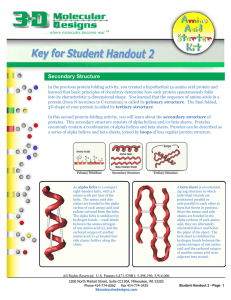
Secondary Structure - 3D Molecular Designs
... Fold the beta sheet and alpha helix into the final tertiary structure of the zinc finger. In its final tertiary structure, the seven side chains will be positioned such that: • The two cysteine and two histidine side chains will be oriented to simultaneously bind to a single zinc atom (not included ...
... Fold the beta sheet and alpha helix into the final tertiary structure of the zinc finger. In its final tertiary structure, the seven side chains will be positioned such that: • The two cysteine and two histidine side chains will be oriented to simultaneously bind to a single zinc atom (not included ...
Lipid Synthesis 1. Fatty acid synthesis
... substance to the conjecture (since acetate was the product of β-oxidation). However, as work progressed a number of significant differences between synthesis and degradation were noted including: 1. β-oxidation occurs in the mitochondria and synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm; 2. citrate is required ...
... substance to the conjecture (since acetate was the product of β-oxidation). However, as work progressed a number of significant differences between synthesis and degradation were noted including: 1. β-oxidation occurs in the mitochondria and synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm; 2. citrate is required ...
Amino Acids and Peptides
... units of proteins. They form short polymer chains called peptides or polypeptides which in turn form structures called proteins. The process of such formation from an mRNA template is known as translation, which is part of protein synthesis. Phenylalanine is one of the standard amino acids. ...
... units of proteins. They form short polymer chains called peptides or polypeptides which in turn form structures called proteins. The process of such formation from an mRNA template is known as translation, which is part of protein synthesis. Phenylalanine is one of the standard amino acids. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • Picks up the appropriate amino acid floating in the cytoplasm • Transports amino acids to the mRNA • Have anticodons that are complementary to mRNA codons • Recognizes the appropriate codons on the mRNA and bonds to them with H-bonds ...
... • Picks up the appropriate amino acid floating in the cytoplasm • Transports amino acids to the mRNA • Have anticodons that are complementary to mRNA codons • Recognizes the appropriate codons on the mRNA and bonds to them with H-bonds ...
Slide 1
... • All these reactions depend on accumulation of negative charge on the carbonyl carbon at which cleavage occurs! • Thiamine pyrophosphate facilitates these reactions by stabilizing this negative charge • The key is the quaternary nitrogen of the thiazolium group – provides electrostatic stabilizatio ...
... • All these reactions depend on accumulation of negative charge on the carbonyl carbon at which cleavage occurs! • Thiamine pyrophosphate facilitates these reactions by stabilizing this negative charge • The key is the quaternary nitrogen of the thiazolium group – provides electrostatic stabilizatio ...
Organic Chemistry and the Four Classes of Macromolecules PPT
... Carbon: The Backbone of Life • Living organisms consist mostly of carbon-based compounds due to its ability to form large, complex, and diverse molecules • Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter are all composed of carbon compounds ...
... Carbon: The Backbone of Life • Living organisms consist mostly of carbon-based compounds due to its ability to form large, complex, and diverse molecules • Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter are all composed of carbon compounds ...
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4
... component of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein MST1/MST2, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylate ...
... component of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein MST1/MST2, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylate ...
Notes: Amino Acids and Proteins:
... -amino acids contain both acidic -COOH and the basic –NH2 groups, these two functional groups allow them to act as a buffer. Unfortunately, though, the picture is not as simple as this. In the solid crystalline state the a-amino acids exist as Zwitter ions, as discussed before they are formed by th ...
... -amino acids contain both acidic -COOH and the basic –NH2 groups, these two functional groups allow them to act as a buffer. Unfortunately, though, the picture is not as simple as this. In the solid crystalline state the a-amino acids exist as Zwitter ions, as discussed before they are formed by th ...
Macromolecules: Their Structure and Function A. Lipids: Water
... plants. β-Carotene can be split to form vitamin A, a lipid vitamin. ...
... plants. β-Carotene can be split to form vitamin A, a lipid vitamin. ...
CH 5 CQ
... c) Cellulose has beta-glycosidic linkages; starch-digesting enzymes cleave only alpha-glycosidic linkages. d) Cellulose has beta-galactoside linkages that only bacterial beta-galactosidases can cleave. e) Cellulose fibers are covalently cross-linked; starch-digesting enzymes cannot cleave these cros ...
... c) Cellulose has beta-glycosidic linkages; starch-digesting enzymes cleave only alpha-glycosidic linkages. d) Cellulose has beta-galactoside linkages that only bacterial beta-galactosidases can cleave. e) Cellulose fibers are covalently cross-linked; starch-digesting enzymes cannot cleave these cros ...
Protein Structure:
... Post-translational regulation: Post-translational modification of a protein can have a profound effect on its structure, and consequently affect its activity or function. Phosphorylation (the covalent attachment of a phosphate group to either serine, threonine or tyrosine) is the most common modific ...
... Post-translational regulation: Post-translational modification of a protein can have a profound effect on its structure, and consequently affect its activity or function. Phosphorylation (the covalent attachment of a phosphate group to either serine, threonine or tyrosine) is the most common modific ...
Urea
... • Ammonia is produced by all tissues from the catabolism of amino acids • Ammonia is mainly disposed is via formation of urea in liver • Blood level of ammoina must be kept very low, otherwise, hyperammonemia & CNS toxicity will occur • To solve this problem, ammonia is transported from peripheral t ...
... • Ammonia is produced by all tissues from the catabolism of amino acids • Ammonia is mainly disposed is via formation of urea in liver • Blood level of ammoina must be kept very low, otherwise, hyperammonemia & CNS toxicity will occur • To solve this problem, ammonia is transported from peripheral t ...
WEEK 10
... To understand protein structure, we discuss it at different levels, referred to as primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Only proteins with more than one chain have a quaternary structure. Primary Structure This is the sequence of amino acids in a protein. For example, are the amino acids ar ...
... To understand protein structure, we discuss it at different levels, referred to as primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Only proteins with more than one chain have a quaternary structure. Primary Structure This is the sequence of amino acids in a protein. For example, are the amino acids ar ...
Biosynthesis of Nucleotides Biosynthesis of Nucleotides
... OMP decarboxylase are contained with a single protein called OMP synthase. ...
... OMP decarboxylase are contained with a single protein called OMP synthase. ...
The Effects of Exogenous Amino Acids on Growth
... 60 h, and reached an ODbb3of approximately 2.0 within 192 h. Unbuffered control cultures increased in pH, reaching 9.0 5 0.2 by 192 h, and had a slightly higher growth rate than cultures buffered at pH 7.3. Additions of amino acids to unbuffered cultures resulted in a range of pH values as measured ...
... 60 h, and reached an ODbb3of approximately 2.0 within 192 h. Unbuffered control cultures increased in pH, reaching 9.0 5 0.2 by 192 h, and had a slightly higher growth rate than cultures buffered at pH 7.3. Additions of amino acids to unbuffered cultures resulted in a range of pH values as measured ...
Amino Acids Proteins, and Enzymes
... subunits (protein chains) Held together by same interactions as tertiary structure Hemoglobin contains four chains The heme group in each subunit picks up oxygen in the blood for transport to the tissues ...
... subunits (protein chains) Held together by same interactions as tertiary structure Hemoglobin contains four chains The heme group in each subunit picks up oxygen in the blood for transport to the tissues ...
Reactions of I,I-Diacetoxyiodobenzene with Proteins: Conversion of
... show that, in unbuffered solutions, I,I-diacetoxyiodobenzene (1) is more effective than the corresponding trifluoroacetoxy derivative (2) for converting the amide side-chains of proteins to amines. Maximum modification of the glutamine residues of insulin and lysozyme occurs within 1-2 h of treatmen ...
... show that, in unbuffered solutions, I,I-diacetoxyiodobenzene (1) is more effective than the corresponding trifluoroacetoxy derivative (2) for converting the amide side-chains of proteins to amines. Maximum modification of the glutamine residues of insulin and lysozyme occurs within 1-2 h of treatmen ...
Document
... Can generate ATP by oxidative phosphorylation and substrate level phosphorylation Substrate level phosphorylation requires the formation of ...
... Can generate ATP by oxidative phosphorylation and substrate level phosphorylation Substrate level phosphorylation requires the formation of ...
Student PPT Notes
... enzymes switch easily between 2 different shapes that either activate or inhibit the enzyme (i.e. ADP) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d5fDEUhjo-M – allosteric Regulation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DHZtOKyMPRY – feedback inhibition ...
... enzymes switch easily between 2 different shapes that either activate or inhibit the enzyme (i.e. ADP) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d5fDEUhjo-M – allosteric Regulation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DHZtOKyMPRY – feedback inhibition ...
Chapter 1
... • Amino acids are white crystalline solids with high melting points and high water solubilities • The two charged groups, the basic amino group and the carboxylic acid, at the two ends lead to internal proton transfer – zwitterions • By changing the pH you can affect the net charge on the zwitterion ...
... • Amino acids are white crystalline solids with high melting points and high water solubilities • The two charged groups, the basic amino group and the carboxylic acid, at the two ends lead to internal proton transfer – zwitterions • By changing the pH you can affect the net charge on the zwitterion ...
Chapter 6: An Introduction to Proteins
... protein and away from the aqueous solvent, while most of the polar and charged residues have their side chains on the outside surface, in contact with the solvent. In a membrane protein such as rhodopsin, the hydrophobic residues occur on the outside, where they contact the lipid bilayer, and the po ...
... protein and away from the aqueous solvent, while most of the polar and charged residues have their side chains on the outside surface, in contact with the solvent. In a membrane protein such as rhodopsin, the hydrophobic residues occur on the outside, where they contact the lipid bilayer, and the po ...
Notes
... making of protein; occurs in nucleus • Translation – uses the information in mRNA to make a specific protein, the sequence of bases of mRNA is “translated” into a sequence of amino acids; occurs in ribosome • These processes are the same in all organisms ...
... making of protein; occurs in nucleus • Translation – uses the information in mRNA to make a specific protein, the sequence of bases of mRNA is “translated” into a sequence of amino acids; occurs in ribosome • These processes are the same in all organisms ...
allosteric activator
... change of enzyme synthesis and degradation so that ultimately determine enzyme level at any point in time. In many instances, transcriptional regulation determines the concentrations of specific enzyme, with enzyme proteins degradation playing a minor role. In other instances, protein synthesis is c ...
... change of enzyme synthesis and degradation so that ultimately determine enzyme level at any point in time. In many instances, transcriptional regulation determines the concentrations of specific enzyme, with enzyme proteins degradation playing a minor role. In other instances, protein synthesis is c ...
Biochemistry Test Review Guide
... 34. Draw the general structure of an amino acid. Label: amino group, carboxyl group and R group. 35. What is the significance of the R group of an amino acid? 36. Draw the synthesis of a protein circling the formation of the peptide bond. 37. What is a chemical reaction and what are the two componen ...
... 34. Draw the general structure of an amino acid. Label: amino group, carboxyl group and R group. 35. What is the significance of the R group of an amino acid? 36. Draw the synthesis of a protein circling the formation of the peptide bond. 37. What is a chemical reaction and what are the two componen ...























