The role of homocysteine in endothelial dysfunction
... to inactivation of MTR. Thus, the enzyme methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) is required for reversion of oxidized cobalamin (II) to CH3-cobalamin (III) to maintain the activity of MTR [22]. The folate-dependent remethylation pathway is present in nearly all cells, except red blood cells [34]. Alte ...
... to inactivation of MTR. Thus, the enzyme methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) is required for reversion of oxidized cobalamin (II) to CH3-cobalamin (III) to maintain the activity of MTR [22]. The folate-dependent remethylation pathway is present in nearly all cells, except red blood cells [34]. Alte ...
Enzyme Mechanisms
... Therefore a controlling influence (e.g. an allosteric effector) will up- or down-regulate both directions If that’s not what the cell needs, it will need asymmetric pathways or pathways involving different enzymes in the two directions ...
... Therefore a controlling influence (e.g. an allosteric effector) will up- or down-regulate both directions If that’s not what the cell needs, it will need asymmetric pathways or pathways involving different enzymes in the two directions ...
Analysis of Nutrient Composition of Feather Meal and Feather Meal
... degradable and undegradable, carbohydrate fractions (structural and nonstructural), lipid and fatty acid content, minerals, and amino acids (total protein basis and borate-phosphate buffer insoluble). Another practical concern is the extent of variability in the feed product among plants and within ...
... degradable and undegradable, carbohydrate fractions (structural and nonstructural), lipid and fatty acid content, minerals, and amino acids (total protein basis and borate-phosphate buffer insoluble). Another practical concern is the extent of variability in the feed product among plants and within ...
1 A multi-platform metabolomics approach identifies novel
... Succinate and lactate abundance are shown in panel E of Fig 2. Succinate levels, and the succinate:lactate ratio have historically been associated with BV (21-23), and succinate has been postulated to play an immunomodulatory role (23). Here we show that succinate is not associated with bacterial di ...
... Succinate and lactate abundance are shown in panel E of Fig 2. Succinate levels, and the succinate:lactate ratio have historically been associated with BV (21-23), and succinate has been postulated to play an immunomodulatory role (23). Here we show that succinate is not associated with bacterial di ...
3 Citrate metabolism and aroma compound production in lactic acid
... the initial step in all citrate fermentation pathways known in bacteria. The holoenzyme has been purified and characterized in several species, but most of the studies have been carried out with the K. pneumoniae enzyme [27]. In this micro-organism the CL consists of three different subunits, α (54. ...
... the initial step in all citrate fermentation pathways known in bacteria. The holoenzyme has been purified and characterized in several species, but most of the studies have been carried out with the K. pneumoniae enzyme [27]. In this micro-organism the CL consists of three different subunits, α (54. ...
The mitochondrial carnitine/acylcarnitine carrier: Function
... Oxidation of fatty acids in mitochondria coupled to oxidative phosphorylation is the most important pathway for the production of metabolic energy during fasting. This process occurs in the mitochondrial matrix where the enzymes of fatty acid b-oxidation are located. Fatty acyl groups are transporte ...
... Oxidation of fatty acids in mitochondria coupled to oxidative phosphorylation is the most important pathway for the production of metabolic energy during fasting. This process occurs in the mitochondrial matrix where the enzymes of fatty acid b-oxidation are located. Fatty acyl groups are transporte ...
chapter 15: answers to selected problems
... (usually a compound that contains a phosphate group attached to an organic fragment). The ATP breaks down into ADP and phosphate. 15.21 In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two pyruvate ions. 15.22 Lactic acid fermentation is anaerobic because it does not make any NADH or FADH2, so the body do ...
... (usually a compound that contains a phosphate group attached to an organic fragment). The ATP breaks down into ADP and phosphate. 15.21 In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two pyruvate ions. 15.22 Lactic acid fermentation is anaerobic because it does not make any NADH or FADH2, so the body do ...
New peptide and gene coding for same
... Figure 7 represents a result of electrophoresis showing expression of a 7-hANP gene. Figure 8 represents a construction process of plasmid pS223-3 from plasmid pS83-3 and a DNA fragment containing a base sequence coding for amino acid sequence of 7-hANP, and a construction process of plasmid pS225-3 ...
... Figure 7 represents a result of electrophoresis showing expression of a 7-hANP gene. Figure 8 represents a construction process of plasmid pS223-3 from plasmid pS83-3 and a DNA fragment containing a base sequence coding for amino acid sequence of 7-hANP, and a construction process of plasmid pS225-3 ...
Metabolic decision making by protein-metabolite - ETH E
... Metabolism lies at the core of microbial life and fuels all cellular activities with building blocks, reducing power, and energy. To regulate metabolic activity, microbes utilize a complex network of regulatory layers, such as transcriptional regulation, covalent posttranslational modificat ...
... Metabolism lies at the core of microbial life and fuels all cellular activities with building blocks, reducing power, and energy. To regulate metabolic activity, microbes utilize a complex network of regulatory layers, such as transcriptional regulation, covalent posttranslational modificat ...
On the mechanism of action of the antifungal agent propionate
... A. nidulans on glucose but not on acetate; the latter was shown to inhibit propionate oxidation. When grown on glucose a methylcitrate synthase deletion mutant is much more sensitive towards the presence of propionate in the medium as compared to the wild-type and accumulates 10-fold higher levels o ...
... A. nidulans on glucose but not on acetate; the latter was shown to inhibit propionate oxidation. When grown on glucose a methylcitrate synthase deletion mutant is much more sensitive towards the presence of propionate in the medium as compared to the wild-type and accumulates 10-fold higher levels o ...
University of Groningen Stress responses and sugar metabolism in
... genes during the growth cycle of B. subtilis as has been shown by transcriptome analysis at different growth phases [154]. Pleiotropicity of ccpA knock‐out mutants has also been shown by various transcriptomics studies performed at mid‐exponential phase of growth [18,150,181,276]. Moreo ...
... genes during the growth cycle of B. subtilis as has been shown by transcriptome analysis at different growth phases [154]. Pleiotropicity of ccpA knock‐out mutants has also been shown by various transcriptomics studies performed at mid‐exponential phase of growth [18,150,181,276]. Moreo ...
Unraveling Biochemical Pathways Affected by Mitochondrial
... The acetyl-CoA molecules formed will then be used to feed other metabolic pathways, such as the TCA cycle [26], or to produce cholesterol or other lipids through lipogenesis [27]. The acyl-CoA can also be transported back to the cytosol by the carnitine acyl-carnitine translocase system to produce a ...
... The acetyl-CoA molecules formed will then be used to feed other metabolic pathways, such as the TCA cycle [26], or to produce cholesterol or other lipids through lipogenesis [27]. The acyl-CoA can also be transported back to the cytosol by the carnitine acyl-carnitine translocase system to produce a ...
http://doc.rero.ch
... aromatic amino acid residue contains a photoexcitable 2-(2,2dimethyl-propionyl)-3-(diphenoxyphosphoryloxy)tetrahydrofuran-2ylmethyl group in the 4-position that forms a tetrahydrofuran radical cation 4 upon UV exposure. If X can be oxidized by the electron acceptor at the C-terminal amino acid, ET o ...
... aromatic amino acid residue contains a photoexcitable 2-(2,2dimethyl-propionyl)-3-(diphenoxyphosphoryloxy)tetrahydrofuran-2ylmethyl group in the 4-position that forms a tetrahydrofuran radical cation 4 upon UV exposure. If X can be oxidized by the electron acceptor at the C-terminal amino acid, ET o ...
Vitamins - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... Polish biochemist Casimir Funk discovered vitamin B1 in 1912 in rice bran. He proposed the complex be named "Vitamin" (vital amines). By the time it was shown that not all vitamins were amines, the word was already ubiquitous. ...
... Polish biochemist Casimir Funk discovered vitamin B1 in 1912 in rice bran. He proposed the complex be named "Vitamin" (vital amines). By the time it was shown that not all vitamins were amines, the word was already ubiquitous. ...
NIH Public Access
... These data were consistent with an allosteric mechanism of SIRT1 activation (4, 15). To elucidate the determinants of activation in SIRT1, we screened for SIRT1 mutant proteins lacking activation (Fig. 2C). The ability of SIRT1 to be activated by resveratrol was attenuated in one mutant that substit ...
... These data were consistent with an allosteric mechanism of SIRT1 activation (4, 15). To elucidate the determinants of activation in SIRT1, we screened for SIRT1 mutant proteins lacking activation (Fig. 2C). The ability of SIRT1 to be activated by resveratrol was attenuated in one mutant that substit ...
chemical structure and properties
... Fat soluble – passive diffusion Water soluble – passive diffusion, but some by active process if low level in the diet ...
... Fat soluble – passive diffusion Water soluble – passive diffusion, but some by active process if low level in the diet ...
Phosphorylation of the F1Fo ATP Synthase Я Subunit
... Conclusions: Taken together, these data show that pseudophosphorylation of specific amino acid residues can have separate and distinctive effects on the F1Fo ATP synthase complex, suggesting the possibility that several of the phosphorylations observed in the rabbit heart can have structural and fun ...
... Conclusions: Taken together, these data show that pseudophosphorylation of specific amino acid residues can have separate and distinctive effects on the F1Fo ATP synthase complex, suggesting the possibility that several of the phosphorylations observed in the rabbit heart can have structural and fun ...
Developement of strategies for the isotopic labeling of methyl
... enhances the intensity of detectable long-range nOes by a factor 4. The described protocol also permits the suppression of spurious correlations, especially harmful for structural studies based on detection/analysis of nOes. To make an efficient use of the obtained high quality NMR spectra using thi ...
... enhances the intensity of detectable long-range nOes by a factor 4. The described protocol also permits the suppression of spurious correlations, especially harmful for structural studies based on detection/analysis of nOes. To make an efficient use of the obtained high quality NMR spectra using thi ...
SCHEMA Recombination of a
... parent CBH II catalytic domains. All of these enzymes were stabilized by the Cys-Ser substitution; the P. chrysosporium CBH II was stabilized by a remarkable 10 °C (supplemental Fig. 4). Eight of the thermostable CBH II chimeras and the parent enzymes containing the equivalent C313S mutation were Hi ...
... parent CBH II catalytic domains. All of these enzymes were stabilized by the Cys-Ser substitution; the P. chrysosporium CBH II was stabilized by a remarkable 10 °C (supplemental Fig. 4). Eight of the thermostable CBH II chimeras and the parent enzymes containing the equivalent C313S mutation were Hi ...
Biochemical characterization of the initial steps of the Kennedy
... (Tb10.6k15.1570); PSD, phosphatidylserine decarboxylase (Tb09.211.1610); PEMT, phosphatidylethanolamine methyltransferases; DAG, diacylglycerol. The dashed box indicates methyltransferase enzymes which are not present in either T. brucei or T. cruzi , but are present in L. major . ...
... (Tb10.6k15.1570); PSD, phosphatidylserine decarboxylase (Tb09.211.1610); PEMT, phosphatidylethanolamine methyltransferases; DAG, diacylglycerol. The dashed box indicates methyltransferase enzymes which are not present in either T. brucei or T. cruzi , but are present in L. major . ...
The Bacterial Toxin RelE Displays Codon
... RelE toxins will appear in the cytoplasm (Christensen et al., 2001). The mechanism of action of RelE has remained unclear, but experimental observations suggested that it targets a factor involved in protein synthesis (Galvani et al., 2001; Pedersen et al., 2002). Induction of transcription of the r ...
... RelE toxins will appear in the cytoplasm (Christensen et al., 2001). The mechanism of action of RelE has remained unclear, but experimental observations suggested that it targets a factor involved in protein synthesis (Galvani et al., 2001; Pedersen et al., 2002). Induction of transcription of the r ...
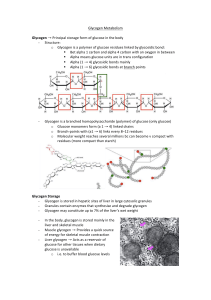
Glycogen!Metabolism! ! Glycogen$→!Principal!storage!form!of
... o AMP!(present!significantly!when!ATP!is!depleted)!activates!glycogen! phosphorylase!(R!conformation!enhanced)!and!glycogen!breakdown!is! activated!bc!more!energy!is!needed! o ATP!and!G6P!inhibit!glycogen!phosphorylase!(enhance!the!T!conformation)! ! ∴!glycogen!breakdown!is!inhibited!when!ATP!and!gl ...
... o AMP!(present!significantly!when!ATP!is!depleted)!activates!glycogen! phosphorylase!(R!conformation!enhanced)!and!glycogen!breakdown!is! activated!bc!more!energy!is!needed! o ATP!and!G6P!inhibit!glycogen!phosphorylase!(enhance!the!T!conformation)! ! ∴!glycogen!breakdown!is!inhibited!when!ATP!and!gl ...