March 21, 1968, Number 12, Page Number 659
... Ma gnes ium is an activator in vitro of a host of enzyme systems that are critical to cellular metabolism. Prominent are the enzymes that hydrolyze and transfer phosphate groups, among them the phos-phatases and those concerned in the reactions involving adenosine triphosphate. Since adenosine triph ...
... Ma gnes ium is an activator in vitro of a host of enzyme systems that are critical to cellular metabolism. Prominent are the enzymes that hydrolyze and transfer phosphate groups, among them the phos-phatases and those concerned in the reactions involving adenosine triphosphate. Since adenosine triph ...
• What are enzymes? They`re special type of protein that accelerates
... • Ligases: connects two materials together so we have two materials and one product, they are usually involved in the building processes so they need energy which they get usually from being coupled to ...
... • Ligases: connects two materials together so we have two materials and one product, they are usually involved in the building processes so they need energy which they get usually from being coupled to ...
Diapositiva 1
... STRING 8—a global view on proteins and their functional interactions in 630 organisms- ...
... STRING 8—a global view on proteins and their functional interactions in 630 organisms- ...
Aerobic Metabolism: The Citric Acid Cycle
... TPP (Thiamine pyrophosphate), FAD, NAD+ and lipoic acid are the required co-enzymes for acetyl-CoA synthesis from pyruvate. ...
... TPP (Thiamine pyrophosphate), FAD, NAD+ and lipoic acid are the required co-enzymes for acetyl-CoA synthesis from pyruvate. ...
Problem-Set Solutions
... 26.57 The equivalent of a total of four ATP molecules is expended in the production of one urea molecule; two ATP molecules are used to produce carbamoyl phosphate, and the equivalent of two ATP molecules are used in Step 2 of the cycle (ATP AMP + 2Pi). 26.58 The carbon atom and one nitrogen atom ...
... 26.57 The equivalent of a total of four ATP molecules is expended in the production of one urea molecule; two ATP molecules are used to produce carbamoyl phosphate, and the equivalent of two ATP molecules are used in Step 2 of the cycle (ATP AMP + 2Pi). 26.58 The carbon atom and one nitrogen atom ...
Facts about Carbon Compounds (Pages 44-48)
... bond. If there is at least one double carbon-to-carbon bond, it is referred to as unsaturated. Lipids whose fatty acids contain more than one double bond are called polyunsaturated. ...
... bond. If there is at least one double carbon-to-carbon bond, it is referred to as unsaturated. Lipids whose fatty acids contain more than one double bond are called polyunsaturated. ...
Aerobic Metabolism: The Citric Acid Cycle
... TPP (Thiamine pyrophosphate), FAD, NAD+ and lipoic acid are the required co-enzymes for acetyl-CoA synthesis from pyruvate. ...
... TPP (Thiamine pyrophosphate), FAD, NAD+ and lipoic acid are the required co-enzymes for acetyl-CoA synthesis from pyruvate. ...
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
... multicomponent mixtures using the differences in their affinity to the stationary and mobile phase. Variety of physicochemical properties (hydrophobicity, pKa, additional functional groups) differing amino acids make a chromatographic separation possible and, what more important very efficient. In o ...
... multicomponent mixtures using the differences in their affinity to the stationary and mobile phase. Variety of physicochemical properties (hydrophobicity, pKa, additional functional groups) differing amino acids make a chromatographic separation possible and, what more important very efficient. In o ...
inhibition of protein synthesis in cell-free systems by
... vessel was used containing non-labeled leucine and the 21 other amino acids. If a significant deacylation occurred during the incubation, then the specific activity or the total counts incorporated into the protein should be greatly lowered. From the results of this experiment, it can be seen that H ...
... vessel was used containing non-labeled leucine and the 21 other amino acids. If a significant deacylation occurred during the incubation, then the specific activity or the total counts incorporated into the protein should be greatly lowered. From the results of this experiment, it can be seen that H ...
Selective Amino Acid-Type Labeling(continued)
... resonances which are otherwise buried in the crowded regions of 2D and 3D NMR spectra. However, a disadvantage of this method is the possible mis-incorporation of 15N label in undesired amino acids (also called as “isotope scrambling”).3 This happens due to metabolic conversion of one amino acid to ...
... resonances which are otherwise buried in the crowded regions of 2D and 3D NMR spectra. However, a disadvantage of this method is the possible mis-incorporation of 15N label in undesired amino acids (also called as “isotope scrambling”).3 This happens due to metabolic conversion of one amino acid to ...
Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in
... derivatized amino acids in less than 8 minutes. The pre-column AQC derivatization results in stable derivatives of primary and secondary amino acids and can be figured out in just one simple step. This step can also be automatized using the autosampler unit at ambient temperature. But caused by the ...
... derivatized amino acids in less than 8 minutes. The pre-column AQC derivatization results in stable derivatives of primary and secondary amino acids and can be figured out in just one simple step. This step can also be automatized using the autosampler unit at ambient temperature. But caused by the ...
Structure and Function at a microscopic scale
... http://sun.menloschool.org/~dspence/biology/chapter3/chapt3_12.html ...
... http://sun.menloschool.org/~dspence/biology/chapter3/chapt3_12.html ...
Biochemistry Note
... called polysaccharides - polysaccharides are insoluble and very large, therefore when eaten, reactions in the digestive system break everything down to glucose molecules - there are three important polysaccharides: glycogen, starches, and fibres ...
... called polysaccharides - polysaccharides are insoluble and very large, therefore when eaten, reactions in the digestive system break everything down to glucose molecules - there are three important polysaccharides: glycogen, starches, and fibres ...
2.4 Molecules to Metabolism NOTES - Proteins
... Nature of science: Looking for patterns, trends and discrepancies—most but not all organisms assemble proteins from the same amino acids. Understandings: • Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. • There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on riboso ...
... Nature of science: Looking for patterns, trends and discrepancies—most but not all organisms assemble proteins from the same amino acids. Understandings: • Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. • There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on riboso ...
What_I_need_to_know_about_Protein_Synthesis_2013
... 20. Protein synthesis is the process of making _________ A gene is the instructions to make a _____________ The protein is the expressed __________ of the organism. 21. Where does protein synthesis occur in the cell? _________________ 22. The process of protein synthesis begins with one ____________ ...
... 20. Protein synthesis is the process of making _________ A gene is the instructions to make a _____________ The protein is the expressed __________ of the organism. 21. Where does protein synthesis occur in the cell? _________________ 22. The process of protein synthesis begins with one ____________ ...
1101Lecture 16 powerpoint
... Food labels will allow you to do this Following Canada’s food guide will allow you to estimate this ...
... Food labels will allow you to do this Following Canada’s food guide will allow you to estimate this ...
Practice Exam 2
... steroids and waxes. Fats are the most common _________________________ molecules in living things. The most common fats in plants and animals are the _________________________. These contain _________________________ fatty acids and _________________________ molecule of glycerol. Fatty acids are lon ...
... steroids and waxes. Fats are the most common _________________________ molecules in living things. The most common fats in plants and animals are the _________________________. These contain _________________________ fatty acids and _________________________ molecule of glycerol. Fatty acids are lon ...
RNA Processing #3 - Pennsylvania State University
... • UAA, UAG, UGA • For the genes identified in E. coli: UAA is used for UGA is used for UAG is used for ...
... • UAA, UAG, UGA • For the genes identified in E. coli: UAA is used for UGA is used for UAG is used for ...
1101Lecture 24 powerpoint
... Food labels will allow you to do this Following Canada’s food guide will allow you to estimate this ...
... Food labels will allow you to do this Following Canada’s food guide will allow you to estimate this ...
Mentor: James A. MacKay Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
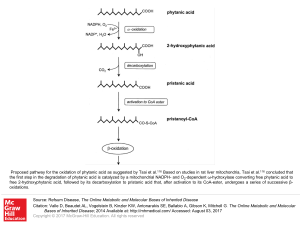
... Proposed pathway for the oxidation of phytanic acid as suggested by Tsai et al.116 Based on studies in rat liver mitochondria, Tsai et al.116 concluded that the first step in the degradation of phytanic acid is catalyzed by a mitochondrial NADPH- and O2-dependent ω-hydroxylase converting free phytan ...
... Proposed pathway for the oxidation of phytanic acid as suggested by Tsai et al.116 Based on studies in rat liver mitochondria, Tsai et al.116 concluded that the first step in the degradation of phytanic acid is catalyzed by a mitochondrial NADPH- and O2-dependent ω-hydroxylase converting free phytan ...