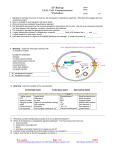
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanisms of Hormone Action: Peptide Hormones
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Wnt signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Notch signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Tyrosine kinase wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Leukotriene B4 receptor 2 wikipedia , lookup
VLDL receptor wikipedia , lookup
Toll-like receptor wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 wikipedia , lookup
Frontiers in Reproductive Endocrinology Serono Symposia International Mechanisms of Hormone Action: Peptide Hormones Kelly Mayo Northwestern University Mechanisms of Cell Communication Endocrine Signaling Paracrine Signaling Autocrine Signaling Juxtacrine Signaling Endocrine Signaling 1 Emergence of Key Concepts in Hormone Action Berthold, 1849 Starling, 1905 Castrated cockerels and restored male sex characteristics by replacing testes in the abdomen Stimulation of pancreatic enzyme secretion by humoral factor (secretin) from intestinal extracts “Endocrinology” “Hormone” Langley, 1906 Sutherland, 1962 Action of nicotine and curare on the ‘receptive substance’ of the neuromuscular junction Glycogen metabolism and hormonal activation of liver phosphorylase enzyme by cAMP “Receptor” “Second Messenger” Structural Diversity in Reproductive Hormonal Signaling Molecules pyroGlu His Trp Ser OH Tyr HOOC Gly OH Leu Arg N O HO Pro OH OH Gly GlyNH2 FSH GnRH Estradiol PGF2a Nitric Oxide Protein 203 aa Peptide 10 aa Steroid MW 272 Eicosanoid MW 330 Gas MW 30 2 ka ! kd R (receptor) + H (hormone)! Ka = [RL] ! [R][L] RH (complex) Kd = [R][L] ! [RL] (units are moles) (units are moles -1) Fractional Binding Measuring Receptor-Ligand Interaction Total Binding Specific Binding Nonspecific Binding Total R, RT= [R] + [RL], so: Kd = [RT-RL][L] [RL] Fraction of receptor [RL] = [L] = 1 ocupied by ligand: [RT] Kd + [L] 1 + Kd ! ! ! ! [L] Fractional Binding Rearrange to: [L] = [RL](K d + [L] [RT] [Hormone] ~Kd At 50% occupancy (1/2), Kd = [L] log [Hormone] General Mechanisms of Action of Steroid and Peptide Hormones Steroid Hormone S S P P Binds to cell surface receptor Hormone-activated receptor S Cytoplasmic or nuclear receptor Protein Hormone Diffuses across plasma membrane Binds to DNA in target genes Regulates gene transcription S Non-genomic effects via protein -protein interaction Changes in enzyme activity Receptor-associated Activation of effector changes in enzyme activity enzymes Generation of second messengers Biological output Activation of transcription factors P Biological output New mRNAs Changes in enzyme activity TF P Biological output New mRNAs Synthesis of new proteins Biological output Synthesis of new proteins Biological output 3 Major Classes of Peptide Hormone Receptors G Protein-Coupled Receptors Largest family (>800), Highly Diverse Receptor Tyrosine Kinases “Growth Factor” Receptors Receptors that Recruit Tyrosine Kinases Cytokine Receptors/Stat Pathway Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinases TGFb/Smad Pathway Developmental Pathway Receptors Hedgehog/Wnt/DSL Ligands “Other Pathways” Diverse and Growing Families of G Protein-Coupled Receptors Family A: Rhodopsin-Like Rs Group I: Olfactory, Adenosine, Melanocortin Rs Group II: Adrenergic, Muscarinic, Serotonin, Dopamine Rs Group III: Neuropeptide Rs and Vertebrate Opsins Group IV: Bradykinin Rs and Invertebrate Opsins Group V: Peptide, Glycoprotein Hormone and Chemokine Rs Group VI: Melatonin and Orphan Rs FSH,LH, Relaxin, GnRH Receptors Family B: Secretin-Like Rs Family C: Glutamate-Like Rs Group I: Calcitonin and CRF Rs Group II: PTH and PTHrP Rs Group III: Glucagon, Secretin, VIP, GHRH Rs Group I: Metabotropic Glutamate Rs Group II: Calcium Sensing Rs Group III: Vertebrate Pheromone Rs Family D: Fungal Pheromone Rs Family E: cAMP Rs Group I: Alpha Factor Pheromone Rs Group II: A Factor Pheromone Rs Group I: Dictyostelium cAR Rs Frizzled/Smoothened Rs Group I: Frizzled Rs Group II: Smoothened Rs 4 Features of a Prototypical G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR), the b-Adrenergic Receptor Glycosylation -NH 2 Agonist Binding Antagonist Binding TMD1 TMD2 TMD3 TMD4 TMD5 TMD6 TMD7 Palmitoylation P P PKA Phosphorylation Required for Catacholamine Binding and Activation Asp 113 Ser 204,207 G Protein Coupling COOH- P P P P P P bARK Phosphorylation Structure of a G Protein-Coupled Receptor, Rhodopsin Cytoplasmic View Membrane-Parallel View Extracellular View Palczewski et al, Science 289: 739, 2000 5 Pathways of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Action Receptor Gas g GDP b AC Adenylyl Cyclase (Effector) H ATP AC Gas GTP Heterotrimeric G protein H AC g b H cAMP Second Messenger Gas GTP ATP Gas GTP AC PP Gas GDP g b GRK + PKA Receptor Internalization Pathways GTP Hydrolysis cAMP cAMP RR g Arrestins PP b ATP P Substrate Phosphorylation Diversity and Specificity in G Protein Signaling Multiple Receptors Activate the Same G Protein One Receptor Activates Multiple G Proteins b a b g Diverse Actions of G Protein Heterotrimers a Signaling Diversity (Gs, Gi, Gq,Go) a and bg Effector Activation Combinatorial Assembly 20 a, 6 b, 12 g=1440 Heterotrimers a b a b a gg g b g G Protein Receptor Specificity Carbachol Somatostatin M4R SSR Go1b3g4 Go Go2b1g3 Ca++ Channel Kleuss et al, Nature 353:43, 1991 6 Current Issues in G Protein Coupled Receptor Research Receptor Trafficking Receptor Signaling Internalization GRK Kinases RAMP Proteins Desensitization RGS Proteins Non G protein pathways Receptor Diversity Receptor Structure Dimerization Alternative Splicing Modifications Molecular Modeling G Protein Interaction Structure Determination Therapeutics Ligand Mimics Altered Regulation Orphan Receptors New Pathways Receptors with Intrinsic Kinase Activity or Associated with Kinase Activity General Features Type I Integral Membrane Proteins Dimerization Critical to Activation Receptor Phosphorylated on Activation Signaling Proteins Bind to Phosphorylated Receptor Proteins that Suppress Signaling Receptor that are Tyrosine Kinases Growth Factor Receptors Insulin Receptor Receptors that Recruit Tyrosine Kinases Cytokine Superfamily Receptors Prolactin Receptor Receptors that are Serine/Threonine Kinases TGFb Superfamily Receptors MIS Receptor 7 Receptors that are Protein Tyrosine Kinases EGFR Examples of RTK Families NGFR EGF Receptor Subfamily PDGFR InsulinR RET (EGFR, HER2/Neu) NGF Receptor Subfamily (TrkA, TrkB, TrkC) SS FGF Receptor Subfamily SS (FGFR1-4, Cek2) HGF Receptor Subfamily (HGFR=MET) PDGF Receptor Subfamily (PDGFR a/b, VEGFR) Insulin Receptor Subfamily (InsulinR, IGF-1R) Tyrosine Kinase Domain Cysteine-rich Domain Immunoglobulin Domain Cadherin Domain EPH Receptor Subfamily (Ephrin AR, Ephrin BR) ROR Receptor Subfamily (RET-GDNF) Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Pathway Hormone RTK Signaling Ligand-induced dimerization K Receptor phosphorylation Receptor Monomer P Effector proteins bind receptor - direct enzymatic function - adaptor proteins K K Dimerized Activated Receptor P GTP sos grb2 ras raf MAPK P Phosphatases Initiation of kinase cascades Changes in gene expression Phosphatases and negative regulation P MEK MAPK P MEK Transcription Factor P Gene Expression RE 8 Receptors that Associate with Cytoplasmic Kinases LIF-R IL-3-R INFg-R PRL-R Families of Cytokine Receptors Type I: Single chain (GH, PRL, EPO, TPO) Type II: Shared gp130 signaling subunit (IL-6, LIF, IL-11, CNTF) Type III: Shared gp140b, ligand-specific a (IL-3, IL-5, GMCF) R1 Type IV: Shared gc, ligand-specific a (HGFR=MET) R2 Type V: Two or more distinct subunits (IFNa/b, IFNg) gp130 bC Janus Family Kinases Jak1 (IL-2, IL-6, GCSF, INFa/b, INFg) Jak2 (GH, PRL, EPO, IL-5) Jak3 (IL-2. IL-4, IL-7) Tyk2 (IL-6, LIF, INFa/b) Stat DBD SH3 SH2 TAD JAK Kinase Stat Proteins Stat Stats 2 and 6 Stats 1, 3, 4, 5A, 5B DBD SH3 SH2 TAD PP Cytokine Receptor Signaling Pathway Hormone Cytokine Signaling Ligand-induced dimerization Receptor association with JAK kinase JAK 2 P Box 1 Receptor Monomer Binding to Site 1 Dimerized Activated Receptor Receptor phosphorylation Effector proteins bind receptor - direct enzymatic function - STAT proteins STATs phosphorylated STATs dimerize STATs migrate to the nucleus K K P P P JAK 2 P STAT Stat Dimer STAT Dimer P P SOCS STAT P P Gene Expression Changes in gene expression GAS SOCS proteins and negative regulation 9 Prolactin-Induced Receptor Dimerization Biological Response + Increasing Prolactin Increasing Prolactin oPL-Receptor Complex Receptor Interaction Sites on oPL Elkins et al, Nature Structural Biology 7:808, 2000 Receptors with Serine/Threonine Kinase Activity Ligand TGF-b Type II Receptor TbR-II Type I Receptor TbR-I Activin ActR-IIB ActR-IB MIS AMHR ActR-I BMP2 BMPR-II BMPR-IA BMP7 ActR-II BMPR-1B GDF5 ActR-IIB ActR-I Dpp Punt Tkv, Sax Receptor Smads CoSmads Inhibitory Smads 1,2,3,5,8 Mad Sma2,3 Smad 4 Medea Sma-4 Smads 6,7 Dad Ligand GS Box TTSGSGSG Kinase Domain Type II Type I MH1 MH2 SSXS MH2 PP SSXS Receptor Kinase MH1 10 Serine/Threonine Receptor Signaling Pathway Hormone TGFb Family Signaling II Ligand binds to type II receptor K Type I and II receptor associate I K P Type II Receptor Type I receptor phosphorylation Effector proteins bind receptor - direct enzymatic function - Smad proteins I II Dimerized Activated Receptor P K P I P K ReceptorSmad (1,2,3,5,8) Type I Receptor Hetero-Oligomer Inhibitory Smad (6,7) P P P P P P Co-Smad (4) Smads phosphorylated Smads heterodimerize Smads migrate to the nucleus Smads bind other TFs FAST-1 Other Changes in gene expression P P P Gene Expression T/ARE Inhibitory Smads and negative regulation Some Key Developmental Signaling Pathways Ligand Receptor Delta/Serrate/ Notch Lag2 Wnt Family Frizzled Patched Hedgehog (Shh,Dhh,Ihh) To Nucleus Partner Notch CSL (Cytoplasmic Domain) b-catenin LEF/TCF CBP Ci/Gli (Full-Length) Comments Receptor proteolysis CSL Repressor to Activator b-catenin stabilized TCF Repressor to Activator Patched/Smoothened Complex Ci-75 Repressor in Basal State Notch: Oogenesis in Drosophila (expressed in mammalian ovary) Notch2: Placental trophoblast development Wnt4: Wnt5a: Wnt7a: Roles in gametogenesis, Mullerian duct development Development of the external genitalia Development of the oviduct and uterus Dhh: Shh: Maturation of testis, Seroli-Leydig cell interations Pituitary cell type determination 11 Commonalities in Developmental Signaling Pathways Famlies of related ligands Involvement of proteolysis Signaling to the nucleus Switching from repression to activation Notch Signaling Wnt Signaling Hh Signaling Wnt Ligand Hh Ligand Sending Cell DSL Ligand Frizzled Receptor Frizzled Receptor Smoothened Receptor Responding Cell Dishevelled Notch Receptor SuFu GSK-3 Axin Cleavage of C-terminus by presenelin protein Notch(C) Coactivator Notch(C) CSL Ci-75 APC b-catenin Corepressor TCF LEF Cos2 Ci/Gli Coactivator b-catenin Gene Expression Fused Ci/Gli Corepressor Gene Expression CBP Ci-75 Repressor Ci/Gli Gene Expression Additional Pathways of Peptide Hormone Action Plasmaprotein Receptors Guanylyl Cyclase Receptors LDL-R, Transferrin-R, M6P/IGF-II-R Endocytosed, deliver cargo to lysosome Recycled to cell surface, highly regulated Inactive kinase/active guanylyl cyclase domains Sperm receptors for egg peptides in sea urchin Mammalian natriuretic peptides and enterotoxins Ligand-Gated Ion Channels Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptors nACh-R, GABA-R, Glutamate-R, ATP-R Multisubunit, 4 TMD proteins Major targets for therapeutics Transmembrane tyrosine phosphatases Ligands unknown, cell-cell interactions Activate signaling via src gamily kinases Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors Receptors Activating NF-kB Lead to caspase activation and apoptosis TNFR1/Fas signal via death domain TNFRII/CD40 signal via TRAF proteins Interleukin-I and TNF receptors Leads to activation of IkB kinase Major pathway of inflammation 12 Mutations of Hormones, Receptors and Signaling Proteins in Reproductive Disease Hormones FSH LH MIS Delayed puberty, primary amenorrhea in females; male hypogonadism Luteal insufficiency, infertility in female; delayed puberty, azoospermia in male Persistence of Mullerian duct derivatives in males Receptors GnRH-R FSH-R LH-R (Loss) LH-R (Gain) Estrogen R Androgen R MIS R-II RET Partial to complete hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, males and females Primary or secondary amenorrhea in females, variable/mild oligospermia in males Amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea in females, range of defects to complete feminization in males Male-limited precocious puberty, no phenotype in females Normal puberty, tall stature and unfused epiphyses in male Many mutations, broad range of phenotypes to complete feminization in males Persistence of Mullerian duct derivatives in males Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 Signaling Proteins Gs protein a McCune-Albright Syndrome (gain), male precocious puberty (loss/gain) Gi protein a Ovarian and adrenal tumors? Smads Mutations in many cancers, including Smad4 mutation in seminoma testicular germ cell tumor Transcription Factors Dax-1 SF-1 Prop-1 Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism/adrenal failure in male XY sex reversal/adrenal failure Variable hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in males and females Additional Readings on Peptide Hormone Action •Hunter (2000) Signaling: 2000 and beyond. Cell 100:113. •Brivanlou and Darnell (2002) Signal transduction and the control of gene expression. Science 295:813. •Scott and Pawson (2000) Cell communication: the inside story. Sci Am 282:72. •Hsu and Hsueh (2000) Discovering new hormones, receptors and signaling mediators in the genomic era. Mol Endocrinol 14:594. •Pierce et al (2002) Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:639. •Wess (1997) G protein-coupled receptors: molecular mechanisms involved in receptor activation and selectivity of G protein activation. FASEB J 11:346. •Van der Gerr et al (1994) Receptor protein tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Ann Rev Cell Biol 10:251. •Schlessinger (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103:211. •Touw et al (2000) Signaling mechanisms of cytokine receptors and their perturbances in disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol 160:1. •Levy and Darnell (2002) Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:651. •Massague (1998) TGF-b signal transduction. Ann Rev Biochem 67:753. •Wrana and Attisano (2000) The Smad pathway. Cyt Growth Factor Rev 11:5. •Moon et al (2002) The promise and perils of Wnt signaling through b-catenin. Science 296:1644. •Locksley et al (2001) The TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 104:487. •Tamura (2001) The regulation and physiological roles of guanyly cyclase receptors. Endocrin J 48:611. •Li and Stark (2002) NF-kappaB dependent signaling pathways. Exp Hematol 30:285. •Tonks (1996) Protein tyrosine phosphatases and the control of cell signaling. Adv Pharmacol 36:91. •Acherman and Jameson (1999) Fertility and infertility: genetic contributions from the HPA axis. Mol Endocrinol 13:812. 13