BIO 212 SI Kukday--Energetics (2) Review 2/7
... Dr. Kukday’s “Can You?” Questions (Highlighted ones are addressed in this worksheet, you will need to address the ones that aren’t highlighted on your own time): Paralysis Case: 1.) Can you identify types of enzyme regulation (emphasis on feedback inhibition)? 2.) Can you predict the consequences o ...
... Dr. Kukday’s “Can You?” Questions (Highlighted ones are addressed in this worksheet, you will need to address the ones that aren’t highlighted on your own time): Paralysis Case: 1.) Can you identify types of enzyme regulation (emphasis on feedback inhibition)? 2.) Can you predict the consequences o ...
UG Curriculum
... student should not be expected to memorise them. An introduction to biochemical genetics and molecular biology is a must but details should be avoided. The exposure to anti vitamins, anti metabolites and enzyme inhibitor at this stage, will provide a basis for the future study of medical subjects. A ...
... student should not be expected to memorise them. An introduction to biochemical genetics and molecular biology is a must but details should be avoided. The exposure to anti vitamins, anti metabolites and enzyme inhibitor at this stage, will provide a basis for the future study of medical subjects. A ...
A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered
... (A) During DNA replication, there was a deletion of a single nucleotide that codes for lysine (Lys), resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that deletion of a single nucleotide during replication wou ...
... (A) During DNA replication, there was a deletion of a single nucleotide that codes for lysine (Lys), resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that deletion of a single nucleotide during replication wou ...
Similarity
... Note: it is possible that two proteins share a high degree of similarity but have two different functions. For example, human gamma-crystallin is a lens protein that has no known enzymatic activity. It shares a high percentage of identity with E. coli quinone oxidoreductase. These proteins likely ha ...
... Note: it is possible that two proteins share a high degree of similarity but have two different functions. For example, human gamma-crystallin is a lens protein that has no known enzymatic activity. It shares a high percentage of identity with E. coli quinone oxidoreductase. These proteins likely ha ...
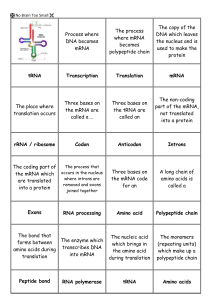
Gene expression flash cards
... The codon found at the end of the mRNA which tells the ribosome to stop translation ...
... The codon found at the end of the mRNA which tells the ribosome to stop translation ...
Statistical Selection of Amino Acids Fortifying a Minimal Defined
... Set 2 contained cysteine at a concentration of 1.0 g/l in the initial medium and 10.0 g/l in the feed medium. Set 3 contained glutamine at a concentration of 0.6 g/l in the initial medium and 6.0 g/l in the feed medium. Set 4 contained glutamine, arginine and cysteine at a concentration of 0.6, 1.2, ...
... Set 2 contained cysteine at a concentration of 1.0 g/l in the initial medium and 10.0 g/l in the feed medium. Set 3 contained glutamine at a concentration of 0.6 g/l in the initial medium and 6.0 g/l in the feed medium. Set 4 contained glutamine, arginine and cysteine at a concentration of 0.6, 1.2, ...
Positive vs Negative Feedback Control
... 2) State how the activity of pepsin will most likely change after it moves with the food from the stomach to the small intestine. ...
... 2) State how the activity of pepsin will most likely change after it moves with the food from the stomach to the small intestine. ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... • Use the triangle water to point to the bond site. Draw an arrow to show if water is being added or released during this reaction. Label as a 4-monomer polypeptide ...
... • Use the triangle water to point to the bond site. Draw an arrow to show if water is being added or released during this reaction. Label as a 4-monomer polypeptide ...
Amino acids
... They are often called macromolecules because of their large size. They are also called polymers because they are made from identical building blocks strung together. The building blocks of polymers are called monomers. Monomers are linked together to form polymers through dehydration reactions, whic ...
... They are often called macromolecules because of their large size. They are also called polymers because they are made from identical building blocks strung together. The building blocks of polymers are called monomers. Monomers are linked together to form polymers through dehydration reactions, whic ...
1) Which residues prefer helix, strand, turn:
... molecule. MHGSKDQILCA (and 3-letter code you can look up) ...
... molecule. MHGSKDQILCA (and 3-letter code you can look up) ...
BIO 220 Chapter 5 lecture outline Metabolism definition Collision
... 5. Describe the general structure and characteristics of an enzyme. 6. Explain the mechanism by which enzymes speed up chemical reactions. 7. Why would a particular enzyme be able to bind to only one or a small number of substrates? 8. What is the function of each type of enzyme listed in table 5.1 ...
... 5. Describe the general structure and characteristics of an enzyme. 6. Explain the mechanism by which enzymes speed up chemical reactions. 7. Why would a particular enzyme be able to bind to only one or a small number of substrates? 8. What is the function of each type of enzyme listed in table 5.1 ...
Sensing DNA? Aim for the cytoplasm in Systemic Lupus
... The region is highly polymorphic. There are multiple SNPs identified in exonic, intronic and promoter regions in genes Ifi202, Ifi203, Ifi205, Mnda and Aim2. A lysine to glutamine switch occurs in Ifi202, Ifi203 and Ifi205. The start codon in Ifi203 contains a switch from methionine to threonine. If ...
... The region is highly polymorphic. There are multiple SNPs identified in exonic, intronic and promoter regions in genes Ifi202, Ifi203, Ifi205, Mnda and Aim2. A lysine to glutamine switch occurs in Ifi202, Ifi203 and Ifi205. The start codon in Ifi203 contains a switch from methionine to threonine. If ...
Which Organic Molecules Are Important For Life? 1. List the 4 major
... 1. List the 4 major groups of organic molecules that are important for life and give the main function(s) of each; for molecules that are composed of monomers, name the general type of monomer. ...
... 1. List the 4 major groups of organic molecules that are important for life and give the main function(s) of each; for molecules that are composed of monomers, name the general type of monomer. ...
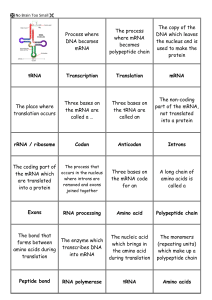
Gene expression flash cards
... The codon found at the end of the mRNA which tells the ribosome to stop translation ...
... The codon found at the end of the mRNA which tells the ribosome to stop translation ...
Browning Reactions
... Important Types of Browning • Enzymatic (polyphenoloxidase). Fresh cut vegetables, non-toxic, no flavor • Caramelization. Sugars at very high temperatures. • Lipid Browning. Polymerization of frying oils • Vitamin C Browning. Similar to Maillard • THE MAILLARD REACTION ...
... Important Types of Browning • Enzymatic (polyphenoloxidase). Fresh cut vegetables, non-toxic, no flavor • Caramelization. Sugars at very high temperatures. • Lipid Browning. Polymerization of frying oils • Vitamin C Browning. Similar to Maillard • THE MAILLARD REACTION ...
Enzyme Notes - Ms. Fox's Science Spot
... • Enzymes lower the activation energy – They make it easier for the reaction to start like lowering a hurdle energy (kJ) ...
... • Enzymes lower the activation energy – They make it easier for the reaction to start like lowering a hurdle energy (kJ) ...
Poster
... Staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which have become increasingly resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics. New ways to combat these bacteria are needed. The Greenfield High School SMART (Students Modeling A Research Topic) Team is modeling the enzyme GatCAB using 3 ...
... Staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which have become increasingly resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics. New ways to combat these bacteria are needed. The Greenfield High School SMART (Students Modeling A Research Topic) Team is modeling the enzyme GatCAB using 3 ...
Lecture 9
... evidence to explain what the earliest life was like, therefore much of what I will present today is hypothetical. Experiments can be done that produce results consistent with different stages in the scenario. Let’s briefly look at some of the key experiments that shed light on these stages. 2. Synth ...
... evidence to explain what the earliest life was like, therefore much of what I will present today is hypothetical. Experiments can be done that produce results consistent with different stages in the scenario. Let’s briefly look at some of the key experiments that shed light on these stages. 2. Synth ...
Building Blocks of Bodybuilding
... Metabolic utilisation of nutritional building blocks as an energy source & for muscle cell growth and repair. ...
... Metabolic utilisation of nutritional building blocks as an energy source & for muscle cell growth and repair. ...
The Effect of Protein Loads on Plasma Amino Acid Levels
... sponding fasting mean (Table 1). The sum of the mean concentrations of each individual amino acid 2 h after the meal was found to be 1-5times the sum of the mean fasting concentrations. Glutamine, the most abundant amino acid in plasma, and glycine showed the smallest changes, their mean concentrati ...
... sponding fasting mean (Table 1). The sum of the mean concentrations of each individual amino acid 2 h after the meal was found to be 1-5times the sum of the mean fasting concentrations. Glutamine, the most abundant amino acid in plasma, and glycine showed the smallest changes, their mean concentrati ...