No Slide Title
... •Biology has protein-based switches, including transcription factors (on/off) and changes in protein conformation by Calcium/Phosphate •The environment interacts with an organism by affecting one or more of these switches. •The environment turns genes on/off using a plasma membrane receptor that act ...
... •Biology has protein-based switches, including transcription factors (on/off) and changes in protein conformation by Calcium/Phosphate •The environment interacts with an organism by affecting one or more of these switches. •The environment turns genes on/off using a plasma membrane receptor that act ...
Chapter 11 - Trimble County Schools
... Fully activated receptor tyrosine kinase (phosphorylated dimer) ...
... Fully activated receptor tyrosine kinase (phosphorylated dimer) ...
Problem Set Chapter 15
... mutation of its phosphorylatable Tyrosine to Serine mutation of its phosphorylatable Tyrosine to Glutamic Acid mutation of its phosphorylatable Tyrosine to Glycine mutation of its phosphorylatable Tyrosine to Alanine ...
... mutation of its phosphorylatable Tyrosine to Serine mutation of its phosphorylatable Tyrosine to Glutamic Acid mutation of its phosphorylatable Tyrosine to Glycine mutation of its phosphorylatable Tyrosine to Alanine ...
Table S1: Transgenic zebrafish strains used in this study Transgenic
... Her GM, Yeh Y-H, Wu J-L. 435-bp liver regulatory sequence in the liver fatty acid binding protein (LFABP) gene is sufficient to modulate liver regional expression in transgenic zebrafish. Dev Dyn ...
... Her GM, Yeh Y-H, Wu J-L. 435-bp liver regulatory sequence in the liver fatty acid binding protein (LFABP) gene is sufficient to modulate liver regional expression in transgenic zebrafish. Dev Dyn ...
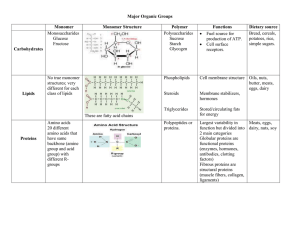
Major Organic Groups - Lemon Bay High School
... Largest variability in Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
... Largest variability in Meats, eggs, function but divided into dairy, nuts, soy 2 main categories Globular proteins are functional proteins (enzymes, hormones, antibodies, clotting factors) Fibrous proteins are structural proteins (muscle fibers, collagen, ligaments) ...
Gene Section SOCS2 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 2) in Oncology and Haematology
... SH2 domains, but also to bind Elongin BC through their SOCS box domains. SOCS family proteins form part of a classical negative feedback system that regulates cytokine signal transduction (Rico-Bautista et al., 2006). SOCS2 appears to be a negative regulator in the growth hormone/IGF1 signaling path ...
... SH2 domains, but also to bind Elongin BC through their SOCS box domains. SOCS family proteins form part of a classical negative feedback system that regulates cytokine signal transduction (Rico-Bautista et al., 2006). SOCS2 appears to be a negative regulator in the growth hormone/IGF1 signaling path ...
Cell Communication Chapter 11
... another protein, which activates another, and so on, until the protein producing the response is activated At each step, the signal is transduced into a different form, usually a shape change in a protein One of the most common methods of regulating the signal is through phosphorylation and ...
... another protein, which activates another, and so on, until the protein producing the response is activated At each step, the signal is transduced into a different form, usually a shape change in a protein One of the most common methods of regulating the signal is through phosphorylation and ...
Biobowl
... 4. The receptor for a polar ligand is found where? 5. The receptor for a non-polar ligand is found where? 6. A non-polar signaling molecule usually acts by doing what in a cell? 7. A protein that binds GTP and is activated by a receptor is known as a 8. What is the benefit of a cascade, when referri ...
... 4. The receptor for a polar ligand is found where? 5. The receptor for a non-polar ligand is found where? 6. A non-polar signaling molecule usually acts by doing what in a cell? 7. A protein that binds GTP and is activated by a receptor is known as a 8. What is the benefit of a cascade, when referri ...
The Cell Cycle - Department of Biology
... -Executioner procaspases, cleave and activate other executioner procaspases and other targets -Targets include: nuclear lamins, endonuclease inhibitor, cytoskeleton components, cell-cell adhesion proteins ...
... -Executioner procaspases, cleave and activate other executioner procaspases and other targets -Targets include: nuclear lamins, endonuclease inhibitor, cytoskeleton components, cell-cell adhesion proteins ...
Summary Cells respond to extracellular cues via receptor signaling
... Cells respond to extracellular cues via receptor signaling. In this manner, cellular behavior is under strict control of hormones, growth factors or neurotransmitters. Binding of a ligand to its cognate receptor triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling events. In general, these cascades branch ...
... Cells respond to extracellular cues via receptor signaling. In this manner, cellular behavior is under strict control of hormones, growth factors or neurotransmitters. Binding of a ligand to its cognate receptor triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling events. In general, these cascades branch ...
Cells Unit Review Jeopardy power point
... Reminder! Jeopardy is just a review to see what you know. It should NOT be the only thing you study!! ...
... Reminder! Jeopardy is just a review to see what you know. It should NOT be the only thing you study!! ...
Crash Course in Biochemistry
... What if shape different? RuBP won’t bind, No reaction. Some mutations change critical active site residues. Genetic Mutations and Disease: sickle cell, PKU ...
... What if shape different? RuBP won’t bind, No reaction. Some mutations change critical active site residues. Genetic Mutations and Disease: sickle cell, PKU ...
receptor
... Ligand-Gated Ion Channel An ion channel receptor acts as a gate when the receptor changes shape ...
... Ligand-Gated Ion Channel An ion channel receptor acts as a gate when the receptor changes shape ...
Homeostasis and Transport Vocabulary Worksheet 1 Answers
... Exocytosis This is the transport of material out of a cell by means of a sac or vesicle that first engulfs the material and then is extruded through an opening in the cell membrane. ...
... Exocytosis This is the transport of material out of a cell by means of a sac or vesicle that first engulfs the material and then is extruded through an opening in the cell membrane. ...
The Specificity of cell signaling
... protein that regulates salt and water secretion. The modified G protein is unable to hydrolyze GTP to GDP and remains stuck in its active form, continuously stimulating adenylyl cyclase to make cAMP. ...
... protein that regulates salt and water secretion. The modified G protein is unable to hydrolyze GTP to GDP and remains stuck in its active form, continuously stimulating adenylyl cyclase to make cAMP. ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... b. Cells communicate over short distances by local regulators that target cells in the vicinity of the emitting cell. c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another type. ...
... b. Cells communicate over short distances by local regulators that target cells in the vicinity of the emitting cell. c. Signals released by one cell type can travel long distances to target cells of another type. ...
Supplement_2_-_PLoS_
... Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a proinflammatory cytokine that elicits its pleiotropic effects through activation of the transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1. ...
... Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a proinflammatory cytokine that elicits its pleiotropic effects through activation of the transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1. ...
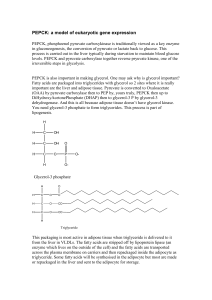
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK protein is synthesised. The protein is also rapidly turned over?? During fasting, a glucocorticoid, cortisol is released and this steroid activates the transcrip ...
... In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK protein is synthesised. The protein is also rapidly turned over?? During fasting, a glucocorticoid, cortisol is released and this steroid activates the transcrip ...
Cells are exposed to DNA damaging agents that can affect their
... do not have any symmetry, especially those of the so-called “molecular machines” where a collection of proteins interact to work in such various processes as DNA repair or RNA splicing. Also, some important molecules in the size range of 100 kDa are multi-domain proteins which are difficult to expre ...
... do not have any symmetry, especially those of the so-called “molecular machines” where a collection of proteins interact to work in such various processes as DNA repair or RNA splicing. Also, some important molecules in the size range of 100 kDa are multi-domain proteins which are difficult to expre ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.