CHAPTER 4 DISTRIBUTION OF CARBON, SULPHUR, NITROGEN
... 4.2.1 Explanation and analysis The protein sequences were taken from the public NCBI database [cited 2008 Feb 17] as given in the table 4.1. The probability analyses were carried out. The idea behind this task is very simple. That is visualize the molecule on actual basis i.e. atom level. The basic ...
... 4.2.1 Explanation and analysis The protein sequences were taken from the public NCBI database [cited 2008 Feb 17] as given in the table 4.1. The probability analyses were carried out. The idea behind this task is very simple. That is visualize the molecule on actual basis i.e. atom level. The basic ...
Section 2.3 Carbon
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules (proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids) are found in all organisms. These molecules form the structures and carry out the functions in all living organisms. ...
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules (proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids) are found in all organisms. These molecules form the structures and carry out the functions in all living organisms. ...
Document
... Peptide bond between the adjacent AA’s. - Uncharged t-RNA shifts to e-site And is released from ribosome, while the mRNA, t-RNA complex shifts to the p-site… - the A-site is now open and across From the next m-RNA codon; ready to accept The next charged t-RNA ...
... Peptide bond between the adjacent AA’s. - Uncharged t-RNA shifts to e-site And is released from ribosome, while the mRNA, t-RNA complex shifts to the p-site… - the A-site is now open and across From the next m-RNA codon; ready to accept The next charged t-RNA ...
effect of short time exposure of rats to extreme low temperature on
... chamber in wooden cages. Body weight of the animals was controlled before and after 5 and 10 d of the experiment. During ether anaesthesia of the animals blood was taken from the right ventricle of the heart and collected into EDTA-containing tubes. Then the animals were killed by the by spinal cord ...
... chamber in wooden cages. Body weight of the animals was controlled before and after 5 and 10 d of the experiment. During ether anaesthesia of the animals blood was taken from the right ventricle of the heart and collected into EDTA-containing tubes. Then the animals were killed by the by spinal cord ...
Nutrisi & Pertumbuhan Mikrobia
... Passive diffusion is the process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration as a result of random thermal agitation. A few substances, such as glycerol, can cross the plasma membrane by passive diffusion. ...
... Passive diffusion is the process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration as a result of random thermal agitation. A few substances, such as glycerol, can cross the plasma membrane by passive diffusion. ...
The Structural Basis of Molecular Adaptation
... anatomy. Not only are the techniques available to dissect the very nature of selective changes, but their history can be explored as well. As these examples illustrate, different molecules respond in different ways to selective pressures—a wealth of evolutionary pathways that is only beginning to be ...
... anatomy. Not only are the techniques available to dissect the very nature of selective changes, but their history can be explored as well. As these examples illustrate, different molecules respond in different ways to selective pressures—a wealth of evolutionary pathways that is only beginning to be ...
A Comparative Genomic Method for Computational
... Sets of 3+ DnaA-regulated, orthologous transcription units containing at least 1 cross-species pair of binding sites displaying conservation of sequence (2+ identical DnaA boxes) or location (within 20 base pairs) (127/88) ...
... Sets of 3+ DnaA-regulated, orthologous transcription units containing at least 1 cross-species pair of binding sites displaying conservation of sequence (2+ identical DnaA boxes) or location (within 20 base pairs) (127/88) ...
Biochemical and genetic analysis of leucine-, isoleucine
... Another early example of the effect of gene mutation on discrete chemical activities of the cell resulted from the studies of Beadle and Taturn (1941). In their studies with Drosophila, they succeeded in relating eye-color changes to mutationally produced blocks in the biosynthesis of eye pig ments ...
... Another early example of the effect of gene mutation on discrete chemical activities of the cell resulted from the studies of Beadle and Taturn (1941). In their studies with Drosophila, they succeeded in relating eye-color changes to mutationally produced blocks in the biosynthesis of eye pig ments ...
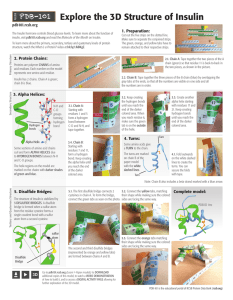
Explore the 3D Structure of Insulin
... To learn more about the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure, watch the What is a Protein? video at bit.ly/1JkBKgZ. ...
... To learn more about the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure, watch the What is a Protein? video at bit.ly/1JkBKgZ. ...
TCA
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
A Support Vector Machine Approach for LTP Using Amino Acid
... (Zea mays), barley (Hordeum vulgare), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and soybean (Glycine max), including a total of 174 data in the training set. In the case of newly developed All-plant model, we have used the simple amino acid approach, which was having an accuracy of 100 % for rice-specific classi ...
... (Zea mays), barley (Hordeum vulgare), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and soybean (Glycine max), including a total of 174 data in the training set. In the case of newly developed All-plant model, we have used the simple amino acid approach, which was having an accuracy of 100 % for rice-specific classi ...
Vitamins and Coenzymes - Rose
... months before symptoms of scurvy begin to appear. Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) Vitamin B12 is a complex compound that is converted into several coenzymes.4 It is used for shifting of hydrogen between carbon atoms, usually in conjunction with a shift of some other group (e.g., NH2, or CH3); Vitamin B12 ca ...
... months before symptoms of scurvy begin to appear. Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) Vitamin B12 is a complex compound that is converted into several coenzymes.4 It is used for shifting of hydrogen between carbon atoms, usually in conjunction with a shift of some other group (e.g., NH2, or CH3); Vitamin B12 ca ...
Regulation of Metabolism
... • Average daily turnover for protein is 150 g/day. • Some protein may be reused for protein synthesis. • Only need 35 g/day. • 9 essential amino acids. • Average daily turnover for fats is 100 g/day. • Little is actually required in the diet. • Fat can be produced from excess carbohydrates. • Essent ...
... • Average daily turnover for protein is 150 g/day. • Some protein may be reused for protein synthesis. • Only need 35 g/day. • 9 essential amino acids. • Average daily turnover for fats is 100 g/day. • Little is actually required in the diet. • Fat can be produced from excess carbohydrates. • Essent ...
ap® biology 2008 scoring guidelines - AP Central
... Overview This question tested knowledge of protein form and function from the basic to the applied level. Students were asked to describe the bonds involved with protein structure and apply their knowledge of protein structure to specific functions, such as muscle contraction, cell signaling, and en ...
... Overview This question tested knowledge of protein form and function from the basic to the applied level. Students were asked to describe the bonds involved with protein structure and apply their knowledge of protein structure to specific functions, such as muscle contraction, cell signaling, and en ...
Extreme variations in the ratios of non
... stability index defined as the mean chemieal distance between the amino acid and its mutational derivatives produced by a single nucleotide substitution. Reliable predictions of mutability could be obtained with an empirical index /,„, based on múltiple linear regression equations involving the freq ...
... stability index defined as the mean chemieal distance between the amino acid and its mutational derivatives produced by a single nucleotide substitution. Reliable predictions of mutability could be obtained with an empirical index /,„, based on múltiple linear regression equations involving the freq ...
Glycerolipids and Glycerophospholipids
... De Novo Synthesis of Phosphatidylcholine (PC) • PC is the most abundant phospholipid in eukaryotic cells • PC is also known as lecithin De Novo Synthesis • Choline is phosphorylated ...
... De Novo Synthesis of Phosphatidylcholine (PC) • PC is the most abundant phospholipid in eukaryotic cells • PC is also known as lecithin De Novo Synthesis • Choline is phosphorylated ...
Differential diagnosis of (inherited) amino acid metabolism or
... acids can be metabolized into other amino acids, hormones, neurotransmitters, pigments, etc. The excess of amino acids can be degraded, mostly into organic acids. The first degradation step is usually the removal of nitrogen by transamination or deamination. Protein and amino acid metabolism is unde ...
... acids can be metabolized into other amino acids, hormones, neurotransmitters, pigments, etc. The excess of amino acids can be degraded, mostly into organic acids. The first degradation step is usually the removal of nitrogen by transamination or deamination. Protein and amino acid metabolism is unde ...
Section 2.5
... 1. Both contain carbonyl and hydroxyl groups. In glucose, the carbonyl group forms an aldehyde and in fructose, the carbonyl group forms a ketone. 2. (a) In animals, starch is used for energy and glycogen is used for energy storage. The orientation of the glucose–glucose linkages favours intrachain ...
... 1. Both contain carbonyl and hydroxyl groups. In glucose, the carbonyl group forms an aldehyde and in fructose, the carbonyl group forms a ketone. 2. (a) In animals, starch is used for energy and glycogen is used for energy storage. The orientation of the glucose–glucose linkages favours intrachain ...
structure and function of bio- molecules - Aditya K Panda, PhD
... Alanine Asparagine Isoleucine Leucine Methionine Phenylalanine Proline Serine Threonine Tryptophane Valine Glutamine Aspartate Glutamate Histidine Cysteine Tyrosine Lysine Arginine ...
... Alanine Asparagine Isoleucine Leucine Methionine Phenylalanine Proline Serine Threonine Tryptophane Valine Glutamine Aspartate Glutamate Histidine Cysteine Tyrosine Lysine Arginine ...
Engineering of factors determining alpha-amylase and
... compared to the three domains of A-amylases (A, B and C). Amino acid residue 196 (Thermoanaerobacterium thermosulfurigenes EM1 CGTase numbering) occupies a dominant position in the active-site cleft. All A-amylases studied have a small residue at this position (Gly, Leu, Ser, Thr or Val), in contras ...
... compared to the three domains of A-amylases (A, B and C). Amino acid residue 196 (Thermoanaerobacterium thermosulfurigenes EM1 CGTase numbering) occupies a dominant position in the active-site cleft. All A-amylases studied have a small residue at this position (Gly, Leu, Ser, Thr or Val), in contras ...