a
... Complete proteins that meet all the body’s amino acid needs are found in eggs, milk, milk products, meat, and fish Incomplete proteins are found in legumes, nuts, seeds, grains, and vegetables ...
... Complete proteins that meet all the body’s amino acid needs are found in eggs, milk, milk products, meat, and fish Incomplete proteins are found in legumes, nuts, seeds, grains, and vegetables ...
Exploring Yeast as a Cell Factory for the Production of Carboxylic
... utilization of renewable resources for the formation of products with commercial value. Among these, poly-3-D-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) is an extensively studied biopolymer naturally accumulated in some bacteria and archaea species through the formation of carbon granules. Its bio-based origin, biodegra ...
... utilization of renewable resources for the formation of products with commercial value. Among these, poly-3-D-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) is an extensively studied biopolymer naturally accumulated in some bacteria and archaea species through the formation of carbon granules. Its bio-based origin, biodegra ...
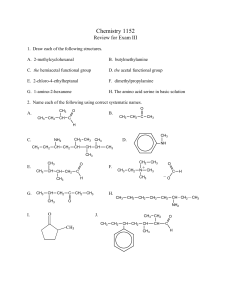
H. Draw a dipeptide from two amino acids
... 17. In general, what are the potential problems associated with a strict vegetarian diet? 18. How many ketone structures can be drawn that are isomeric with the aldehyde pentanal? 19. Aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling points than alcohols of similar mass. Why? 20. Write reactions to create a ...
... 17. In general, what are the potential problems associated with a strict vegetarian diet? 18. How many ketone structures can be drawn that are isomeric with the aldehyde pentanal? 19. Aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling points than alcohols of similar mass. Why? 20. Write reactions to create a ...
The Maillard Reaction
... browning itself is subdivided roughly (again because there is an overlap) into three types of reactions. The first, called the Maillard reaction,1 occurs between a carbonyl compound, which here is usually a reducing sugar, and an amine, which here is usually an amino acid, a peptide, or a protein. T ...
... browning itself is subdivided roughly (again because there is an overlap) into three types of reactions. The first, called the Maillard reaction,1 occurs between a carbonyl compound, which here is usually a reducing sugar, and an amine, which here is usually an amino acid, a peptide, or a protein. T ...
The N-Terminal Region of Arabidopsis
... Cystathionine ␥-synthase (CGS) is a key enzyme of Met biosynthesis in bacteria and plants. Aligning the amino acid sequences revealed that the plant enzyme has an extended N-terminal region that is not found in the bacterial enzyme. However, this region is not essential for the catalytic activity of ...
... Cystathionine ␥-synthase (CGS) is a key enzyme of Met biosynthesis in bacteria and plants. Aligning the amino acid sequences revealed that the plant enzyme has an extended N-terminal region that is not found in the bacterial enzyme. However, this region is not essential for the catalytic activity of ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
... Unless otherwise indicated herein, any third-party trademarks that may appear in this work are the property of their respective owners and any references to third-party trademarks, logos or other trade dress are for demonstrative or descriptive purposes only. Such references are not intended to impl ...
... Unless otherwise indicated herein, any third-party trademarks that may appear in this work are the property of their respective owners and any references to third-party trademarks, logos or other trade dress are for demonstrative or descriptive purposes only. Such references are not intended to impl ...
Chapter 29 The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
... Catabolic reactions "pay off" in ATP by synthesizing it Anabolic reactions "spend" ATP by transferring the ...
... Catabolic reactions "pay off" in ATP by synthesizing it Anabolic reactions "spend" ATP by transferring the ...
Chapter 29 The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
... Catabolic reactions "pay off" in ATP by synthesizing it Anabolic reactions "spend" ATP by transferring the ...
... Catabolic reactions "pay off" in ATP by synthesizing it Anabolic reactions "spend" ATP by transferring the ...
Citrate metabolism in lactic acid bacteria
... Abstract: Citrate metabolism plays an important role in many food fermentations involving lactic acid bacteria. Since citrate is a highly oxidized substrate, no reducing equivalents are produced during its degradation, resulting in the formation of metabolic end products other than lactic acid. Some ...
... Abstract: Citrate metabolism plays an important role in many food fermentations involving lactic acid bacteria. Since citrate is a highly oxidized substrate, no reducing equivalents are produced during its degradation, resulting in the formation of metabolic end products other than lactic acid. Some ...
endoglucanase in cellulose biosynthesis is not very clear
... Although the gene for cellulose synthase was first identified in A. xylinum in 1990, it was not until 1996 that the first cellulose synthase gene was identified from a higher plant (17). Unexpectedly, the plant gene was not identified by DNA-DNA hybridization experiments using the bacterial gene as ...
... Although the gene for cellulose synthase was first identified in A. xylinum in 1990, it was not until 1996 that the first cellulose synthase gene was identified from a higher plant (17). Unexpectedly, the plant gene was not identified by DNA-DNA hybridization experiments using the bacterial gene as ...
Comparative Estimation of Total Protein Content and Enzymatic
... species in all continents, causing a considerable public health problems in many regions of the world [2]. Furthermore, it is also common in Iraq [1]. E. multilocularis, causing alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is more widely distributed in the northern hemisphere, and represents a considerable public h ...
... species in all continents, causing a considerable public health problems in many regions of the world [2]. Furthermore, it is also common in Iraq [1]. E. multilocularis, causing alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is more widely distributed in the northern hemisphere, and represents a considerable public h ...
Excess amino acid supply improves methionine and leucine
... adaptation to treatment and 4 d for total fecal and urinary collections. Short adaptation periods are adequate because cattle rapidly adapt to changes in nutrients supplied postruminally (Moloney et al., 1998), and 2-d adaptations have been validated for our experimental model (Schroeder et al., 200 ...
... adaptation to treatment and 4 d for total fecal and urinary collections. Short adaptation periods are adequate because cattle rapidly adapt to changes in nutrients supplied postruminally (Moloney et al., 1998), and 2-d adaptations have been validated for our experimental model (Schroeder et al., 200 ...
Specific features of glycogen metabolism in the liver
... each lobe contains two αβγδ protomers [42]. The δ-subunit (17 kDa) is identical with calmodulin and confers on phosphorylase kinase activation by Ca#+. Unlike most calmodulinregulated enzymes, phosphorylase kinase retains its δ-subunit, even in the absence of Ca#+. The catalytic centre resides on th ...
... each lobe contains two αβγδ protomers [42]. The δ-subunit (17 kDa) is identical with calmodulin and confers on phosphorylase kinase activation by Ca#+. Unlike most calmodulinregulated enzymes, phosphorylase kinase retains its δ-subunit, even in the absence of Ca#+. The catalytic centre resides on th ...
This paper is published in a part-themed issue of Photochemical
... the solutions contained two different compounds: in the cold water solution both were intact, but in the hot water solution, the heat had destroyed one of the components. When the hot solution was cooled and added to the exhausted cold solution it became luminous again because the component that was ...
... the solutions contained two different compounds: in the cold water solution both were intact, but in the hot water solution, the heat had destroyed one of the components. When the hot solution was cooled and added to the exhausted cold solution it became luminous again because the component that was ...
Disorders of Propionate and Methylmalonate Metabolism
... CHAPTER 94 / DISORDERS OF PROPIONATE AND METHYLMALONATE METABOLISM ...
... CHAPTER 94 / DISORDERS OF PROPIONATE AND METHYLMALONATE METABOLISM ...
213 porters and neurotransmitter transporters
... apparent common motifs in all of these transporters. However, a dimeric structure of six helices was proposed as a common structure for membrane transporters (Maloney, 1990). Fig. 1 depicts the general structure of some transporters containing 12 transmembrane helices. Although the number 12 has bee ...
... apparent common motifs in all of these transporters. However, a dimeric structure of six helices was proposed as a common structure for membrane transporters (Maloney, 1990). Fig. 1 depicts the general structure of some transporters containing 12 transmembrane helices. Although the number 12 has bee ...
The Enolase Superfamily: A General Strategy for Enzyme
... We have discovered a superfamily of enzymes related by their ability to catalyze the abstraction of the R-proton of a carboxylic acid to form an enolic intermediate. Although each reaction catalyzed by these enzymes is initiated by this common step, their overall reactions (including racemization, β ...
... We have discovered a superfamily of enzymes related by their ability to catalyze the abstraction of the R-proton of a carboxylic acid to form an enolic intermediate. Although each reaction catalyzed by these enzymes is initiated by this common step, their overall reactions (including racemization, β ...
Dateien anzeigen - Universität Düsseldorf
... incomplete tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle were selected as promising targets and implemented by construction and characterization of several integration/deletion mutants: The succinate dehydrogenase from Acetobacter pasteurianus was introduced into G. oxydans, which naturally lacks this TCA cycle en ...
... incomplete tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle were selected as promising targets and implemented by construction and characterization of several integration/deletion mutants: The succinate dehydrogenase from Acetobacter pasteurianus was introduced into G. oxydans, which naturally lacks this TCA cycle en ...
Identification of the Amino Terminus of Neuronal Ca2
... In some experiments niflumic acid was omitted, and oocytes were injected with 30 – 40 nl of a 100 mM solution of K3-1,2bis(aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N9,N9-tetra-acetic acid (BAP TA) to suppress endogenous C a 21-activated C l 2 currents. Electrodes contained 3 M KC l and had resistances of 0.3–2 MV. T ...
... In some experiments niflumic acid was omitted, and oocytes were injected with 30 – 40 nl of a 100 mM solution of K3-1,2bis(aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N9,N9-tetra-acetic acid (BAP TA) to suppress endogenous C a 21-activated C l 2 currents. Electrodes contained 3 M KC l and had resistances of 0.3–2 MV. T ...
Cholesterol Homeostasis - Sigma
... Cholesterol Biosynthesis Cholesterol levels in the body come from two sources, dietary intake and biosynthesis. The majority of cholesterol utilized by healthy adults is synthesized in the liver, which produces ~70% of the total daily cholesterol requirement (~1 gram). The other 30% comes from dieta ...
... Cholesterol Biosynthesis Cholesterol levels in the body come from two sources, dietary intake and biosynthesis. The majority of cholesterol utilized by healthy adults is synthesized in the liver, which produces ~70% of the total daily cholesterol requirement (~1 gram). The other 30% comes from dieta ...