integrated-principles-of-zoology-16th-edition-hickman
... e. The term amphiphilic describes compounds, like phospholipids, that are polar and watersoluble on one end and non-polar on the other end. 5. Steroids (Figure 2.13) a. Steroids are complex alcohols with fat-like properties. b. They are biologically important. c. Steroids include cholesterol, vitami ...
... e. The term amphiphilic describes compounds, like phospholipids, that are polar and watersoluble on one end and non-polar on the other end. 5. Steroids (Figure 2.13) a. Steroids are complex alcohols with fat-like properties. b. They are biologically important. c. Steroids include cholesterol, vitami ...
chapter 2 the origin and chemistry of life
... e. The term amphiphilic describes compounds, like phospholipids, that are polar and watersoluble on one end and non-polar on the other end. 5. Steroids (Figure 2.13) a. Steroids are complex alcohols with fat-like properties. b. They are biologically important. c. Steroids include cholesterol, vitami ...
... e. The term amphiphilic describes compounds, like phospholipids, that are polar and watersoluble on one end and non-polar on the other end. 5. Steroids (Figure 2.13) a. Steroids are complex alcohols with fat-like properties. b. They are biologically important. c. Steroids include cholesterol, vitami ...
Chapter 22, Proteins
... classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ¾A dipeptide is a molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ¾A tripeptide is a molecule containing three amino acids joined by two peptide bonds. ¾A polypeptide is a macromolecule containing many amino acids joined by peptide ...
... classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ¾A dipeptide is a molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ¾A tripeptide is a molecule containing three amino acids joined by two peptide bonds. ¾A polypeptide is a macromolecule containing many amino acids joined by peptide ...
Model Description Sheet
... excite the cell and control multiple intracellular signaling pathways. In the presence of alcohol, this essential ion gate is often shut, inhibiting the flow of ions and therefore leading to the well-known symptoms of intoxication. The NMDA receptor is composed of 4 subunits: 2 GluN1 and 2 GluN2A, t ...
... excite the cell and control multiple intracellular signaling pathways. In the presence of alcohol, this essential ion gate is often shut, inhibiting the flow of ions and therefore leading to the well-known symptoms of intoxication. The NMDA receptor is composed of 4 subunits: 2 GluN1 and 2 GluN2A, t ...
Water Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds Non
... Water molecules attached to ions in hydration shell due to ionic attraction and water’s polarity. There is an energy involved in taking the water molecules away in order to work with the ions (with bodily processes) ...
... Water molecules attached to ions in hydration shell due to ionic attraction and water’s polarity. There is an energy involved in taking the water molecules away in order to work with the ions (with bodily processes) ...
Protein Synthesis - Issaquah Connect
... • RNA is one of the three major biological macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life. • It works with DNA to create proteins by reading the DNA’s code, copying the code, taking the code out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, joining amino acids together forming proteins at a ri ...
... • RNA is one of the three major biological macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life. • It works with DNA to create proteins by reading the DNA’s code, copying the code, taking the code out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, joining amino acids together forming proteins at a ri ...
classification of enzymes
... – Bile acid formation – Conversion of cholesterol into 7-hydroxylcholesterol – Maintain metallic co-factors like Cu+ in Monooxygenases and Fe in dioxygenases in reduced form – Conversion of cholesterol into steroid hormone in adrenal ...
... – Bile acid formation – Conversion of cholesterol into 7-hydroxylcholesterol – Maintain metallic co-factors like Cu+ in Monooxygenases and Fe in dioxygenases in reduced form – Conversion of cholesterol into steroid hormone in adrenal ...
Chemistry of Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins Biologists depend
... glucose molecules attached to form these polysaccharides is not known. The two most common polysaccharides in biology are starch and cellulose. They consist of long chains of glucose molecules joined together. With another team construct a starch molecule by joining four glucose molecules. This repr ...
... glucose molecules attached to form these polysaccharides is not known. The two most common polysaccharides in biology are starch and cellulose. They consist of long chains of glucose molecules joined together. With another team construct a starch molecule by joining four glucose molecules. This repr ...
Unit 3 Review Sheet – Biochemistry
... What are the characteristics of water that make it important to life? Polar, high heat capacity, resists temperature change, abililty to bond and attract other molecules (cohesion and adhesion), ice is less dense than liquid water, universal solvent, most abundant compound in living things What does ...
... What are the characteristics of water that make it important to life? Polar, high heat capacity, resists temperature change, abililty to bond and attract other molecules (cohesion and adhesion), ice is less dense than liquid water, universal solvent, most abundant compound in living things What does ...
Lecture notes Chapter 22-23
... whales, which allow them to stay under the water for long periods. Myoglobin contains 153 amino acids in a single polypeptide chain with about three-fourths of the chain in the α-helix secondary structure. Within the tertiary structure, a pocket of amino acids and a heme group binds and store oxygen ...
... whales, which allow them to stay under the water for long periods. Myoglobin contains 153 amino acids in a single polypeptide chain with about three-fourths of the chain in the α-helix secondary structure. Within the tertiary structure, a pocket of amino acids and a heme group binds and store oxygen ...
Module 10: Catabolism of Amino Acids
... phosphate indicating how the numbers indicated in the fructose above. At the end of this test there is a scheme of the glycolysis pathway. Just by the molecules involved in the pathway: a. Which step of the glycolysis pathway will yield a molecule of reduced NADH? b. Why does the overall glycolysis ...
... phosphate indicating how the numbers indicated in the fructose above. At the end of this test there is a scheme of the glycolysis pathway. Just by the molecules involved in the pathway: a. Which step of the glycolysis pathway will yield a molecule of reduced NADH? b. Why does the overall glycolysis ...
chirality
... • Provide answers to the case study questions in Part 1 (a–e) at the start of your report. • Critical Analysis Report: Using the answers to the case study questions in Parts 2–4, describe the major points of the case in essay format. Summarize the outcomes and concepts discussed in your lab session. ...
... • Provide answers to the case study questions in Part 1 (a–e) at the start of your report. • Critical Analysis Report: Using the answers to the case study questions in Parts 2–4, describe the major points of the case in essay format. Summarize the outcomes and concepts discussed in your lab session. ...
Identification of α-amino acids by hydrophilic interaction
... was selected for further optimization due to slightly better resolution and lower peak tailing obtained in this phase. Next, various mobile phase additives, namely acetic and formic acids, ammonium acetate and ammonium formate, were tested in terms of retention, resolution and MS signal response. Th ...
... was selected for further optimization due to slightly better resolution and lower peak tailing obtained in this phase. Next, various mobile phase additives, namely acetic and formic acids, ammonium acetate and ammonium formate, were tested in terms of retention, resolution and MS signal response. Th ...
metabolism in muscle and nerves
... • Inflate blood pressure cuff and perform repetitive rapid grip exercise • Once fatigued, remove cuff and obtain blood samples for lactate and ammonia levels • Normal result is elevated lactate and ammonia then return to baseline in 10-15 minutes ...
... • Inflate blood pressure cuff and perform repetitive rapid grip exercise • Once fatigued, remove cuff and obtain blood samples for lactate and ammonia levels • Normal result is elevated lactate and ammonia then return to baseline in 10-15 minutes ...
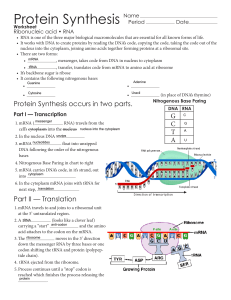
Name
... a-With codons being 3 bases long, there are _________ different combinations. Since there are only _______ amino acids, there is quite enough for each amino acid to have its own “word” to stand for it. b-If you discovered a planet whose residents had 2-base codons, what is the maximum number of amin ...
... a-With codons being 3 bases long, there are _________ different combinations. Since there are only _______ amino acids, there is quite enough for each amino acid to have its own “word” to stand for it. b-If you discovered a planet whose residents had 2-base codons, what is the maximum number of amin ...
Bacterial Physiology Lec-8 Catabolism: Tricarboxylic acid cycle
... In the first reaction acetyl –CoA is condensed with a four-carbon intermediate , oxaloacetate, to form citrate and to begin the six–carbon stage. Citrate (a tertiary alcohol) is rearranged to give isocitrate which is oxidized and decarboxylated twice to yield α-ketoglutarate, then succinyl-CoA. 2NAD ...
... In the first reaction acetyl –CoA is condensed with a four-carbon intermediate , oxaloacetate, to form citrate and to begin the six–carbon stage. Citrate (a tertiary alcohol) is rearranged to give isocitrate which is oxidized and decarboxylated twice to yield α-ketoglutarate, then succinyl-CoA. 2NAD ...
Biochemistry
... molecule of DNA. The DNA molecule is the same in every cell of the same animal and it is inherited from a combination of the parents’ DNA. Each organism and each individual has a different DNA. The only exception is with identical twins. A single strand of DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleoti ...
... molecule of DNA. The DNA molecule is the same in every cell of the same animal and it is inherited from a combination of the parents’ DNA. Each organism and each individual has a different DNA. The only exception is with identical twins. A single strand of DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleoti ...
reading - Science with Ms. Wang
... larger molecules. Two monosaccharides can combine in a condensation reaction to form a disaccharide. For example, fructose and glucose combine to form sucrose, which is common table sugar. Maltose (malt sugar) and lactose (milk sugar) are other ...
... larger molecules. Two monosaccharides can combine in a condensation reaction to form a disaccharide. For example, fructose and glucose combine to form sucrose, which is common table sugar. Maltose (malt sugar) and lactose (milk sugar) are other ...
Macromolecules - Uplift Education
... Macromolecules Macromolecules are large organic molecules that consist of chains of repeating subunits called monomers. ...
... Macromolecules Macromolecules are large organic molecules that consist of chains of repeating subunits called monomers. ...