Aspects of Lipid Metabolism in Crustaceans Department of
... indicates either that some small percentage of the glucose is oxidized to acetate and then synthesized into fatty acids, or that the label from the glucose finds its way into lipid via a-glycerophosphate. The former suggestion is ...
... indicates either that some small percentage of the glucose is oxidized to acetate and then synthesized into fatty acids, or that the label from the glucose finds its way into lipid via a-glycerophosphate. The former suggestion is ...
Recent Advances Towards New Anti-Infective Agents that Inhibit
... amino acid), a hydrophobic domain, and a tail of mostly positively charged residues. The charged amino acids at the C-terminal end of the CWS are believed to prevent the protein from being released into the extracellular milieu. (3) The partially exported protein is then processed by the SrtA sortas ...
... amino acid), a hydrophobic domain, and a tail of mostly positively charged residues. The charged amino acids at the C-terminal end of the CWS are believed to prevent the protein from being released into the extracellular milieu. (3) The partially exported protein is then processed by the SrtA sortas ...
Carbohydrate Storage and Synthesis in Liver and Muscle: Glycogen
... In Liver: goes to glycogenesis reserve: for maintaining post absorptive blood [glc]. glycolysis: after glycogen reserve is full. energy/ATP synthesis and triglycerides: FAS and TGs exported to adipose tissue for storage. In muscle: glucose stored in glycogen; glycolytic pyruvate formed. ...
... In Liver: goes to glycogenesis reserve: for maintaining post absorptive blood [glc]. glycolysis: after glycogen reserve is full. energy/ATP synthesis and triglycerides: FAS and TGs exported to adipose tissue for storage. In muscle: glucose stored in glycogen; glycolytic pyruvate formed. ...
9. Wakil, S. J., Green, DE, Mii, S., and Mahler, HR (1954) Studies on
... enzymes that constitute the pathway for fatty acid synthesis in bacteria which offering additional weights into the construction of fatty acid chains in animals. Using the bacterial system, he helped elucidate the role of a protein as the coenzyme for fatty acid synthesis named the acyl carrier prot ...
... enzymes that constitute the pathway for fatty acid synthesis in bacteria which offering additional weights into the construction of fatty acid chains in animals. Using the bacterial system, he helped elucidate the role of a protein as the coenzyme for fatty acid synthesis named the acyl carrier prot ...
Molecular Cloning and Expression Analysis of IgD in Nile
... comprise the major lymphoid organs of fish, yet bone marrow and lymph nodes constitute the immune organs of mammals. The fish immune system is far simpler than that of primates and rodents [8]. It is necessary to analyze IgD in teleosts, as it will provide a reference for further research in this fi ...
... comprise the major lymphoid organs of fish, yet bone marrow and lymph nodes constitute the immune organs of mammals. The fish immune system is far simpler than that of primates and rodents [8]. It is necessary to analyze IgD in teleosts, as it will provide a reference for further research in this fi ...
Evolution of the Aldose Reductase-Related Gecko Eye Lens Protein
... these sequences (not shown) confirmed that this superfamily of proteins, the aldo-keto reductases, is highly divergent, with multiple representatives in diverse proand eukaryotes. However, most vertebrate sequences clustered together, as observed earlier (Jez et al. 1997; Seery et al. 1998). Therefo ...
... these sequences (not shown) confirmed that this superfamily of proteins, the aldo-keto reductases, is highly divergent, with multiple representatives in diverse proand eukaryotes. However, most vertebrate sequences clustered together, as observed earlier (Jez et al. 1997; Seery et al. 1998). Therefo ...
REDESIGN OF CARNITINE ACETYLTRANSFERASE SPECIFICITY BY PROTEIN ENGINEERING UNIVERSIDAD DE BARCELONA
... A novel compound, the fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor C75, has been proposed to pharmacologically regulate CPT I activity (Price, 2001). Structurally, C75 is a cell-permeable α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone designed to be less reactive and potentially safer than cerulenin, a natural product obtained ...
... A novel compound, the fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor C75, has been proposed to pharmacologically regulate CPT I activity (Price, 2001). Structurally, C75 is a cell-permeable α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone designed to be less reactive and potentially safer than cerulenin, a natural product obtained ...
Details of the scope analysis for each organism
... Reed et al. [25] (http://gcrg.ucsd.edu/organisms/ecoli/ecoli_reactions.html) was used as is. ...
... Reed et al. [25] (http://gcrg.ucsd.edu/organisms/ecoli/ecoli_reactions.html) was used as is. ...
Malic acid production by Aspergillus oryzae
... from the mitochondrion in the cytosol, the whole process seems more like a bioconversion of glucose to citrate with maximum yields of about 95%. The above described pathway shows the origin of pyruvate as a direct result of glycolysis. But it was shown that considerable amounts of citric acid must h ...
... from the mitochondrion in the cytosol, the whole process seems more like a bioconversion of glucose to citrate with maximum yields of about 95%. The above described pathway shows the origin of pyruvate as a direct result of glycolysis. But it was shown that considerable amounts of citric acid must h ...
Molecular basis of hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency
... of CPT II expressed in all tissues. On the other hand, two different isoforms of CPT I have been described with distinct tissue distributions. These two forms are called the hepatic (CPT IA) and muscle form (CPT IB) and are encoded by different genes localized on chromosome 11q13.1-13.5 and 22q13.31 ...
... of CPT II expressed in all tissues. On the other hand, two different isoforms of CPT I have been described with distinct tissue distributions. These two forms are called the hepatic (CPT IA) and muscle form (CPT IB) and are encoded by different genes localized on chromosome 11q13.1-13.5 and 22q13.31 ...
Substrate Specificity and Mechanism from the Structure of
... A – D, respectively) lies below the minimum range found in an analysis of other dimeric proteins.22 Gel filtration of Pf GalK resulted in elution at the ...
... A – D, respectively) lies below the minimum range found in an analysis of other dimeric proteins.22 Gel filtration of Pf GalK resulted in elution at the ...
Membrane transporters in a human genome
... Membrane transporters enable efficient cellular metabolism, aid in nutrient sensing, and have been associated with various diseases, such as obesity and cancer. Genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions capture genomic, physiological, and biochemical knowledge of a target organism, along with a ...
... Membrane transporters enable efficient cellular metabolism, aid in nutrient sensing, and have been associated with various diseases, such as obesity and cancer. Genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions capture genomic, physiological, and biochemical knowledge of a target organism, along with a ...
Mammalian CSAD and GADL1 have distinct biochemical properties
... 2010) and also in humans dietary intake of taurine in the form of energy drinks or vitamin supplements is widespread, although with unclear health implications (Bigard, 2010). In mammalian tissues taurine is mainly synthesized from cysteine in a three step sequential pathway, involving oxidation by ...
... 2010) and also in humans dietary intake of taurine in the form of energy drinks or vitamin supplements is widespread, although with unclear health implications (Bigard, 2010). In mammalian tissues taurine is mainly synthesized from cysteine in a three step sequential pathway, involving oxidation by ...
Characterization of the Sucrose Phosphate Phosphatase (SPP
... Suc-6-P from UDP-glucose and fructose-6-phosphate (Fru6P). In the second step of the pathway, SPP catalyses the irreversible hydrolysis of Suc-6-P to sucrose and displaces the reaction catalysed by SPS in the direction of sucrose synthesis [9, 10]. SPP encoding genes have been described in different ...
... Suc-6-P from UDP-glucose and fructose-6-phosphate (Fru6P). In the second step of the pathway, SPP catalyses the irreversible hydrolysis of Suc-6-P to sucrose and displaces the reaction catalysed by SPS in the direction of sucrose synthesis [9, 10]. SPP encoding genes have been described in different ...
The Amino Acid Sequences of the Fd Fragments of Two Human y1
... shown to be attached to the aspartic residue of this peptide, presumably involving the ,B-carboxyl group, and as sialic acid is unlikely to be present for 3h) and the digest was fractionated. The on the peptide (see section below on carbohydrate compositions of the chymotryptic peptides are of Cor F ...
... shown to be attached to the aspartic residue of this peptide, presumably involving the ,B-carboxyl group, and as sialic acid is unlikely to be present for 3h) and the digest was fractionated. The on the peptide (see section below on carbohydrate compositions of the chymotryptic peptides are of Cor F ...
Effects of Molecular Crowding on Binding Affinity of Dihydrofolate to
... The enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) is a critical enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway for nucleotides and proteins in the cell. DHFR contributes to the production of purines by forming tetrahydrofolate (THF) using dihydrofolate (DHF) as the reactant and NADPH as the cofactor. Furthermore, tetra ...
... The enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) is a critical enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway for nucleotides and proteins in the cell. DHFR contributes to the production of purines by forming tetrahydrofolate (THF) using dihydrofolate (DHF) as the reactant and NADPH as the cofactor. Furthermore, tetra ...
RIBOZYMES
... It was first identified in the minus strand of the tobacco ring spot virus (TRSV) satellite RNA where it catalyzes self-cleavage and joining (ligation) reactions to process the products of rolling circle virus replication into linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. The hairpin ribozyme is ...
... It was first identified in the minus strand of the tobacco ring spot virus (TRSV) satellite RNA where it catalyzes self-cleavage and joining (ligation) reactions to process the products of rolling circle virus replication into linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. The hairpin ribozyme is ...
Multiomics of tomato glandular trichomes reveals
... quantified, rutin alone contributed to 25 ± 3% of the corresponding trichome dry weight in LA4024, whereas the sum of two major sesquiterpene carboxylic acids ((+)-(E)-α-santalene12-oic acid and (+)-(E)-endo-bergamotene-12-oic acid) added up to 23 ± 2% of the GT dry weight in LA1777. ...
... quantified, rutin alone contributed to 25 ± 3% of the corresponding trichome dry weight in LA4024, whereas the sum of two major sesquiterpene carboxylic acids ((+)-(E)-α-santalene12-oic acid and (+)-(E)-endo-bergamotene-12-oic acid) added up to 23 ± 2% of the GT dry weight in LA1777. ...
The Miraculous Benefits of Non Denatured Whey Protein Powder
... roots toxicity. Resurrecting the body’s production of glutathione is a dynamic key to cellular and whole body detoxification. Using Unheated Whey Protein Powder delivers high amounts of the key amino acids glutamyl-cysteine. Glutamyl-cysteine is converted by glutathione synthetase into glutathione. ...
... roots toxicity. Resurrecting the body’s production of glutathione is a dynamic key to cellular and whole body detoxification. Using Unheated Whey Protein Powder delivers high amounts of the key amino acids glutamyl-cysteine. Glutamyl-cysteine is converted by glutathione synthetase into glutathione. ...
Rhizopus Raw-Starch-Degrading Glucoamylase: Its
... lases are knownto exist in multiple forms of the glucoamylase gene are also described. varying in size. A few distinct forms of As- ...
... lases are knownto exist in multiple forms of the glucoamylase gene are also described. varying in size. A few distinct forms of As- ...
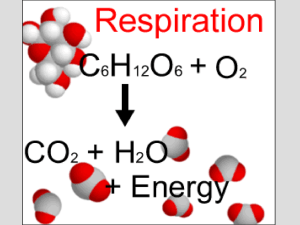
lecture 6 ppt
... C. Citric Acid Cycle (aka Krebs/TCA cycle) D. Electron Transport Chain (ETC) E. Chemiosmosis ...
... C. Citric Acid Cycle (aka Krebs/TCA cycle) D. Electron Transport Chain (ETC) E. Chemiosmosis ...
Glycolysis - WordPress.com
... tissues to bloodstream and then to aerobic tissues, such as liver and heart. In these aerobic tissues lactate can be catabolized further or can be converted back through gluconeogenesis. One step conversion of Pyruvate to Lactate catalysed by Lactate dehydrogenase. ...
... tissues to bloodstream and then to aerobic tissues, such as liver and heart. In these aerobic tissues lactate can be catabolized further or can be converted back through gluconeogenesis. One step conversion of Pyruvate to Lactate catalysed by Lactate dehydrogenase. ...