Workshop IV Signal Transduction Chair: Miguel Peñalva 100
... exposed to a highly variable environment with significant changes affecting, temperature, pH, oxygen, andwater and nutrient availability. Many of these changes occur during Trichoderma life cycle, triggering specific stress responses to external factors. In some cases, stress-related responses can a ...
... exposed to a highly variable environment with significant changes affecting, temperature, pH, oxygen, andwater and nutrient availability. Many of these changes occur during Trichoderma life cycle, triggering specific stress responses to external factors. In some cases, stress-related responses can a ...
Doc
... Large-scale discovery of new human genes, gene families and isozymes creates an exciting biomedical opportunity. The sequence-structure gap is rapidly increasing despite the efforts of the companies and centers for high-throughput structural proteomics. However, advanced modeling by homology techniq ...
... Large-scale discovery of new human genes, gene families and isozymes creates an exciting biomedical opportunity. The sequence-structure gap is rapidly increasing despite the efforts of the companies and centers for high-throughput structural proteomics. However, advanced modeling by homology techniq ...
Ch 11 Cell Communication
... involve inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as additional second ...
... involve inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as additional second ...
PDF
... components and astral microtubules. The molecular machinery that regulates spindle apicobasal orientation during asymmetric cell division is well understood but what orientates the spindle along the epithelial plane in symmetrically dividing epithelial cells? On p. 503, Rui Gonçalo Martinho and coll ...
... components and astral microtubules. The molecular machinery that regulates spindle apicobasal orientation during asymmetric cell division is well understood but what orientates the spindle along the epithelial plane in symmetrically dividing epithelial cells? On p. 503, Rui Gonçalo Martinho and coll ...
PDF
... components and astral microtubules. The molecular machinery that regulates spindle apicobasal orientation during asymmetric cell division is well understood but what orientates the spindle along the epithelial plane in symmetrically dividing epithelial cells? On p. 503, Rui Gonçalo Martinho and coll ...
... components and astral microtubules. The molecular machinery that regulates spindle apicobasal orientation during asymmetric cell division is well understood but what orientates the spindle along the epithelial plane in symmetrically dividing epithelial cells? On p. 503, Rui Gonçalo Martinho and coll ...
Are You suprised ?
... superfamily and is implicated in the generation and modulation of various cognitive, behavioral and developmental functions. We previously demonstrated that membrane cholesterol is necessary for ligand binding, and G-protein coupling of serotonin1A receptors. Interestingly, recently reported crystal ...
... superfamily and is implicated in the generation and modulation of various cognitive, behavioral and developmental functions. We previously demonstrated that membrane cholesterol is necessary for ligand binding, and G-protein coupling of serotonin1A receptors. Interestingly, recently reported crystal ...
Cell Communication
... There are three main types of plasma membrane receptors: G-protein-linked ...
... There are three main types of plasma membrane receptors: G-protein-linked ...
AP Cell Signaling
... You should now be able to: 1. Describe the nature of a ligand-receptor interaction and state how such interactions initiate a signal-transduction system 2. Compare and contrast G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and ligand-gated ion channels 3. List two advantages of a multiste ...
... You should now be able to: 1. Describe the nature of a ligand-receptor interaction and state how such interactions initiate a signal-transduction system 2. Compare and contrast G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and ligand-gated ion channels 3. List two advantages of a multiste ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... The atypical cadherins Fat (Ft) and Dachsous (Ds) control tissue growth through the Salvador-Warts-Hippo (SWH) pathway, and also regulate planar cell polarity and morphogenesis. Ft and Ds engage in reciprocal signalling as both proteins can serve as receptor and ligand for each other. The intracellu ...
... The atypical cadherins Fat (Ft) and Dachsous (Ds) control tissue growth through the Salvador-Warts-Hippo (SWH) pathway, and also regulate planar cell polarity and morphogenesis. Ft and Ds engage in reciprocal signalling as both proteins can serve as receptor and ligand for each other. The intracellu ...
No Slide Title
... -cAMP acts as a signal within the cell = second messenger – effects cell activity -BUT some G proteins can inhibit this pathway!!!! (no AC activation, no cAMP production) 5 players in this mechanism: ...
... -cAMP acts as a signal within the cell = second messenger – effects cell activity -BUT some G proteins can inhibit this pathway!!!! (no AC activation, no cAMP production) 5 players in this mechanism: ...
SB-431542: Potent and selective inhibitor of activin receptor
... renal ouabain-insensitive H+,K+-ATPase, but not colonic ouabain-sensitive H+,K+-ATPase [2]. The inhibition of ATPase activity by ouabain (Prod. No. O 3125) has been widely used as a marker of Na+ pump activity in vitro, while inhibition by SCH-28080 has been used as a marker of H+,K+-ATPase activity ...
... renal ouabain-insensitive H+,K+-ATPase, but not colonic ouabain-sensitive H+,K+-ATPase [2]. The inhibition of ATPase activity by ouabain (Prod. No. O 3125) has been widely used as a marker of Na+ pump activity in vitro, while inhibition by SCH-28080 has been used as a marker of H+,K+-ATPase activity ...
Gene7-26
... principle that the form bound to GDP is inactive, but the form bound to GTP is active. Receptor is a transmembrane protein, located in the plasma membrane, that binds a ligand in a domain on the extracellular side, and as a result has a change in activity of the cytoplasmic domain. (The same term is ...
... principle that the form bound to GDP is inactive, but the form bound to GTP is active. Receptor is a transmembrane protein, located in the plasma membrane, that binds a ligand in a domain on the extracellular side, and as a result has a change in activity of the cytoplasmic domain. (The same term is ...
Catching signals surfing the net
... focus on (i) how graded, analogue signals from growth factor receptors can be converted into diverse patterns of mitogenic and survival signalling, which are further decoded by transcriptional circuits to create discrete, digital outputs leading to specific cell-fate decisions (3,4); and (ii) how co ...
... focus on (i) how graded, analogue signals from growth factor receptors can be converted into diverse patterns of mitogenic and survival signalling, which are further decoded by transcriptional circuits to create discrete, digital outputs leading to specific cell-fate decisions (3,4); and (ii) how co ...
Electronic supplementary material consisting of: ... figures, Supplementary materials and methods, and Supplementary reference
... crosslinked complexes are indicated on the right side: -glycan (also termed TGF- type III receptor), endoglin, TRII and TRI. M1 and M4 show intense TGF- binding to -glycan, and binding of TRII is particularly strong in M2. The TGF-endoglin complex is only weakly visible. At the bottom (front ...
... crosslinked complexes are indicated on the right side: -glycan (also termed TGF- type III receptor), endoglin, TRII and TRI. M1 and M4 show intense TGF- binding to -glycan, and binding of TRII is particularly strong in M2. The TGF-endoglin complex is only weakly visible. At the bottom (front ...
CHAPTER 11 CELL COMMUNICATION
... The G protein can also act as a GTPase enzyme to hydrolyze GTP to GDP. This change turns the G protein off. Now inactive, the G protein leaves the enzyme, which returns to its original state. The whole system can be shut down quickly when the extracellular signal molecule is no longer presen ...
... The G protein can also act as a GTPase enzyme to hydrolyze GTP to GDP. This change turns the G protein off. Now inactive, the G protein leaves the enzyme, which returns to its original state. The whole system can be shut down quickly when the extracellular signal molecule is no longer presen ...
CHAPTER 11 CELL COMMUNICATION
... In synaptic signaling, a nerve cell produces a neurotransmitter that diffuses across a synapse to a single cell that is almost touching the sender. The neurotransmitter stimulates the target cell. The transmission of a signal through the nervous system can also be considered an ...
... In synaptic signaling, a nerve cell produces a neurotransmitter that diffuses across a synapse to a single cell that is almost touching the sender. The neurotransmitter stimulates the target cell. The transmission of a signal through the nervous system can also be considered an ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... It produces tRNA molecules with their CCA 3' ends covalently linked to an amino acid Each tRNA is aminoacylated(or charged) with a specific amino acid by an aminoacyl tRNA synthase. There is normally a single aminoacyl tRNA synthetase for each amino acid, despite the fact that there can be more than ...
... It produces tRNA molecules with their CCA 3' ends covalently linked to an amino acid Each tRNA is aminoacylated(or charged) with a specific amino acid by an aminoacyl tRNA synthase. There is normally a single aminoacyl tRNA synthetase for each amino acid, despite the fact that there can be more than ...
Endocrinology 2
... absence of cAMP, R2C2 is inactive. The binding of cAMP to the R chains releases the C chains from the R2 complex, which are then catalytically active. Activated PKA phosphorylates specific serine and threonine residues in many target proteins to alter their function. Examples of target proteins ...
... absence of cAMP, R2C2 is inactive. The binding of cAMP to the R chains releases the C chains from the R2 complex, which are then catalytically active. Activated PKA phosphorylates specific serine and threonine residues in many target proteins to alter their function. Examples of target proteins ...
IGF1
... IGFBPs and IGF1R for the available ligands in tissue and in blood [5]. This potential for competition leads to the latter effect of increasing IGF1R activation. Further, The IGF2R binds to IGF2, but has no tyrosine kinase domain and appears to act as a negative influence on proliferation by reducing ...
... IGFBPs and IGF1R for the available ligands in tissue and in blood [5]. This potential for competition leads to the latter effect of increasing IGF1R activation. Further, The IGF2R binds to IGF2, but has no tyrosine kinase domain and appears to act as a negative influence on proliferation by reducing ...
Lecture 17 and 18: Cellular Signaling Reference: Lieberman and
... MEK phosphorolyates MAPK MAPK phosphorolyates others MAPK translocates to the nucleus Phosphorolyation of transcription factors Alters gene expression o Jak – Stat Receptor Tyrosine associated receptor frequently used by cytokines to regulate proliferation of certain cells involved in th ...
... MEK phosphorolyates MAPK MAPK phosphorolyates others MAPK translocates to the nucleus Phosphorolyation of transcription factors Alters gene expression o Jak – Stat Receptor Tyrosine associated receptor frequently used by cytokines to regulate proliferation of certain cells involved in th ...
Mech133-RvwMolecBasisNeoplasia
... ~many tumor suppressor gene dysfunctions inherit one mutation and then over the course of life may receive a second hit affecting the normal gene ~cancer ususally arrises due to a somatic mutation leading to an activation/modification of a normal cellular gene and becomes an oncogene (a gene that ca ...
... ~many tumor suppressor gene dysfunctions inherit one mutation and then over the course of life may receive a second hit affecting the normal gene ~cancer ususally arrises due to a somatic mutation leading to an activation/modification of a normal cellular gene and becomes an oncogene (a gene that ca ...
MS Word File
... Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Responses • Ultimately, a signal transduction pathway leads to regulation of one or more cellular activities • The response may occur in the cytoplasm or may involve action in the nucleus • Many signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually b ...
... Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Responses • Ultimately, a signal transduction pathway leads to regulation of one or more cellular activities • The response may occur in the cytoplasm or may involve action in the nucleus • Many signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually b ...
Rat LIFR Protein (His Tag)
... LIFR (leukemia inhibitory factor receptor) belongs to the family of cytokine receptors. LIFR forms a high-affinity receptor complex with gp130, which mediates the activity of LIF (leukemia inhibitory factor) and thus affects the differentiation, proliferation, and survival of a wide variety of cells ...
... LIFR (leukemia inhibitory factor receptor) belongs to the family of cytokine receptors. LIFR forms a high-affinity receptor complex with gp130, which mediates the activity of LIF (leukemia inhibitory factor) and thus affects the differentiation, proliferation, and survival of a wide variety of cells ...
Q: How does GA induce gene expression in the aleurone cells?
... For example, the RGA/GAI proteins also prove to be repressors for alpha-amylase expression in aleurone cells; the GA-Myb type of transcription factors required for aleurone gene expression is also positive regulator of stem growth. d) Transcription factor genes like GA-Myb are activated before the a ...
... For example, the RGA/GAI proteins also prove to be repressors for alpha-amylase expression in aleurone cells; the GA-Myb type of transcription factors required for aleurone gene expression is also positive regulator of stem growth. d) Transcription factor genes like GA-Myb are activated before the a ...
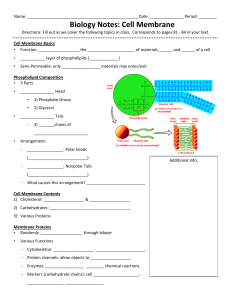
Biology Notes: Cell Membrane
... - Protein channels: allow objects to __________________ - Enzymes: _________________ ________ chemical reactions - Markers (carbohydrate chains): cell ____________________; ________________ _________________ ...
... - Protein channels: allow objects to __________________ - Enzymes: _________________ ________ chemical reactions - Markers (carbohydrate chains): cell ____________________; ________________ _________________ ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.