Solutions to 7.014 Quiz I
... cellular functions as culture B that derives 36 molecules of ATP/molecule of glucose through respiration. iii) At the time when both cultures run out of food, will there be approximately the same number of cells in each? Why or why not? No. Because culture B utilizes its food stores more efficiently ...
... cellular functions as culture B that derives 36 molecules of ATP/molecule of glucose through respiration. iii) At the time when both cultures run out of food, will there be approximately the same number of cells in each? Why or why not? No. Because culture B utilizes its food stores more efficiently ...
Defining the role of Histidyl tRNA Synthetase in the Zebrafish... Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases are critical enzymes responsible for attaching specific
... Defining the role of Histidyl tRNA Synthetase in the Zebrafish Eye and Ear ...
... Defining the role of Histidyl tRNA Synthetase in the Zebrafish Eye and Ear ...
Powerpoint
... Some R groups are reactive and will interact with other reactive R groups in the chain. These are the amino acids that are either charged or that have a sulphur atom. The interactions ( + and – attractions and S-S bridges) will fold the molecule over into a highly specific 3-dimensional shape. It is ...
... Some R groups are reactive and will interact with other reactive R groups in the chain. These are the amino acids that are either charged or that have a sulphur atom. The interactions ( + and – attractions and S-S bridges) will fold the molecule over into a highly specific 3-dimensional shape. It is ...
Carlson, Scott M.: Sequence Motifs are Necessary but not Sufficient for Predicting Post-translational Modifications
... nodes (sparse coding of 16 positions with 20 inputs each), 320 2nd layer neurons, 3 3rd layer neurons, and a single output neuron. Specificity of 95.4% is very high, but it was only achieved using a somewhat over-trained classifier with 1,611 degrees of freedom. Low selectivity and high specificity ...
... nodes (sparse coding of 16 positions with 20 inputs each), 320 2nd layer neurons, 3 3rd layer neurons, and a single output neuron. Specificity of 95.4% is very high, but it was only achieved using a somewhat over-trained classifier with 1,611 degrees of freedom. Low selectivity and high specificity ...
Amino Acids Proteins, and Enzymes
... Catalysis: Almost all chemical reactions in a living cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. ...
... Catalysis: Almost all chemical reactions in a living cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. ...
Unit 1 PPT 3 (2biii-iv Binding and conformation)
... Negative modulators • End product inhibition occurs when the final product of a cascade of enzyme reactions interacts with an allosteric site of the first enzyme in the cascade to inhibit it and thus the production of the end product. • This is an example of negative feedback. • End product inhibit ...
... Negative modulators • End product inhibition occurs when the final product of a cascade of enzyme reactions interacts with an allosteric site of the first enzyme in the cascade to inhibit it and thus the production of the end product. • This is an example of negative feedback. • End product inhibit ...
Chapter 2b Packet
... 13. Lipids that are solid at room temperature are __________________ fats. 14. DNA and RNA are made up of ______________, which contain a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group. 15. Protein folding is determined by the sequence of the __________ _________. 16. Examples of _____________ in your body in ...
... 13. Lipids that are solid at room temperature are __________________ fats. 14. DNA and RNA are made up of ______________, which contain a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group. 15. Protein folding is determined by the sequence of the __________ _________. 16. Examples of _____________ in your body in ...
Proteins are made of chains of amino acids
... ability of an enzyme to perform its function? – Heating/boiling denatures enzymes (unfolds them) and makes them lose their function ...
... ability of an enzyme to perform its function? – Heating/boiling denatures enzymes (unfolds them) and makes them lose their function ...
Slide 1
... • Essential and non-essential amino acids. • “non-essential” just means that the body produce them endogenously… but body has to “work” to generate these. ...
... • Essential and non-essential amino acids. • “non-essential” just means that the body produce them endogenously… but body has to “work” to generate these. ...
Amino acids
... Myoglobin consists of single polypeptide chain, while functional hemoglobin molecule contains four polypeptide chains (which are very similar to myoglobin ones) Myoglobin (single chain) ...
... Myoglobin consists of single polypeptide chain, while functional hemoglobin molecule contains four polypeptide chains (which are very similar to myoglobin ones) Myoglobin (single chain) ...
Document
... is also regulated • Sucrose 6phosphate synthase is regulate by phosphorylation/de phosphorylation. ...
... is also regulated • Sucrose 6phosphate synthase is regulate by phosphorylation/de phosphorylation. ...
Workshop VII Secondary metabolism Chair: Christian Hertweck 161
... Institut für Botanik, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Schlossgarten 3, 251 8324801; Fax: (0049) 251 8323823; E-mail: [email protected] ...
... Institut für Botanik, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Schlossgarten 3, 251 8324801; Fax: (0049) 251 8323823; E-mail: [email protected] ...
Digestion of Proteins
... carbohydrate calories consumed. These starches are polysaccharides, containing 10,000 to 1 million glucosyl units. ...
... carbohydrate calories consumed. These starches are polysaccharides, containing 10,000 to 1 million glucosyl units. ...
Chem 465 Biochemistry II
... complex. It uses TPP to cleave the terminal CO2 from pyruvate and transfers the remaining part of the pyruvate to E2 (Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase) where this acetate group is temporarily attached to lippoate. The acetate is then transferred to free CoASH to make acetyl CoA which diffuses away from ...
... complex. It uses TPP to cleave the terminal CO2 from pyruvate and transfers the remaining part of the pyruvate to E2 (Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase) where this acetate group is temporarily attached to lippoate. The acetate is then transferred to free CoASH to make acetyl CoA which diffuses away from ...
2013 ProSyn PREAP
... Plant and animal breeders often take advantage of such beneficial mutations. ...
... Plant and animal breeders often take advantage of such beneficial mutations. ...
Protein Synthesis - Katy Independent School District
... Plant and animal breeders often take advantage of such beneficial mutations. ...
... Plant and animal breeders often take advantage of such beneficial mutations. ...
PATTERNS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE
... *R represents a carbon side chain which may contain even the elements nitrogen and sulphur. ...
... *R represents a carbon side chain which may contain even the elements nitrogen and sulphur. ...
Latinos take on bigger role in Obama inauguration
... lowest-energy shape. Any other shape would be unstable. Because a protein’s lowest20 energy shape is determined by its primary structure, its active shape is determined by its primary structure. Scientist 2 The active shape of a protein is dependent upon its primary structure. However, a protein’s a ...
... lowest-energy shape. Any other shape would be unstable. Because a protein’s lowest20 energy shape is determined by its primary structure, its active shape is determined by its primary structure. Scientist 2 The active shape of a protein is dependent upon its primary structure. However, a protein’s a ...
(1) Identify the secondary structure described in each of the
... (7) Enzymes are potent catalysts because they: a. are consumed in the reactions they catalyze. b. are very specific and can prevent the conversion of products back to substrates. c. drive reactions to completion while other catalysts drive reactions to equilibrium. d. increase the equilibrium consta ...
... (7) Enzymes are potent catalysts because they: a. are consumed in the reactions they catalyze. b. are very specific and can prevent the conversion of products back to substrates. c. drive reactions to completion while other catalysts drive reactions to equilibrium. d. increase the equilibrium consta ...
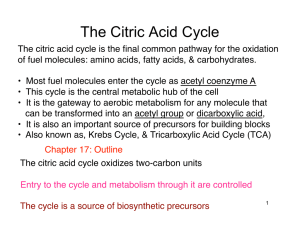
The Citric Acid Cycle
... The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic metabolism for any mol ...
... The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules: amino acids, fatty acids, & carbohydrates. • Most fuel molecules enter the cycle as acetyl coenzyme A • This cycle is the central metabolic hub of the cell • It is the gateway to aerobic metabolism for any mol ...
chapt06b_lecture
... glucose. The enzyme for lactose use is turned on by genetic control. In enzyme repression, the product of a biochemical pathway inhibits the functioning of a key enzyme of a previous step in the pathway. 6P2-23 ...
... glucose. The enzyme for lactose use is turned on by genetic control. In enzyme repression, the product of a biochemical pathway inhibits the functioning of a key enzyme of a previous step in the pathway. 6P2-23 ...
Isoleucine Synthesis by Clostridium sporogenes from
... donors and acceptors (the Stickland reaction) have been studied extensively (Barker, 1981). Less consideration has been given to the synthesis of amino acids by strictly anaerobic bacteria. The development in our laboratory of a simple defined medium for C . sporogenes (Hadioetomo, 1980) has allowed ...
... donors and acceptors (the Stickland reaction) have been studied extensively (Barker, 1981). Less consideration has been given to the synthesis of amino acids by strictly anaerobic bacteria. The development in our laboratory of a simple defined medium for C . sporogenes (Hadioetomo, 1980) has allowed ...
22. Analysis of Haloarchaeal Genomes
... ● produces pentoses for RNA, DNA synthesis ● produces NADPH for biosynthesis of amino acids, etc. ...
... ● produces pentoses for RNA, DNA synthesis ● produces NADPH for biosynthesis of amino acids, etc. ...
Biological Molecules continued
... Two amino acids can bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. These amino acids can bond to each other in a long chain to form what is commonly called a polypeptide. These long chains can have hundreds of amino acids and their shape is influenced by several factors such as hydrogen bondin ...
... Two amino acids can bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. These amino acids can bond to each other in a long chain to form what is commonly called a polypeptide. These long chains can have hundreds of amino acids and their shape is influenced by several factors such as hydrogen bondin ...