New insight into pathogenesis of medical diseases
... and so on. In order for this energy to be used in basal conditions, or physical activity it must undergo certain biochemical reactions. These biochemical reactions are termed Metabolism. What is metabolism ? Metabolism is life. Metabolism involves two fundamental processes, anabolism and catabolism. ...
... and so on. In order for this energy to be used in basal conditions, or physical activity it must undergo certain biochemical reactions. These biochemical reactions are termed Metabolism. What is metabolism ? Metabolism is life. Metabolism involves two fundamental processes, anabolism and catabolism. ...
ProteinPrediction
... Each amino acid has two parts, a backbone and a side chain. The side chain, R, distinguishes the different amino acids. Backbone is constant for all 20 amino acids. It consists of an amide (--NH2) group, an alpha carbon, and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. ...
... Each amino acid has two parts, a backbone and a side chain. The side chain, R, distinguishes the different amino acids. Backbone is constant for all 20 amino acids. It consists of an amide (--NH2) group, an alpha carbon, and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. ...
Predicting Secondary Structures of Proteins
... n important assumption of all protein prediction methods is that the amino acid sequence completely and uniquely determines the three-dimensional (3-D) structure of protein. Proof that protein structure is dictated by the amino acid sequence alone is based on experiments first carried out by C. Anfi ...
... n important assumption of all protein prediction methods is that the amino acid sequence completely and uniquely determines the three-dimensional (3-D) structure of protein. Proof that protein structure is dictated by the amino acid sequence alone is based on experiments first carried out by C. Anfi ...
Protein thermostability in Archaea and Eubacteria
... Higher CG content in coding sequences in thermophiles (Bao et al., 2002; Saunders et al., 2003) as compared to mesophiles (McDonald et al., 1999; Zhu et al., 1999; Kreil and Ouzounis, 2001) affects the amino acid content and hence protein stability with some exceptions (Farias and Bonato, 2003; Paz ...
... Higher CG content in coding sequences in thermophiles (Bao et al., 2002; Saunders et al., 2003) as compared to mesophiles (McDonald et al., 1999; Zhu et al., 1999; Kreil and Ouzounis, 2001) affects the amino acid content and hence protein stability with some exceptions (Farias and Bonato, 2003; Paz ...
Chapter 26
... • Net protein utilization—the percentage of amino acids in a protein that the human body uses – 70% to 90% of animal proteins – 40% to 70% of plant proteins • 14 oz of rice and beans provides same amount of usable protein as 4 oz hamburger ...
... • Net protein utilization—the percentage of amino acids in a protein that the human body uses – 70% to 90% of animal proteins – 40% to 70% of plant proteins • 14 oz of rice and beans provides same amount of usable protein as 4 oz hamburger ...
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of the chemol
... The pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex catalyses the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate generating acetyl-CoA and NADH, and releasing CO,, thereby providing a link between glycolysis and the Kreb's cycle. The reaction takes place in several steps. In the first, pyruvate decarboxylase converts p ...
... The pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex catalyses the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate generating acetyl-CoA and NADH, and releasing CO,, thereby providing a link between glycolysis and the Kreb's cycle. The reaction takes place in several steps. In the first, pyruvate decarboxylase converts p ...
2-7 Active-Site Geometry
... molecule may rearrange during the reaction), then in a simple reaction in which two molecules combine, both of them must collide reactive side-to-reactive side. Any other orientation and the collision will be non-productive. Thus, if both molecules first bind to an enzyme active site, and do so in s ...
... molecule may rearrange during the reaction), then in a simple reaction in which two molecules combine, both of them must collide reactive side-to-reactive side. Any other orientation and the collision will be non-productive. Thus, if both molecules first bind to an enzyme active site, and do so in s ...
Definitions of Acids and Bases Electrolytes
... a solution of a strong electrolyte conducts a strong electrical current high concentration of mobile ions present in solution substance dissolves and dissociates 100% into ions strong electrolytes: strong acids, strong bases and soluble ionic compounds ...
... a solution of a strong electrolyte conducts a strong electrical current high concentration of mobile ions present in solution substance dissolves and dissociates 100% into ions strong electrolytes: strong acids, strong bases and soluble ionic compounds ...
LIPID METABOLISM
... In each cycle FADH2 and NADH+H+ is produced & transported to respiratory chain FADH2 ------------------ 2 ATP NADH+H+ ------------- 3 ATP So 7 cycles 5X7=35 ATP ...
... In each cycle FADH2 and NADH+H+ is produced & transported to respiratory chain FADH2 ------------------ 2 ATP NADH+H+ ------------- 3 ATP So 7 cycles 5X7=35 ATP ...
- Pacific Biomarkers
... including neuropeptide Y and pancreatic polypeptide (PP). The peptides of this family mediate their effects through several G protein-coupled receptors. PYY is primarily released from endocrine cells of the distal digestive tract and plays an important role in regulating food intake and energy balan ...
... including neuropeptide Y and pancreatic polypeptide (PP). The peptides of this family mediate their effects through several G protein-coupled receptors. PYY is primarily released from endocrine cells of the distal digestive tract and plays an important role in regulating food intake and energy balan ...
Genetic and biochemical identification of the
... State Key Laboratory of Microbial Resources, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, PR China Environmental Microbiology and Biotechnology Research Center, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, PR China ...
... State Key Laboratory of Microbial Resources, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, PR China Environmental Microbiology and Biotechnology Research Center, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, PR China ...
Biochemistry - Bonham Chemistry
... Reactions Far From Equilibrium are Common Points of Regulation ...
... Reactions Far From Equilibrium are Common Points of Regulation ...
Enzyme Specificity and Selectivity
... The specificity of trypsin, chymotrypsin and elastase arises from the three-dimensional structure of their respective active sites. Although the overall structures of these proteases are very similar, each enzyme has an active site that is sterically and electrostatically complementary to its substra ...
... The specificity of trypsin, chymotrypsin and elastase arises from the three-dimensional structure of their respective active sites. Although the overall structures of these proteases are very similar, each enzyme has an active site that is sterically and electrostatically complementary to its substra ...
Fermentation and Cellular Respiration
... As explained above, glycolysis is used to catabolize glucose into two pyruvic acid molecules, but the pathway does not stop there. Instead, the pyruvic acids serve as final electron acceptors, the two molecules of NADH+H+ are oxidized to NAD and the two pyruvic acid molecules are converted into lact ...
... As explained above, glycolysis is used to catabolize glucose into two pyruvic acid molecules, but the pathway does not stop there. Instead, the pyruvic acids serve as final electron acceptors, the two molecules of NADH+H+ are oxidized to NAD and the two pyruvic acid molecules are converted into lact ...
Bioenergetics and High Energy Compounds
... (Fe2+). This is achieved by the transfer of electrons, as the electrons picked up by CoQ from the other complexes are passed on. ...
... (Fe2+). This is achieved by the transfer of electrons, as the electrons picked up by CoQ from the other complexes are passed on. ...
PDF
... Research Centre); of 10 genotypes were by Ministry of Agriculture of Yemen; of 4 genotypes were by GAP International Agricultural Research and Education Centre; of 20 genotypes were by Aegean Agricultural Institute Management Gene Center; of 43 genotypes were by Bahri Dagdas International Agricultur ...
... Research Centre); of 10 genotypes were by Ministry of Agriculture of Yemen; of 4 genotypes were by GAP International Agricultural Research and Education Centre; of 20 genotypes were by Aegean Agricultural Institute Management Gene Center; of 43 genotypes were by Bahri Dagdas International Agricultur ...
Purine Biosynthesis. Big in Cell Division, Even
... why purine/ureides in some species and not in others and what advantages/disadvantages might accrue as a result of this trait? Despite the biochemical complexity of the pathway, the “cost” in terms of ATP and reductant expended per N assimilated is not much different from that required for Asn. Urei ...
... why purine/ureides in some species and not in others and what advantages/disadvantages might accrue as a result of this trait? Despite the biochemical complexity of the pathway, the “cost” in terms of ATP and reductant expended per N assimilated is not much different from that required for Asn. Urei ...
4.2 - Alfred State College
... • Small hydrophobic residues such as Ala and Leu are strong helix formers • Pro acts as a helix breaker because the rotation around the N-Ca bond is impossible • Gly acts as a helix breaker because the tiny Rgroup supports other conformations ...
... • Small hydrophobic residues such as Ala and Leu are strong helix formers • Pro acts as a helix breaker because the rotation around the N-Ca bond is impossible • Gly acts as a helix breaker because the tiny Rgroup supports other conformations ...
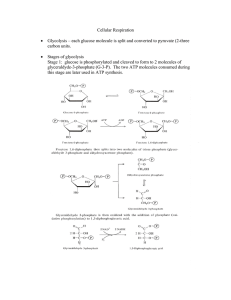
Cellular Respiration - Seattle Central College
... 2 electrons) are removed from the organic metabolite. When electrons are transferred from a metabolite by NAD+, NAD+ additionally removes two protons, hydrogen ions, H+ MH2 + NAD+ → NADH + H+ + M + energy This converts NAD+ into NADH + H+ In such reactions NAD+ serves as the electron acceptor and th ...
... 2 electrons) are removed from the organic metabolite. When electrons are transferred from a metabolite by NAD+, NAD+ additionally removes two protons, hydrogen ions, H+ MH2 + NAD+ → NADH + H+ + M + energy This converts NAD+ into NADH + H+ In such reactions NAD+ serves as the electron acceptor and th ...
CHAPTER 4 DISTRIBUTION OF CARBON, SULPHUR, NITROGEN
... 4.2.1 Explanation and analysis The protein sequences were taken from the public NCBI database [cited 2008 Feb 17] as given in the table 4.1. The probability analyses were carried out. The idea behind this task is very simple. That is visualize the molecule on actual basis i.e. atom level. The basic ...
... 4.2.1 Explanation and analysis The protein sequences were taken from the public NCBI database [cited 2008 Feb 17] as given in the table 4.1. The probability analyses were carried out. The idea behind this task is very simple. That is visualize the molecule on actual basis i.e. atom level. The basic ...