BIO-5002A - BIOCHEMISTRY
... achieved through the use of membrane proteins by either facilitated diffusion or active transport. Describe, using one appropriate example of each mechanism, how the selective membrane transport of sodium and potassium is achieved. ...
... achieved through the use of membrane proteins by either facilitated diffusion or active transport. Describe, using one appropriate example of each mechanism, how the selective membrane transport of sodium and potassium is achieved. ...
Document
... 0.50__A___ 7. The hyperbolic relationship between initial velocity and [S] concentration is described by the equation: A. v=Vmax [S]/ Km + [S] B. v=Km + [S]/Vmax [S] C. v=Km [S]/Vmax + [S] D. v=Vmax [S]/Km [S] 1.0__B___ 8. Plotting initial velocity against various pH values in an enzyme-catalyzed re ...
... 0.50__A___ 7. The hyperbolic relationship between initial velocity and [S] concentration is described by the equation: A. v=Vmax [S]/ Km + [S] B. v=Km + [S]/Vmax [S] C. v=Km [S]/Vmax + [S] D. v=Vmax [S]/Km [S] 1.0__B___ 8. Plotting initial velocity against various pH values in an enzyme-catalyzed re ...
The Play is the thing… - Biology Learning Center
... Blinding you with Science (jargon) RNA Polymerase: joins RNA links into a chain mRNA: messenger RNA; RNA string copied (‘transcribed’) from DNA tRNA: transfer RNA; one of many RNA molecules that carry specific amino acids ribosome: giant machine (>200 proteins, 4 RNAs (2 > 1000 nucleotides) that ov ...
... Blinding you with Science (jargon) RNA Polymerase: joins RNA links into a chain mRNA: messenger RNA; RNA string copied (‘transcribed’) from DNA tRNA: transfer RNA; one of many RNA molecules that carry specific amino acids ribosome: giant machine (>200 proteins, 4 RNAs (2 > 1000 nucleotides) that ov ...
Presentazione standard di PowerPoint
... Carbohydrates, for example, contain sugar and polysaccharides. Sugars are compounds that can be found in fruit, but also in milk and many other kinds of food. Generally they are easily recognized by their sweet taste. Polysaccharides are not sweet, though they are made of sugars. However, they are t ...
... Carbohydrates, for example, contain sugar and polysaccharides. Sugars are compounds that can be found in fruit, but also in milk and many other kinds of food. Generally they are easily recognized by their sweet taste. Polysaccharides are not sweet, though they are made of sugars. However, they are t ...
Acids and Bases - Personal.kent.edu
... Buffers A buffer solution is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate weak base. Buffers are important because they prevent drastic pH changes from occurring. The pH of a buffer solution can be calculated using the HendersonHasselbalch equation: ...
... Buffers A buffer solution is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate weak base. Buffers are important because they prevent drastic pH changes from occurring. The pH of a buffer solution can be calculated using the HendersonHasselbalch equation: ...
Regulation of metabolic pathways at the cellular level
... synthesis of FA takes place in the cytoplasm and their degradation in the mitochondria • Subsequent processes are close to each other (KC and RC) - the local accumulation of substrate • Transport of excess citrate from MIT to the cytoplasm - AcCoA transfer and regulation of glycolysis and FA synthes ...
... synthesis of FA takes place in the cytoplasm and their degradation in the mitochondria • Subsequent processes are close to each other (KC and RC) - the local accumulation of substrate • Transport of excess citrate from MIT to the cytoplasm - AcCoA transfer and regulation of glycolysis and FA synthes ...
Slide 1
... Ionic liquid [bmim]PF6 Mediated Synthesis of 1,2-Orthoesters of Carbohydrates 1,2-Orthoesters- Important Intermediates in Synthetic Carbohydrate Chemistry For eg: n-Pentenyl Orthoesters as Glycoside Donors ...
... Ionic liquid [bmim]PF6 Mediated Synthesis of 1,2-Orthoesters of Carbohydrates 1,2-Orthoesters- Important Intermediates in Synthetic Carbohydrate Chemistry For eg: n-Pentenyl Orthoesters as Glycoside Donors ...
05. Clinical enzymology (1)
... tissue damage is their lack of specificity to a particular tissue or cell type. Many enzymes are common to more than one tissue. ...
... tissue damage is their lack of specificity to a particular tissue or cell type. Many enzymes are common to more than one tissue. ...
5. CH 5 PPT The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... • When phospholipids are added to water, they selfassemble into a bilayer, with the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the interior • The structure of phospholipids results in a bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes • Phospholipids are the major component of all cell ...
... • When phospholipids are added to water, they selfassemble into a bilayer, with the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the interior • The structure of phospholipids results in a bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes • Phospholipids are the major component of all cell ...
jcby1101-tutorial2
... What are the two types of nucleic acids? •Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) •Ribonucleic acid (RNA) What are the roles of nucleic acids? • Storage of genetic information • Transmission of genetic information •DNA -> RNA -> Protein ...
... What are the two types of nucleic acids? •Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) •Ribonucleic acid (RNA) What are the roles of nucleic acids? • Storage of genetic information • Transmission of genetic information •DNA -> RNA -> Protein ...
9. Unit 2 Study Guide_Honors
... Low-density of C-H bonds… not much energy! What is a pigment? What is an enzyme? Structure of amino acids: amino group, carboxyl, central carbon, R group 20 different amino acids…. Different R groups! Formed through dehydration synthesis…… connected by peptide bonds! 4 levels of protein structure… 1 ...
... Low-density of C-H bonds… not much energy! What is a pigment? What is an enzyme? Structure of amino acids: amino group, carboxyl, central carbon, R group 20 different amino acids…. Different R groups! Formed through dehydration synthesis…… connected by peptide bonds! 4 levels of protein structure… 1 ...
Name 1 BIO 451 14 December, 1998 FINAL EXAM
... (5) Utilizes " -keto acids from amino acid degradation as an important fuel (6) Can store glycogen but cannot release glucose into the blood (7) Can synthesize fatty acids, triacylglycerols and VLDL when fuels are abundant ...
... (5) Utilizes " -keto acids from amino acid degradation as an important fuel (6) Can store glycogen but cannot release glucose into the blood (7) Can synthesize fatty acids, triacylglycerols and VLDL when fuels are abundant ...
inhibition of very long chain fatty acid synthesis in barley and wild
... interfere with surface wax formation. We have shown that they have a major effect on the synthesis of very long chain fatty acidswhich are precursors for surface waxes. However, the inhibitory characteristics are such that a metabolite, probably the sulphoxide, rather than the parent compound is the ...
... interfere with surface wax formation. We have shown that they have a major effect on the synthesis of very long chain fatty acidswhich are precursors for surface waxes. However, the inhibitory characteristics are such that a metabolite, probably the sulphoxide, rather than the parent compound is the ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Amino acids are monomers of proteins. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids have an amine group (NH2) and a carboxyl group (COOH) ...
... • Amino acids are monomers of proteins. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids have an amine group (NH2) and a carboxyl group (COOH) ...
Requirements - Department of Medical Biochemistry, Semmelweis
... the lectures and the seminars. The theoretical written test is divided in three blocks (i) block#A set of biochemistry problems (containing questions for 30 points) (ii) block#B 30 multiple choice type test questions (carbohydrates, metabolic integration) (iii) block#C 30 multiple choice type test q ...
... the lectures and the seminars. The theoretical written test is divided in three blocks (i) block#A set of biochemistry problems (containing questions for 30 points) (ii) block#B 30 multiple choice type test questions (carbohydrates, metabolic integration) (iii) block#C 30 multiple choice type test q ...
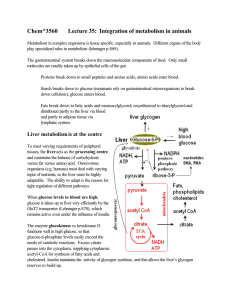
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... organisms (e.g. humans) must deal with varying input of nutrients, so the liver must be highly adaptable. The ability to adapt is the reason for tight regulation of different pathways. When glucose levels in blood are high, glucose is taken up in liver very efficiently by the GluT2 transporter (Lehn ...
... organisms (e.g. humans) must deal with varying input of nutrients, so the liver must be highly adaptable. The ability to adapt is the reason for tight regulation of different pathways. When glucose levels in blood are high, glucose is taken up in liver very efficiently by the GluT2 transporter (Lehn ...
Unit 3 Exam Enzymes REVIEW
... (choose one) spontaneous? Explain why. Given a delta G less than 0, will the reaction release or absorb energy? Explain why. Metabolism: Compare anabolism and catabolism. Give an example of each. Explain how anabolic and catabolic reactions differ in their transfer of energy. What is a metabolic pat ...
... (choose one) spontaneous? Explain why. Given a delta G less than 0, will the reaction release or absorb energy? Explain why. Metabolism: Compare anabolism and catabolism. Give an example of each. Explain how anabolic and catabolic reactions differ in their transfer of energy. What is a metabolic pat ...
doc - University of California, Santa Cruz
... about the biological and evolutionary significance of introns. We therefore need a simple way of investigating those, and the enzymes involved in the intron turnover pathway. The target enzyme of the study, the RNA lariat debranching enzyme (DBR) from mosquito-borne parasitic protozoan Plasmodium fa ...
... about the biological and evolutionary significance of introns. We therefore need a simple way of investigating those, and the enzymes involved in the intron turnover pathway. The target enzyme of the study, the RNA lariat debranching enzyme (DBR) from mosquito-borne parasitic protozoan Plasmodium fa ...
practice mid-term 1
... 15. Consider the uncatalyzed reaction A B. If I start with 1 mole of A, at equilibrium, I am left with 0.8 moles of A. It takes 30 minutes for this reaction to reach equilibrium. For the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme: A) ...
... 15. Consider the uncatalyzed reaction A B. If I start with 1 mole of A, at equilibrium, I am left with 0.8 moles of A. It takes 30 minutes for this reaction to reach equilibrium. For the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme: A) ...
Lecture 2 - Websupport1
... • Activation energy is the amount of energy needed to begin a reaction • Enzymes are catalysts • Reduce energy of activation without being permanently changed or used up • Promote chemical reactions ...
... • Activation energy is the amount of energy needed to begin a reaction • Enzymes are catalysts • Reduce energy of activation without being permanently changed or used up • Promote chemical reactions ...
lec-04-transcript
... polymers built of monomers (amino acids). These are most versatile macromolecules in living systems. They are crucial for various essential functions for all the biological processes and they play very critical role both from structural and functional point of view. Therefore studying about proteins ...
... polymers built of monomers (amino acids). These are most versatile macromolecules in living systems. They are crucial for various essential functions for all the biological processes and they play very critical role both from structural and functional point of view. Therefore studying about proteins ...
The Chemistry of Biology
... C. Amino-proteins D. Hydroxyl-alcohols E. Carboxyl-fatty acids 32. Organic chemicals always have a basic framework of the element _____ bonded to other atoms. A. Carbon B. Nitrogen C. Oxygen D. Hydrogen E. Phosphorous 33. Most biochemical macromolecules are polymers, which are A. Chains of hydrophob ...
... C. Amino-proteins D. Hydroxyl-alcohols E. Carboxyl-fatty acids 32. Organic chemicals always have a basic framework of the element _____ bonded to other atoms. A. Carbon B. Nitrogen C. Oxygen D. Hydrogen E. Phosphorous 33. Most biochemical macromolecules are polymers, which are A. Chains of hydrophob ...
107105_pku
... ~125,000 base pairs codes for a protein of 454 amino acids only 1362 base pairs code for amino ac ids 13 exons containing 41-184 base pairs coding for protein 12 introns from 1, 200 to 23,500 base pairs in length ...
... ~125,000 base pairs codes for a protein of 454 amino acids only 1362 base pairs code for amino ac ids 13 exons containing 41-184 base pairs coding for protein 12 introns from 1, 200 to 23,500 base pairs in length ...