7. Protein Function
... There are two classes of MHC proteins which differ in their distribution among cell types and in the source of digested proteins Class I MHC - are found on the surface of virtually all vertebrate cells. These complexes of peptides and class I MHC proteins are the recognition targets of the T-cell re ...
... There are two classes of MHC proteins which differ in their distribution among cell types and in the source of digested proteins Class I MHC - are found on the surface of virtually all vertebrate cells. These complexes of peptides and class I MHC proteins are the recognition targets of the T-cell re ...
READ MORE - Bicycle Therapeutics
... Cambridge, U.K., with U.S. operations in Cambridge, Massachusetts. For more information, visit: www.bicycletherapeutics.com. We have a new opportunity for a Cell Culture Research Associate This candidate will be primarily responsible for maintaining the Bicycle tissue culture facility and its upkeep ...
... Cambridge, U.K., with U.S. operations in Cambridge, Massachusetts. For more information, visit: www.bicycletherapeutics.com. We have a new opportunity for a Cell Culture Research Associate This candidate will be primarily responsible for maintaining the Bicycle tissue culture facility and its upkeep ...
Recombinant Human IL-35-Fc fusion protein (ELISA Std.)
... the Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene product 3 (EBI-3). IL-35 belongs to the IL-12 family which includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27, and IL-35. These cytokines are heterodimeric proteins comprised of an α chain (p19, p28, or p35) and a β chain (p40 or Ebi3). Mouse IL-35-Fc fusion protein enhances the prolif ...
... the Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene product 3 (EBI-3). IL-35 belongs to the IL-12 family which includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27, and IL-35. These cytokines are heterodimeric proteins comprised of an α chain (p19, p28, or p35) and a β chain (p40 or Ebi3). Mouse IL-35-Fc fusion protein enhances the prolif ...
Caspase 3
... located in or adjacent to the plasma membrane (ii), which may require the presence of “adaptor” proteins, which target the ER to the membrane. Activation of the membrane ER leads to a rapid change in cellular signaling molecules and stimulation of kinase activity, which in turn may affect transcript ...
... located in or adjacent to the plasma membrane (ii), which may require the presence of “adaptor” proteins, which target the ER to the membrane. Activation of the membrane ER leads to a rapid change in cellular signaling molecules and stimulation of kinase activity, which in turn may affect transcript ...
Gene Section NRIP1 (nuclear receptor interacting protein 1)
... liver X receptor, PPARs, steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1) and ERR. RIP140 has been shown to regulate retinoic acid mediated differentiation and growth suppression of human embryonal carcinoma cells and the proliferation of breast cancer cells in vitro. A potential role for RIP140 in cancer cachexia has ...
... liver X receptor, PPARs, steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1) and ERR. RIP140 has been shown to regulate retinoic acid mediated differentiation and growth suppression of human embryonal carcinoma cells and the proliferation of breast cancer cells in vitro. A potential role for RIP140 in cancer cachexia has ...
The P53-Mdm2 Network: From Oscillations To Apoptosis
... Department of Physics, Bose Institute, 93/1, A. P. C. Road Kolkata-700009 Abstract. The p53 tumour suppressor gene, often characterized as the “guardian of the genome” plays a central role in protecting cells from malignant transformation. It is the most frequently mutated of genes in human cancer. ...
... Department of Physics, Bose Institute, 93/1, A. P. C. Road Kolkata-700009 Abstract. The p53 tumour suppressor gene, often characterized as the “guardian of the genome” plays a central role in protecting cells from malignant transformation. It is the most frequently mutated of genes in human cancer. ...
Ch. 14 Part 5
... Cell membrane plays big role in cell signaling – Contains protein “receptors” Stimulus (signal) receptor transmission of signal “signal transduction” target (effector) response ...
... Cell membrane plays big role in cell signaling – Contains protein “receptors” Stimulus (signal) receptor transmission of signal “signal transduction” target (effector) response ...
answers_ch06
... 5) When the Ras protein is activated, it has an autocatalytic property which means that it has a catalytic property which leads to its own deactivation without the need for any external influence. If the autocatalytic property was lost, the Ras protein would remain permanantly activated and this wou ...
... 5) When the Ras protein is activated, it has an autocatalytic property which means that it has a catalytic property which leads to its own deactivation without the need for any external influence. If the autocatalytic property was lost, the Ras protein would remain permanantly activated and this wou ...
CASE 1
... on the “sensing” cells that sense the chemical change (specifically bind the chemical) and then respond by activating biochemical pathways (signal transduction pathways) within the cell that can lead to a defined response by the cell. These receptors may reside on the surface of the cell, within the ...
... on the “sensing” cells that sense the chemical change (specifically bind the chemical) and then respond by activating biochemical pathways (signal transduction pathways) within the cell that can lead to a defined response by the cell. These receptors may reside on the surface of the cell, within the ...
III. Exam Section III Intercellular Communication 1. Review of
... 3. Intracellular second messenger cascades 4. One or more target mechanisms 2. Consensus signal pathways and molecules (Chapter 15) a. Classic signal transduction pathways 1. G-protein linked receptor --- G-protein --- adenyl cyclase 2. G-protein linked receptor --- G-protein --- phospholipase C 3. ...
... 3. Intracellular second messenger cascades 4. One or more target mechanisms 2. Consensus signal pathways and molecules (Chapter 15) a. Classic signal transduction pathways 1. G-protein linked receptor --- G-protein --- adenyl cyclase 2. G-protein linked receptor --- G-protein --- phospholipase C 3. ...
Gene Section PTCH2 (patched homolog 2 (Drosophila)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Overexpression of PTCH2 in basal cell carcinomas cannot compensate for mutated PTCH1 implying distinct roles of the two homologs. This can be rationalized by the very weak capacity of PTCH2 relative to PTCH1 in inhibiting the signaling molecule Smoothened. Additionally, based mostly on chromosomal d ...
... Overexpression of PTCH2 in basal cell carcinomas cannot compensate for mutated PTCH1 implying distinct roles of the two homologs. This can be rationalized by the very weak capacity of PTCH2 relative to PTCH1 in inhibiting the signaling molecule Smoothened. Additionally, based mostly on chromosomal d ...
Adenosine
... genes encoding the , , isoforms of calcineurin A 2. and isoforms serve different roles in neuronal signaling 3. isoform is expressed in the testis 4. calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation is a central event in signal transduction, which responses to Ca2-mobilizin ...
... genes encoding the , , isoforms of calcineurin A 2. and isoforms serve different roles in neuronal signaling 3. isoform is expressed in the testis 4. calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation is a central event in signal transduction, which responses to Ca2-mobilizin ...
Gene Section ATF1 (activating transcription factor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Characterised by the translocation t(12;22)(q13;q12). Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' EWSR1- 3' ATF1. Abnormal protein The chimaeric protein is composed of the N-terminal domain of EWS linked to the bZIP domain of ATF-1. ...
... Characterised by the translocation t(12;22)(q13;q12). Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' EWSR1- 3' ATF1. Abnormal protein The chimaeric protein is composed of the N-terminal domain of EWS linked to the bZIP domain of ATF-1. ...
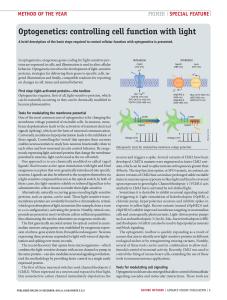
Optogenetics: controlling cell function with light
... First step: light-activated proteins—the toolbox Optogenetics requires, first of all, light-sensitive proteins, which can be naturally occurring or they can be chemically modified to become photosensitive. Tools for modulating the membrane potential One of the most common uses of optogenetics is for ...
... First step: light-activated proteins—the toolbox Optogenetics requires, first of all, light-sensitive proteins, which can be naturally occurring or they can be chemically modified to become photosensitive. Tools for modulating the membrane potential One of the most common uses of optogenetics is for ...
Snails, Synapses and Smokers
... in snails is significant in its own right. It also advances our understanding of the vertebrate neurotransmitter receptor that responds to nicotine. n pages 261 and 269 of this issue1,2, Sixma and colleagues describe how they identified a protein, found in snails, that controls communication between ...
... in snails is significant in its own right. It also advances our understanding of the vertebrate neurotransmitter receptor that responds to nicotine. n pages 261 and 269 of this issue1,2, Sixma and colleagues describe how they identified a protein, found in snails, that controls communication between ...
So why do cells need to communicate?
... receptors / Heterotrimeric G proteins - many seven pass receptors with unknown number of ligands / hormones - all receptors act through G proteins ...
... receptors / Heterotrimeric G proteins - many seven pass receptors with unknown number of ligands / hormones - all receptors act through G proteins ...
6 per page - University of San Diego Home Pages
... receptors / Heterotrimeric G proteins - many seven pass receptors with unknown number of ligands / hormones - all receptors act through G proteins ...
... receptors / Heterotrimeric G proteins - many seven pass receptors with unknown number of ligands / hormones - all receptors act through G proteins ...
The Development and Evaluation of Highly Specific
... responsible for cancer initiation, development and metastasis. The identification of cancer stem cells is considered as one of the most important objectives for clinical diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Research evidences indicated that Leucine-rich repeat containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 ...
... responsible for cancer initiation, development and metastasis. The identification of cancer stem cells is considered as one of the most important objectives for clinical diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Research evidences indicated that Leucine-rich repeat containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 ...
March 22 – signals in frog embryos
... Activin can induce different mesodermal cell types at different concentrations ...
... Activin can induce different mesodermal cell types at different concentrations ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Section C: Signal-Transduction Pathways 1. Pathways relay signals from receptors to cellular responses 2. Protein phosphorylation, a common mode of regulation in cells, is a major mechanism of signal transduction 3. Certain small molecules and ions are key components of signaling pathways ...
... Section C: Signal-Transduction Pathways 1. Pathways relay signals from receptors to cellular responses 2. Protein phosphorylation, a common mode of regulation in cells, is a major mechanism of signal transduction 3. Certain small molecules and ions are key components of signaling pathways ...
Supplementary Information (docx 146K)
... (Roche Diagnostics). Cells (20x103 cells/100µl) were incubated in a 96-wells plate with effectors. The WST-1 reagent added to each well is transformed into an orange formazan dye (490 nm) by metabolically active cells. Each assay was performed in quadruplicate. ...
... (Roche Diagnostics). Cells (20x103 cells/100µl) were incubated in a 96-wells plate with effectors. The WST-1 reagent added to each well is transformed into an orange formazan dye (490 nm) by metabolically active cells. Each assay was performed in quadruplicate. ...
Monoclonal Antibody To Human GPR50
... GPR50 or melatonin-related receptor is a 617 amino acid protein that belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, containing one disulfide bond. GPR50 does not bind melatonin and its endogenous ligand is still unknown. Nevertheless, this receptor has been shown to behave as an antagonist of t ...
... GPR50 or melatonin-related receptor is a 617 amino acid protein that belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, containing one disulfide bond. GPR50 does not bind melatonin and its endogenous ligand is still unknown. Nevertheless, this receptor has been shown to behave as an antagonist of t ...
Mouse VEGFA / VEGF164 Protein
... VEGF-A is a glycosylated mitogen that specifically acts on endothelial cells and has various effects, including mediating increased vascular permeability, inducing angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth, promoting cell migration, and inhibiting apoptosis. As its name implies, VEGF- ...
... VEGF-A is a glycosylated mitogen that specifically acts on endothelial cells and has various effects, including mediating increased vascular permeability, inducing angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth, promoting cell migration, and inhibiting apoptosis. As its name implies, VEGF- ...
Aim What are protein molecules?
... Base your answer on the diagram and on your knowledge of biology. Which statement best describes the diagram? 1.Nerve cell X is releasing receptor molecules. 2.Nerve cell Y is signaling nerve cell X. 3.Nerve cell X is attaching to nerve cell Y. 4.Nerve cell Y contains receptor molecules for substan ...
... Base your answer on the diagram and on your knowledge of biology. Which statement best describes the diagram? 1.Nerve cell X is releasing receptor molecules. 2.Nerve cell Y is signaling nerve cell X. 3.Nerve cell X is attaching to nerve cell Y. 4.Nerve cell Y contains receptor molecules for substan ...
G protein-coupled receptor - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.