KEY - chem.uwec.edu
... run in reverse from oxaloacetate to succinate.. This produces NAD+ and FAD. Simultaneously the cycle runs forward from citrate to succinate. producing two NADH. Assuming the oysters have a steady supply of oxaloacetate (from amino acids), how much energy could they derive from this process (per “cyc ...
... run in reverse from oxaloacetate to succinate.. This produces NAD+ and FAD. Simultaneously the cycle runs forward from citrate to succinate. producing two NADH. Assuming the oysters have a steady supply of oxaloacetate (from amino acids), how much energy could they derive from this process (per “cyc ...
Prot Structure - USD Home Pages
... • Compare the various specialty structures for their biochemical structural elements (keratin, silk, collagen…) • Relate the change in function in collagen when primary acid, enzyme or enzyme co-factor is altered. • Understand the thermodynamic forces and the process by which fold and maintain terti ...
... • Compare the various specialty structures for their biochemical structural elements (keratin, silk, collagen…) • Relate the change in function in collagen when primary acid, enzyme or enzyme co-factor is altered. • Understand the thermodynamic forces and the process by which fold and maintain terti ...
Ch. 2 – Bio Chem
... http://thescienceofeating.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Book-Fats-Butter-Oils-2.jpg ...
... http://thescienceofeating.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Book-Fats-Butter-Oils-2.jpg ...
Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in
... Studies show that three additional reactions are required for the primary alcohol to under bg oxidation. Propose a pathway for the conversion of a long-chain primary alcohol to a substrate that can undergo b oxidation. Include cofactors and electron acceptors that might be required. ...
... Studies show that three additional reactions are required for the primary alcohol to under bg oxidation. Propose a pathway for the conversion of a long-chain primary alcohol to a substrate that can undergo b oxidation. Include cofactors and electron acceptors that might be required. ...
Macromolecule Lecture
... – monosaccharides consist of only one monomer subunit • an example is the sugar glucose (C6H12O6) – disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides • an example is the sugar sucrose, which is formed by joining together glucose and fructose ...
... – monosaccharides consist of only one monomer subunit • an example is the sugar glucose (C6H12O6) – disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides • an example is the sugar sucrose, which is formed by joining together glucose and fructose ...
End-product control of enzymes of branched
... increase, while all three amino acids caused a 5- to 8-fold decrease. Growth of an ilv auxotroph in media with limiting isoleucine gave enzyme specific activities 4- to 6-fold higher than in unsupplemented minimal medium. Spontaneous mutants were obtained b y growing 5. coelicolor on minimal medium ...
... increase, while all three amino acids caused a 5- to 8-fold decrease. Growth of an ilv auxotroph in media with limiting isoleucine gave enzyme specific activities 4- to 6-fold higher than in unsupplemented minimal medium. Spontaneous mutants were obtained b y growing 5. coelicolor on minimal medium ...
Protein Conformation and Function
... acid residue with the free NH2 group is called the N-terminal. • Peptide and protein chains are always written with the N-terminal residue on the left. ...
... acid residue with the free NH2 group is called the N-terminal. • Peptide and protein chains are always written with the N-terminal residue on the left. ...
CSU Agricultural Research Initiative
... time of analysis, no hazardous solvents, and low costs as compared with others (more than 1000 analysis were run with the same capillary without lost of resolutionç; in the case of HPLC, columns must be deeply cleaned and regenerated after a few analysis). Nevertheless, the principal advantage is th ...
... time of analysis, no hazardous solvents, and low costs as compared with others (more than 1000 analysis were run with the same capillary without lost of resolutionç; in the case of HPLC, columns must be deeply cleaned and regenerated after a few analysis). Nevertheless, the principal advantage is th ...
Chapter 9
... • R is the remainder of the molecule attached to the C atom associated with the α-amino group of the amino acid. ...
... • R is the remainder of the molecule attached to the C atom associated with the α-amino group of the amino acid. ...
Word Count: 1390 An experiment to determine the amount of urea in
... My average titre for the unknown sample was 11.2cm3. When I applied this to the graph I found the concentration of urea to be 0.58g/100 cm3. Figure 2.2 clearly shows that as the concentration of urea increases, the volume of HCl required for neutralisation also increases. This is to be expected as t ...
... My average titre for the unknown sample was 11.2cm3. When I applied this to the graph I found the concentration of urea to be 0.58g/100 cm3. Figure 2.2 clearly shows that as the concentration of urea increases, the volume of HCl required for neutralisation also increases. This is to be expected as t ...
NSAIDs - Virtual Medic
... a. Reye’s syndrome b. Gastritis (less) i. Except INDOMETHACIN c. Hyperuriceamia 2. Fewer DDI 3. Nephrotoxic if use in long time 4. No anti-platelete effects ...
... a. Reye’s syndrome b. Gastritis (less) i. Except INDOMETHACIN c. Hyperuriceamia 2. Fewer DDI 3. Nephrotoxic if use in long time 4. No anti-platelete effects ...
Amino Acids and Proteins - Gadarif University Repository
... electric field. Isoelectric points are different from one amino acid to an other. ...
... electric field. Isoelectric points are different from one amino acid to an other. ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... Each amino acid has the same structure except for a section called the R group. R stands for radical which mean that the structure varies. There are 20 different variations so there are 20 amino acids. Each amino acid has different properties that interact with each other when they are joined togeth ...
... Each amino acid has the same structure except for a section called the R group. R stands for radical which mean that the structure varies. There are 20 different variations so there are 20 amino acids. Each amino acid has different properties that interact with each other when they are joined togeth ...
Organic Compounds
... complicated carbon compounds found in cells • German chemists in the 1800’s learned how to do this in the lab, showing that “organic” compounds can be created by non-organic means. • Today, organic compounds are those that contain carbon. (with a few exceptions such as carbon dioxide and diamonds) ...
... complicated carbon compounds found in cells • German chemists in the 1800’s learned how to do this in the lab, showing that “organic” compounds can be created by non-organic means. • Today, organic compounds are those that contain carbon. (with a few exceptions such as carbon dioxide and diamonds) ...
What is your DNA Alias - mychandlerschools.org
... Cytosine, and Guanine, respectively. The letters are read in groups of three by various enzymes and organelles in your cells. A group of three is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making ...
... Cytosine, and Guanine, respectively. The letters are read in groups of three by various enzymes and organelles in your cells. A group of three is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making ...
Proteins - Cathkin High School
... acids known as essential amino acids. Only eight amino acids are regarded as being essential for humans although a further two are required in childhood. Some amino acids have more than one amino group or more than one carboxyl group and these allow chains to form branches. With twenty different ami ...
... acids known as essential amino acids. Only eight amino acids are regarded as being essential for humans although a further two are required in childhood. Some amino acids have more than one amino group or more than one carboxyl group and these allow chains to form branches. With twenty different ami ...
Topic 2
... Alanine Arginine Asparagine Aspartic acid Cysteine Glutamic acid Glutamine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Proline Serine Threonine Tryptophan Tyrosine Valine ...
... Alanine Arginine Asparagine Aspartic acid Cysteine Glutamic acid Glutamine Glycine Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Proline Serine Threonine Tryptophan Tyrosine Valine ...
Protein Synthesis
... Amino acids floating freely in the cytoplasm are transported to the ribosome's by the tRNA ...
... Amino acids floating freely in the cytoplasm are transported to the ribosome's by the tRNA ...
In organic chemistry, we studied a lot about the essential elements
... very important in our circulation system. For instance, the cell Hemoglobin could not perform its crucial function without Oxygen. And our body needs Oxygen to generate energy (ATP) in our activities. For instant, breaking down the carbohydrate, called glycolysis, needs oxygen in the stage of “Elect ...
... very important in our circulation system. For instance, the cell Hemoglobin could not perform its crucial function without Oxygen. And our body needs Oxygen to generate energy (ATP) in our activities. For instant, breaking down the carbohydrate, called glycolysis, needs oxygen in the stage of “Elect ...
Finals Practice Exam
... Spring 2004 BCHS 3304 Final Exam Review Student Copy1). The TR transition of hemoglobin upon binding of oxygen to the heme has been thoroughly investigated. On a thermodynamic level, this TR transition can be described as (primarily) an enthalpically driven process. Which of the following phenomen ...
... Spring 2004 BCHS 3304 Final Exam Review Student Copy1). The TR transition of hemoglobin upon binding of oxygen to the heme has been thoroughly investigated. On a thermodynamic level, this TR transition can be described as (primarily) an enthalpically driven process. Which of the following phenomen ...
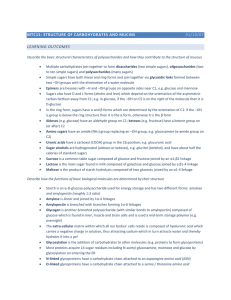
MTC15 - toddgreen
... Describe the basic structural characteristics of polysaccharides and how they contribute to the structure of mucous ...
... Describe the basic structural characteristics of polysaccharides and how they contribute to the structure of mucous ...