salinity stress. Full length PR10 was isol ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 5 cellular communication click here
... called kinases – kinases act to phosphorylate their targets – either activating them or inhibiting them – this speeds up/slows down physiological responses within the cell – phosphodiesterase inactivates cAMP quickly many second messengers are made in cells in response to specific hormones ...
... called kinases – kinases act to phosphorylate their targets – either activating them or inhibiting them – this speeds up/slows down physiological responses within the cell – phosphodiesterase inactivates cAMP quickly many second messengers are made in cells in response to specific hormones ...
PsychedelicAgents_JacobBarnes
... Mutations cause enhanced cyclins or inhibited p16 leading to unrestricted cell cycle Mutation in p53 inhibits apoptosis Metastasis ...
... Mutations cause enhanced cyclins or inhibited p16 leading to unrestricted cell cycle Mutation in p53 inhibits apoptosis Metastasis ...
Cell signalling
... • very potent neurotoxins • bind to receptor and prevent opening of Na+ channel – e.g. cobratoxin from Indian cobra ...
... • very potent neurotoxins • bind to receptor and prevent opening of Na+ channel – e.g. cobratoxin from Indian cobra ...
Plasma Membrane/ Cell Wall Continuum
... RGD-binding proteins • RGD: amino acid sequence of extracellular adhesive ...
... RGD-binding proteins • RGD: amino acid sequence of extracellular adhesive ...
presentation Prof Khwaja
... •Erythropoietin and prevention of apoptosis in erythroid progenitors •G-CSF and proliferation in myeloid progenitors ...
... •Erythropoietin and prevention of apoptosis in erythroid progenitors •G-CSF and proliferation in myeloid progenitors ...
Snímek 1
... mediate psychosocial effects on cancer progression . Arrow (A) represents activation of endocrine stress-responses associated with psychological distress and other psychosocial factors. Repeated stress-response activation may hypothetically lead to dysregulation of circadian rhythms (B), while aberr ...
... mediate psychosocial effects on cancer progression . Arrow (A) represents activation of endocrine stress-responses associated with psychological distress and other psychosocial factors. Repeated stress-response activation may hypothetically lead to dysregulation of circadian rhythms (B), while aberr ...
Cell Structure and Function - Crossword
... 2. Converted to pyruvate during glycolysis 3. Bodies which pinch off vesicles at end. 4. Site of protein manufacture. 5. Keeps cell contents separate from external environment. 6. Strong substance that makes up cell walls. 7. Spaces between cells are called ____________ cellular spaces. 8. Network o ...
... 2. Converted to pyruvate during glycolysis 3. Bodies which pinch off vesicles at end. 4. Site of protein manufacture. 5. Keeps cell contents separate from external environment. 6. Strong substance that makes up cell walls. 7. Spaces between cells are called ____________ cellular spaces. 8. Network o ...
Unit 1 PPT 6 (2cii Signal transduction)
... Once bound to cAMP these kinases are activated, releasing active catalytic subunits. These can diffuse through the nuclear pores where, for instance, they can phosphorylate gene regulatory proteins called cAMP response element binding proteins (CREBs), which can then stimulate gene transcription. ...
... Once bound to cAMP these kinases are activated, releasing active catalytic subunits. These can diffuse through the nuclear pores where, for instance, they can phosphorylate gene regulatory proteins called cAMP response element binding proteins (CREBs), which can then stimulate gene transcription. ...
Cell Communication
... 2. Transduction - binding leads to a change in the receptor that triggers a series of changes along a signal-transduction ...
... 2. Transduction - binding leads to a change in the receptor that triggers a series of changes along a signal-transduction ...
Chapter 15 Regulation of Cell Number Normal and Cancer Cells
... small molecules such as steroids or vitamin D. Most (but not all) endocrine signals are small molecules, such as the mammalian steroid hormones that are responsible for male (androgen) or female (estrogen) sex-specific phenotypes. In contrast, most paracrine signals are proteins. Here we focus on pa ...
... small molecules such as steroids or vitamin D. Most (but not all) endocrine signals are small molecules, such as the mammalian steroid hormones that are responsible for male (androgen) or female (estrogen) sex-specific phenotypes. In contrast, most paracrine signals are proteins. Here we focus on pa ...
1998 warkany lecture: Signaling pathways in development
... these signal ligands are complex proteins, although some are small molecules (e.g. steroids). Some require several steps of processing in the extracellular space before they can be bound by a receptor, and some require the presence of extracellular matrix (ECM) components before they act as signals. ...
... these signal ligands are complex proteins, although some are small molecules (e.g. steroids). Some require several steps of processing in the extracellular space before they can be bound by a receptor, and some require the presence of extracellular matrix (ECM) components before they act as signals. ...
Lecture 1: Brief Outline:
... - Initial cell movements of gastrulation establish axes that subsequently are further divided by one population of cells signaling to another to modify local gene expression. - Further differentiation of the organizer: how it progresses from the node/spemann organizer to a “head” and “tail” organize ...
... - Initial cell movements of gastrulation establish axes that subsequently are further divided by one population of cells signaling to another to modify local gene expression. - Further differentiation of the organizer: how it progresses from the node/spemann organizer to a “head” and “tail” organize ...
b-cells - APBiology2015-2016
... • The fragments will later appear on the cell surface inside a molecule because it is now a plasma cell. • T-cells help b-cells function properly by releasing chemicals that signal the b-cells to divide in multiples and attack invaders inside the cell that may interfere with the signal ...
... • The fragments will later appear on the cell surface inside a molecule because it is now a plasma cell. • T-cells help b-cells function properly by releasing chemicals that signal the b-cells to divide in multiples and attack invaders inside the cell that may interfere with the signal ...
Lecture 8 Cell Signalling
... • Ultimately, a signal transduction pathway leads to regulation of one or more cellular activities • The response may occur in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus • Many signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually by turning genes on or off in the nucleus or by activa ...
... • Ultimately, a signal transduction pathway leads to regulation of one or more cellular activities • The response may occur in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus • Many signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually by turning genes on or off in the nucleus or by activa ...
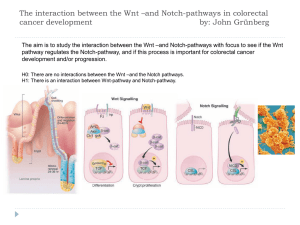
The interaction between the Wnt –and Notch-pathways in
... Is accomplished by the Tcf/Lef target gene program, shown by transfecting the cells with siRNA against β-catenin. This total down regulation of the Notch pathway upon Wnt deactivation shows a correlation between the two signaling pathways in colorectal cancer. We did not find any correlation the oth ...
... Is accomplished by the Tcf/Lef target gene program, shown by transfecting the cells with siRNA against β-catenin. This total down regulation of the Notch pathway upon Wnt deactivation shows a correlation between the two signaling pathways in colorectal cancer. We did not find any correlation the oth ...
The Role of Patched in Basal Cell Carcinoma
... Patch is a key suppressor in the SHH pathway and essential for embryonic growth Patch directly regulates cell cycle progression Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of cancer Patch can still be present and cause BCC Other mutations in the SHH pathway along with decreased expression of Patch ...
... Patch is a key suppressor in the SHH pathway and essential for embryonic growth Patch directly regulates cell cycle progression Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of cancer Patch can still be present and cause BCC Other mutations in the SHH pathway along with decreased expression of Patch ...
Dr. Bryan Ballif identifies phosphorylation sites on key proteins regulating cell growth and proliferation.
... Genetics Network Proteomics Facility, which he co‐directs. ...
... Genetics Network Proteomics Facility, which he co‐directs. ...
Protein kinases
... • Many signal molecules trigger formation of cAMP • Other components of cAMP pathways are G proteins, G protein-coupled receptors, and protein kinases • cAMP usually activates protein kinase A, which phosphorylates various other proteins • Further regulation of cell metabolism is provided by G-prot ...
... • Many signal molecules trigger formation of cAMP • Other components of cAMP pathways are G proteins, G protein-coupled receptors, and protein kinases • cAMP usually activates protein kinase A, which phosphorylates various other proteins • Further regulation of cell metabolism is provided by G-prot ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.