Connect the dots…DNA to Disease, Oltmann
... specific matches? Explain your answer. How would you conduct an experiment using the sequences you’ve been given and the BLAST server to provide evidence for your answer. 6. How would scientists all over the world check to see what a newly sequenced region of DNA is similar to? What do you think the ...
... specific matches? Explain your answer. How would you conduct an experiment using the sequences you’ve been given and the BLAST server to provide evidence for your answer. 6. How would scientists all over the world check to see what a newly sequenced region of DNA is similar to? What do you think the ...
Biology Chapter 2 Organic Molecules 9-26
... Speed up all chemical reactions (not good) Denature proteins Why use enzymes (special enzyme catalysts)? Speed up specific chemical reactions by lowering the Energy of Activation. o How do they work? Position molecules for bonding or weaken bonds before breaking. Enzymes are proteins. Rememb ...
... Speed up all chemical reactions (not good) Denature proteins Why use enzymes (special enzyme catalysts)? Speed up specific chemical reactions by lowering the Energy of Activation. o How do they work? Position molecules for bonding or weaken bonds before breaking. Enzymes are proteins. Rememb ...
Biochemistry 3 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... UDP Glucose is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of which of the following? GLYCOGEN Linoleic Acid is an essential Fatty Acid in humans due to the body’s inability to synthesize which Fatty Acid? OMEGA 6 FATTY ACID DNA synthesis is called which of the following? REPLICATION Which of the following ...
... UDP Glucose is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of which of the following? GLYCOGEN Linoleic Acid is an essential Fatty Acid in humans due to the body’s inability to synthesize which Fatty Acid? OMEGA 6 FATTY ACID DNA synthesis is called which of the following? REPLICATION Which of the following ...
Research with L-glutamate, a prototypical L-amino acid that activates umami... two G-protein coupled receptors, T1R1+T1R3 and t-mGluR4, are important in...
... than glutamate also utilize the PLC-β2 mediated pathway, and (3) L-amino acids also use a cAMPdependent pathway. In our calcium imaging study, we found that response patterns elicited by L-amino acids vary across TSCs. Further, TSCs also show synergy for different L-amino acids when mixed with IMP. ...
... than glutamate also utilize the PLC-β2 mediated pathway, and (3) L-amino acids also use a cAMPdependent pathway. In our calcium imaging study, we found that response patterns elicited by L-amino acids vary across TSCs. Further, TSCs also show synergy for different L-amino acids when mixed with IMP. ...
#24926 HAAO A Antibod
... Hydroxyanthrranilate 3, 4--dioxygenase e) is a mono omeric cytoso olic protein of o the family of in ntramolecular dioxygenasses containin ng non-heme e ferrous iron n. It is widelyy distributed in periphera al organs, succh as liver and kidney, k and is present in n low amoun nts in the cen ntral n ...
... Hydroxyanthrranilate 3, 4--dioxygenase e) is a mono omeric cytoso olic protein of o the family of in ntramolecular dioxygenasses containin ng non-heme e ferrous iron n. It is widelyy distributed in periphera al organs, succh as liver and kidney, k and is present in n low amoun nts in the cen ntral n ...
Evidences of Evolution
... share structural similarity, but not function, analogous structures share function but not structural similarity since they evolved independently ...
... share structural similarity, but not function, analogous structures share function but not structural similarity since they evolved independently ...
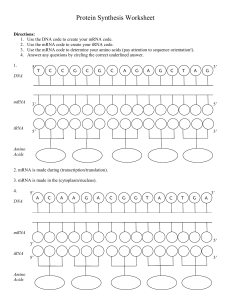
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 23. (large ribosomal subunit/MET tRNA) Second item to bind to the developing translation complex (after ...
... 23. (large ribosomal subunit/MET tRNA) Second item to bind to the developing translation complex (after ...
Fate of Carbon Skeleton
... The last 3 steps occur in cytoplasm It utilizes 3 ATP and 4 high energy bonds It is catalyzed by five enzymes Any defect in one of these enzymes leads to ammonia intoxication ...
... The last 3 steps occur in cytoplasm It utilizes 3 ATP and 4 high energy bonds It is catalyzed by five enzymes Any defect in one of these enzymes leads to ammonia intoxication ...
Unit 2 - Protein Synthesis AAB - bushelman-hap
... 1. A second tRNA bonds with the next three bases of the mRNA, the amino acid links onto the amino acid of the first tRNA via a peptide bond. (Reminder) Each tRNA specific for one amino acid only, but some amino acids coded for by up to 6 codons. Order of bases in mRNA codons determine which tRNA ant ...
... 1. A second tRNA bonds with the next three bases of the mRNA, the amino acid links onto the amino acid of the first tRNA via a peptide bond. (Reminder) Each tRNA specific for one amino acid only, but some amino acids coded for by up to 6 codons. Order of bases in mRNA codons determine which tRNA ant ...
bioknowledgy study guide
... 2.1.A1 Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms but can also be artificially synthesized. 11. Vitalism is a theory that nowadays has no credit. a. Describe the central tenant that Wöhler falsified. ...
... 2.1.A1 Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms but can also be artificially synthesized. 11. Vitalism is a theory that nowadays has no credit. a. Describe the central tenant that Wöhler falsified. ...
Decoding mRNA
... DNA. This copy is called 5. _________________________ and can leave the cell’s nucleus. It travels to the 6.___________________ in the cytoplasm of the cell where DNA’s message can be decoded into a sequence of amino acids. The steps of creating an mRNA transcript need to be put in order. 7. Place t ...
... DNA. This copy is called 5. _________________________ and can leave the cell’s nucleus. It travels to the 6.___________________ in the cytoplasm of the cell where DNA’s message can be decoded into a sequence of amino acids. The steps of creating an mRNA transcript need to be put in order. 7. Place t ...
Amino Acid Starter Kit – In Brief
... Shake the protein noting that the protein maintains its basic shape. Create an active site on the surface of your protein by adding three amino acid side chains – a serine, a histidine and a glutamic acid. The three amino acid side chains that make up your protein’s active site may bind with a subst ...
... Shake the protein noting that the protein maintains its basic shape. Create an active site on the surface of your protein by adding three amino acid side chains – a serine, a histidine and a glutamic acid. The three amino acid side chains that make up your protein’s active site may bind with a subst ...
Unit 2 - Part 1
... Reactions occur very slow on their own Enzymes speed up reactions 2. How are enzymes specific? They have a specific shape that only allows them to work on specific substrates. ...
... Reactions occur very slow on their own Enzymes speed up reactions 2. How are enzymes specific? They have a specific shape that only allows them to work on specific substrates. ...
Water as a Solvent
... of chirality: The left hand is a non superposable mirror image of the right of chirality: The left hand is a non‐superposable mirror image of the right hand; no matter how the two hands are oriented, it is impossible for all the major features of both hands to coincide. This difference in symmetry ...
... of chirality: The left hand is a non superposable mirror image of the right of chirality: The left hand is a non‐superposable mirror image of the right hand; no matter how the two hands are oriented, it is impossible for all the major features of both hands to coincide. This difference in symmetry ...
Practice Questions
... genital region and the patient’s gametes (sperm or egg cells) were severely mutated as a result of the high powered rays. Will this mutation be passed down the offspring? The Ribosome shifts along the mRNA over to the next codon __ The polypeptide chain becomes the actual protein by folding into the ...
... genital region and the patient’s gametes (sperm or egg cells) were severely mutated as a result of the high powered rays. Will this mutation be passed down the offspring? The Ribosome shifts along the mRNA over to the next codon __ The polypeptide chain becomes the actual protein by folding into the ...
Document
... a. Disulfide bonds are a type of interaction between amino acid residues found in the tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure. b. The peptide bonds in the sequence of amino acids form the primary level of protein structure. c. The hydrogen bonds between the peptide bonds along the polype ...
... a. Disulfide bonds are a type of interaction between amino acid residues found in the tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure. b. The peptide bonds in the sequence of amino acids form the primary level of protein structure. c. The hydrogen bonds between the peptide bonds along the polype ...
ECA Biochemistry Gizmos
... Science 10 – Biochem Last time we focused on Vocab, this time on function within the system ...
... Science 10 – Biochem Last time we focused on Vocab, this time on function within the system ...
Integrating the universal metabolism into a phylogenetic analysis
... pathways for phylogenetic analysis. As in Cunchillos and Lecointre (2000), taxa are defined from the tip of the pathway to its point of contact into the Krebs cycle. To name pathways, prefixes ‘‘d’’ and ‘‘s’’ are used to refer to degradation and synthesis, respectively. For example, dGLN is the set ...
... pathways for phylogenetic analysis. As in Cunchillos and Lecointre (2000), taxa are defined from the tip of the pathway to its point of contact into the Krebs cycle. To name pathways, prefixes ‘‘d’’ and ‘‘s’’ are used to refer to degradation and synthesis, respectively. For example, dGLN is the set ...
Chapter 5 - Fernando Haro
... and amino acids Brush border of small intestine makes several peptidases – enzymes that break down short peptide chains into amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides As dipeptides and tripeptides enter the intestinal cells, they are split into amino acids Amino acids travel in blood to liver a ...
... and amino acids Brush border of small intestine makes several peptidases – enzymes that break down short peptide chains into amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides As dipeptides and tripeptides enter the intestinal cells, they are split into amino acids Amino acids travel in blood to liver a ...
01 Structure, properties and biological functions of proteins
... Immunoglobulin G molecules are the principal antibody species found circulating free in the blood plasma. Many membrane proteins are glycosylated on their extracellular segments. Lipoproteins. Blood plasma lipoproteins are prominent examples of the class of proteins conjugated with lipid. The plasma ...
... Immunoglobulin G molecules are the principal antibody species found circulating free in the blood plasma. Many membrane proteins are glycosylated on their extracellular segments. Lipoproteins. Blood plasma lipoproteins are prominent examples of the class of proteins conjugated with lipid. The plasma ...
biochemistry - living environment
... The Chemistry of Life What are living creatures made of? Why do we have to eat? ...
... The Chemistry of Life What are living creatures made of? Why do we have to eat? ...