design of energy metabolism
... Evolutionary trend is toward higher levels of activity in advanced invertebrates. This trend continues throughout vertebrate evolution. Associated with this trend is a tendency for lesser reliance on sustained anaerobic pathways and greater used of arginine phosphate (cephalopods), creatine phosphat ...
... Evolutionary trend is toward higher levels of activity in advanced invertebrates. This trend continues throughout vertebrate evolution. Associated with this trend is a tendency for lesser reliance on sustained anaerobic pathways and greater used of arginine phosphate (cephalopods), creatine phosphat ...
You should be able to identify each of the following functional
... You should be able to identify each of the following functional groups within organic molecules: amino group within an amine molecule (both the form found at low pH and high pH) carbonyl group within an aldehyde molecule (you need to know it is within an aldehyde vs a ketone) carbonyl group within a ...
... You should be able to identify each of the following functional groups within organic molecules: amino group within an amine molecule (both the form found at low pH and high pH) carbonyl group within an aldehyde molecule (you need to know it is within an aldehyde vs a ketone) carbonyl group within a ...
3.3 teacher Notes
... • The cell’s boundary is made of phospholipids. The structure of cell membranes depends on how this molecule interacts with water. • Waxes, found on the surfaces of plants and aquatic bird feathers, help prevent evaporation of water from the cells of the organism. ...
... • The cell’s boundary is made of phospholipids. The structure of cell membranes depends on how this molecule interacts with water. • Waxes, found on the surfaces of plants and aquatic bird feathers, help prevent evaporation of water from the cells of the organism. ...
Chapter 7: Gene Expression: The Flow of Genetic Information from
... together the remaining exons. Alternative splicing makes it possible to produce different mRNAs from the same primary transcript. Translation is the stage of gene expression when the cell synthesizes proteins according to instructions in the mRNA. a. tRNAs carry amino acids to the translation machin ...
... together the remaining exons. Alternative splicing makes it possible to produce different mRNAs from the same primary transcript. Translation is the stage of gene expression when the cell synthesizes proteins according to instructions in the mRNA. a. tRNAs carry amino acids to the translation machin ...
Macromolecule notes
... What is an Organic Compound? • Anything that contains the following two elements: Carbon & Hydrogen ...
... What is an Organic Compound? • Anything that contains the following two elements: Carbon & Hydrogen ...
Citric Acid Cycle 2
... the first round of the citric acid cycle that could possibly release a carbon atom originating from this acetyl CoA? A) First round. B) Second round. C) Third round. D) Fourth round. 3. What type of enzyme is involved in all four redox reactions of the citric acid cycle? ...
... the first round of the citric acid cycle that could possibly release a carbon atom originating from this acetyl CoA? A) First round. B) Second round. C) Third round. D) Fourth round. 3. What type of enzyme is involved in all four redox reactions of the citric acid cycle? ...
Proleins: Chem[siry And
... 7. HOW does the number of hydrogen atoms compare to the number of oxygen atoms in eaeh ...
... 7. HOW does the number of hydrogen atoms compare to the number of oxygen atoms in eaeh ...
Lecture PPT
... separated and analysed by mass spectrometry and/or tandem mass spectrometry for the purpose of identifying the proteins contained in the sample and determining their relative abundance. The patterns of isotopic mass differences generated by each method are indicated schematically. The mass differenc ...
... separated and analysed by mass spectrometry and/or tandem mass spectrometry for the purpose of identifying the proteins contained in the sample and determining their relative abundance. The patterns of isotopic mass differences generated by each method are indicated schematically. The mass differenc ...
Lysinuric protein intolerance: one gene, many
... this mechanism. LPI is therefore treated by strict avoidance of protein-rich food and supplementation of citrulline. Citrulline is absorbed by neutral amino acid transporters and can subsequently replenish the urea cycle (9). The reduced capacity of the urea cycle probably also causes a compensatory ...
... this mechanism. LPI is therefore treated by strict avoidance of protein-rich food and supplementation of citrulline. Citrulline is absorbed by neutral amino acid transporters and can subsequently replenish the urea cycle (9). The reduced capacity of the urea cycle probably also causes a compensatory ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA, functioning as the hereditary
... The DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is found in the nucleus of the cell, yet protein synthesis occurs outside the nucleus on ribosomes within the cytoplasm. Molecules of RNA (ribonucleic acid) carry a transcribed genetic message from the DNA to the ribosome, where other molecules of RNA function in the ...
... The DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is found in the nucleus of the cell, yet protein synthesis occurs outside the nucleus on ribosomes within the cytoplasm. Molecules of RNA (ribonucleic acid) carry a transcribed genetic message from the DNA to the ribosome, where other molecules of RNA function in the ...
fermentations
... In the presence of a fermetable sugar and L-malate, Leuconostoc, Lactobacillus Carry out the malo-lactic fermentation: Malic enzyme ...
... In the presence of a fermetable sugar and L-malate, Leuconostoc, Lactobacillus Carry out the malo-lactic fermentation: Malic enzyme ...
Powerpoint Slides for Chapter Seven
... Three carbon fragment moves into mitochondria losing a carbon in the process. (acetyl CoA) Inside the mitochondria, the two carbon piece left from the sugar is converted to carbon dioxide, water, and lots of ATP (TCA & ETS) ...
... Three carbon fragment moves into mitochondria losing a carbon in the process. (acetyl CoA) Inside the mitochondria, the two carbon piece left from the sugar is converted to carbon dioxide, water, and lots of ATP (TCA & ETS) ...
1. Substrate level phosphorylation A) is part
... group with the methyl carbon labeled with 14C is used in the last reaction cycle. All other reactions before and after use unlabeled acetate. Which carbon is labeled in the resulting product molecule? As you know, fatty acids are numbered with the carboxyl group being number 1. A) carbon number 2 B) ...
... group with the methyl carbon labeled with 14C is used in the last reaction cycle. All other reactions before and after use unlabeled acetate. Which carbon is labeled in the resulting product molecule? As you know, fatty acids are numbered with the carboxyl group being number 1. A) carbon number 2 B) ...
Amines and amino acids
... a good understanding of the units that make up the protein chain is important. Unlike polysaccharides, which are composed of the same type of unit linked in different ways, protein chains can contain any or all of the naturally-occurring amino acids Table 20.1: each amino acid makes up somewhere b ...
... a good understanding of the units that make up the protein chain is important. Unlike polysaccharides, which are composed of the same type of unit linked in different ways, protein chains can contain any or all of the naturally-occurring amino acids Table 20.1: each amino acid makes up somewhere b ...
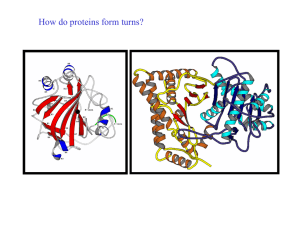
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and generally occur at the surface of the molecule. It has been suggested that turn regions act as nucleation centres during protein folding ...
... Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and generally occur at the surface of the molecule. It has been suggested that turn regions act as nucleation centres during protein folding ...
4 MolLife2
... All proteins are constructed from a common set of 20 kinds of monomers known as amino acids or peptides Each amino acid consists of: 1. A central carbon atom bonded to four covalent partners 2. An amino (NH2) group, which is basic and polar 3. A carboxyl ( ...
... All proteins are constructed from a common set of 20 kinds of monomers known as amino acids or peptides Each amino acid consists of: 1. A central carbon atom bonded to four covalent partners 2. An amino (NH2) group, which is basic and polar 3. A carboxyl ( ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... Linking Amino Acids Cells link amino acids together to make proteins The process is called dehydration synthesis Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together Proteins as Enzymes Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes contr ...
... Linking Amino Acids Cells link amino acids together to make proteins The process is called dehydration synthesis Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together Proteins as Enzymes Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes contr ...
Chemistry in Living Things - Mercer Island School District
... When sugars, proteins or lipids are broken down into their subunits, the opposite process occurs. Water is used in this process to break apart the polymer, so it is called a hydrolysis reaction. ...
... When sugars, proteins or lipids are broken down into their subunits, the opposite process occurs. Water is used in this process to break apart the polymer, so it is called a hydrolysis reaction. ...
Lecture 4
... amino acids or to the group of uncharged ones, depending on the local pH. Lysine is classified as a charged residue because its terminal amino group is ionized under most physiological conditions, but its sidechain also contains a hydrophobic segment of four methylene groups. Likewise, the arginine ...
... amino acids or to the group of uncharged ones, depending on the local pH. Lysine is classified as a charged residue because its terminal amino group is ionized under most physiological conditions, but its sidechain also contains a hydrophobic segment of four methylene groups. Likewise, the arginine ...
University of Groningen Stereoselective synthesis of glycerol
... cite from it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record ...
... cite from it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record ...