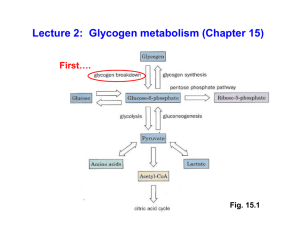
Lecture 2: Glycogen metabolism (Chapter 15)
... groups of glucose residues. Each transferred segment must come from a chain of at least 11 residues, and the attachment point must be at least 4 residues away from another branch point. Segment can be moved to the same or a different chain. ...
... groups of glucose residues. Each transferred segment must come from a chain of at least 11 residues, and the attachment point must be at least 4 residues away from another branch point. Segment can be moved to the same or a different chain. ...
CHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS : A TOOL FOR PROTEIN
... structure. In this regard, the chemical synthesis of proteins appears a key tool, as it allows the unlimited modification of a polypeptide chain with any kind and number of labels. The last decade has seen the introduction of several techniques of chemical protein synthesis that allow the manipulati ...
... structure. In this regard, the chemical synthesis of proteins appears a key tool, as it allows the unlimited modification of a polypeptide chain with any kind and number of labels. The last decade has seen the introduction of several techniques of chemical protein synthesis that allow the manipulati ...
Random Mutagenesis of Luciola mingrelica Firefly Luciferase
... color of bioluminescence. Dishes obtained during the primary screening as described above were incubated overnight at 37°C and then for 6-8 h at room temperature. In vivo luminescence of colonies was registered according to the protocol from [20]: dishes were filled with solution of 1 mM luciferin i ...
... color of bioluminescence. Dishes obtained during the primary screening as described above were incubated overnight at 37°C and then for 6-8 h at room temperature. In vivo luminescence of colonies was registered according to the protocol from [20]: dishes were filled with solution of 1 mM luciferin i ...
Read more about this
... Synthesis of urea leads to removal of ammonia. (Ammonia is very toxic and if not rapidly and efficiently removed from circulation, it will have adverse impact on the central nervous system.) ...
... Synthesis of urea leads to removal of ammonia. (Ammonia is very toxic and if not rapidly and efficiently removed from circulation, it will have adverse impact on the central nervous system.) ...
Characterization of the Plasmodium falciparum and P. berghei
... experimental evidence to support or distinguish these hypotheses. As in other organisms, malaria parasites are predicted to synthesize phospholipids and the lipid moieties of GPI anchors from a precursor known as phosphatidic acid (Déchamps et al., 2010). Phosphatidic acid is produced via a two-step ...
... experimental evidence to support or distinguish these hypotheses. As in other organisms, malaria parasites are predicted to synthesize phospholipids and the lipid moieties of GPI anchors from a precursor known as phosphatidic acid (Déchamps et al., 2010). Phosphatidic acid is produced via a two-step ...
Molecular Plant-Microbio Interactions
... Cells were grown in modified Vogel Bonner medium (MVB1) in the presence or absence of 0.05% casamino acids with various carbon sources, such that equal concentrations of carbon atoms were present. Optical density was measured at stationary phase and PCN concentrations of the supernatant fluids were ...
... Cells were grown in modified Vogel Bonner medium (MVB1) in the presence or absence of 0.05% casamino acids with various carbon sources, such that equal concentrations of carbon atoms were present. Optical density was measured at stationary phase and PCN concentrations of the supernatant fluids were ...
ARIUS MACULATUS EAST COAST OF INDIA
... Stargazers and some species of Shark, Ratfish, Catfish, Surgeonfish and Blenny are known or suspected to be venomous [1]. The production of toxins by aquatic animals is an important strategy that guarantees its survival in a highly competitive ecosystem. In this way, these animals defend themselves ...
... Stargazers and some species of Shark, Ratfish, Catfish, Surgeonfish and Blenny are known or suspected to be venomous [1]. The production of toxins by aquatic animals is an important strategy that guarantees its survival in a highly competitive ecosystem. In this way, these animals defend themselves ...
Electron transport chain…
... – resulting organic acids converted to pyruvate, acetyl-CoA, or TCA cycle intermediate • can be oxidized via TCA cycle • can be used for biosynthesis ...
... – resulting organic acids converted to pyruvate, acetyl-CoA, or TCA cycle intermediate • can be oxidized via TCA cycle • can be used for biosynthesis ...
biochemical investigation into initiation of fatty acid synthesis in the
... parasite T. brucei. In my dissertation, I addressed various aspects of the regulation of TbACC, which catalyzes the first committed step in FA synthesis. In the second chapter, I hypothesized that TbACC is regulated in response to environmental lipids. I examined changes in TbACC RNA, protein abunda ...
... parasite T. brucei. In my dissertation, I addressed various aspects of the regulation of TbACC, which catalyzes the first committed step in FA synthesis. In the second chapter, I hypothesized that TbACC is regulated in response to environmental lipids. I examined changes in TbACC RNA, protein abunda ...
Room-temperature-curable resin composition
... The vinyl polymer (B) having both of the above containing group in the compound (a-4) is about 0.5 to 20 reactive groups may be prepared by applying any known methods. Examples of simple methods include 3 equivalents per equivalent of the acid anhydride (i) the radical solution copolymerization of v ...
... The vinyl polymer (B) having both of the above containing group in the compound (a-4) is about 0.5 to 20 reactive groups may be prepared by applying any known methods. Examples of simple methods include 3 equivalents per equivalent of the acid anhydride (i) the radical solution copolymerization of v ...
Dr: Mohamed I Kotb El
... Creatinine is formed from creatine and creatine phosphate in muscle and is excreted into the plasma at a constant rate related to muscle mass. Plasma creatinine is inversely related to glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and, although an imperfect measure, it is commonly used to assess glomeular fi ...
... Creatinine is formed from creatine and creatine phosphate in muscle and is excreted into the plasma at a constant rate related to muscle mass. Plasma creatinine is inversely related to glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and, although an imperfect measure, it is commonly used to assess glomeular fi ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... into several energy-releasing steps (Figure 9.5b). An electron transport chain consists of a number of molecules, mostly proteins, built into the inner membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and the plasma membrane of aerobically respiring prokaryotes. Electrons removed from glucose are sh ...
... into several energy-releasing steps (Figure 9.5b). An electron transport chain consists of a number of molecules, mostly proteins, built into the inner membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and the plasma membrane of aerobically respiring prokaryotes. Electrons removed from glucose are sh ...
The Application of Hydrolytic Enzymes for Biotransformations of
... antioxidant activity. Other potential pharmaceutical applications of flavonoids can be related to their enzyme inhibition, anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial and anti-cancer properties. Lipases have been used effectively in the production of flavonoid ester derivatives that have shown ...
... antioxidant activity. Other potential pharmaceutical applications of flavonoids can be related to their enzyme inhibition, anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial and anti-cancer properties. Lipases have been used effectively in the production of flavonoid ester derivatives that have shown ...
video slide
... no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
O 2 - SchoolRack
... What are the products of glycolysis? Where are the products of glycolysis ...
... What are the products of glycolysis? Where are the products of glycolysis ...
Salai guggal, the oleogum resin of the Boswellia serrata has been
... the energy factories of the cell. Furthermore, sulfur participates in the vitamin B Thiamine (B1) en Biotin. These vitamins are essential for converting carbohydrates into energy, by burning glucose. Insulin is a hormone excreted by the pancreas which mainly functions to regulate the blood sugar lev ...
... the energy factories of the cell. Furthermore, sulfur participates in the vitamin B Thiamine (B1) en Biotin. These vitamins are essential for converting carbohydrates into energy, by burning glucose. Insulin is a hormone excreted by the pancreas which mainly functions to regulate the blood sugar lev ...
dbPSP: a curated database for protein phosphorylation sites in
... involved in almost all of biological processes through temporally and spatially modifying substrate proteins. Recently, phosphorylation in prokaryotes attracted much attention for its critical roles in various cellular processes such as signal transduction. Thus, an integrative data resource of the ...
... involved in almost all of biological processes through temporally and spatially modifying substrate proteins. Recently, phosphorylation in prokaryotes attracted much attention for its critical roles in various cellular processes such as signal transduction. Thus, an integrative data resource of the ...
Attachment 2 - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... via the shikimate metabolic pathway. This metabolic pathway is present in all plants, bacteria and fungi (Haslam, 1993). Plant variants of the EPSPS enzyme are inhibited by the herbicide glyphosate, however, bacterial variants of the EPSPS enzyme are, in general, not inhibited due to reduced binding ...
... via the shikimate metabolic pathway. This metabolic pathway is present in all plants, bacteria and fungi (Haslam, 1993). Plant variants of the EPSPS enzyme are inhibited by the herbicide glyphosate, however, bacterial variants of the EPSPS enzyme are, in general, not inhibited due to reduced binding ...
PORPHYRINS
... (catalase and peroxidase) Nitric Oxide Synthesis Regulation of cellular processes Effector of apoptosis ...
... (catalase and peroxidase) Nitric Oxide Synthesis Regulation of cellular processes Effector of apoptosis ...
N-terminal portion acts as an initiator of the inactivation of pepsin at
... 0.099/min (open circles in Figure 1A). At this rate, virtually all activity ceased within 1 h. At pH 7.5, pepsin was rapidly inactivated and lost activity in 5 min (open circles in Figure 2B). Lin et al. suggested that inactivation was caused by irreversible denaturation which was triggered by the d ...
... 0.099/min (open circles in Figure 1A). At this rate, virtually all activity ceased within 1 h. At pH 7.5, pepsin was rapidly inactivated and lost activity in 5 min (open circles in Figure 2B). Lin et al. suggested that inactivation was caused by irreversible denaturation which was triggered by the d ...
Hydrolysis of a Series of Synthetic Peptide Substrates by the Human
... poliovirus 2A protein which occurs while the polypeptide is still nascent on the ribosome. The peptide bond hydrolysed in this initial processing step is between a tyrosine and a glycine residue which connect the P1 and P2 regions (Nicklin et al., 1987; Toyoda et al., 1986a, b) (Fig. 1) whereas most ...
... poliovirus 2A protein which occurs while the polypeptide is still nascent on the ribosome. The peptide bond hydrolysed in this initial processing step is between a tyrosine and a glycine residue which connect the P1 and P2 regions (Nicklin et al., 1987; Toyoda et al., 1986a, b) (Fig. 1) whereas most ...