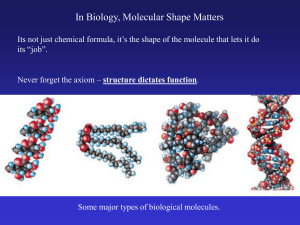
In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
Cells Notes
... cells. Cell theory, written in the 1800s, says three things: 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from existing cells. ...
... cells. Cell theory, written in the 1800s, says three things: 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. All cells come from existing cells. ...
Cell Wall Cell Membrane Nucleus Nuclear Membrane
... The cell membrane controls what substances come into and out of a cell. Everything the cell needs, from food to oxygen, enters the cell through the cell membrane. Fortunately, your ship can slip through, too. Harmful waste products leave the cell through the cell membrane. For a cell to survive, the ...
... The cell membrane controls what substances come into and out of a cell. Everything the cell needs, from food to oxygen, enters the cell through the cell membrane. Fortunately, your ship can slip through, too. Harmful waste products leave the cell through the cell membrane. For a cell to survive, the ...
CH 7 Exam - Deer Creek Schools
... 13. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a. an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration b. an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration c. an area of equilibrium to an area of high concentration d. all of the above 14. When the concentration of molecules on ...
... 13. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a. an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration b. an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration c. an area of equilibrium to an area of high concentration d. all of the above 14. When the concentration of molecules on ...
Cell Project Rubric
... choose to make an animal cell or a plant cell. You can work with many different types of materials, but here are some ideas: Styrofoam ball with various items stuck in, representing organelle (available at Michael’s) Jell-O, with jellybeans, pasta, etc. Clay model mounted on foam board Felt ...
... choose to make an animal cell or a plant cell. You can work with many different types of materials, but here are some ideas: Styrofoam ball with various items stuck in, representing organelle (available at Michael’s) Jell-O, with jellybeans, pasta, etc. Clay model mounted on foam board Felt ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... - How do individual cells maintain homeostasis? - How do the cells of multicellular organisms work together to maintain homeostasis? ...
... - How do individual cells maintain homeostasis? - How do the cells of multicellular organisms work together to maintain homeostasis? ...
File
... If there was a problem in a cell where the nucleolus stopped functioning, what affect would this have on the following organelles? -Ribosomes -Lysosomes ...
... If there was a problem in a cell where the nucleolus stopped functioning, what affect would this have on the following organelles? -Ribosomes -Lysosomes ...
1.2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life
... General Structure of a Cell A cell can be viewed as a factory with different departments, each carrying out specialized tasks that help keep the cell alive. Whether they are nerve cells in the brain of an animal, or epidermal cells in the leaf of a plant, cells are bathed in an aqueous (water-based) ...
... General Structure of a Cell A cell can be viewed as a factory with different departments, each carrying out specialized tasks that help keep the cell alive. Whether they are nerve cells in the brain of an animal, or epidermal cells in the leaf of a plant, cells are bathed in an aqueous (water-based) ...
Structure, function and growth of prokaryote and eukaryote cells
... Connecting structures between cells that allow a continuous cytoplasmic link. ...
... Connecting structures between cells that allow a continuous cytoplasmic link. ...
Cell Project Rubric
... g. Ribosomes on ER and free ribosomes h. Golgi apparatus / complex i. Vacuole if plant cell j. Mitochondria k. Chloroplast if plant cell 4. All organelles must be labaled 5. Model must include some sort of stand 6. Model must include student name and period on reverse side To attain a grade of A on ...
... g. Ribosomes on ER and free ribosomes h. Golgi apparatus / complex i. Vacuole if plant cell j. Mitochondria k. Chloroplast if plant cell 4. All organelles must be labaled 5. Model must include some sort of stand 6. Model must include student name and period on reverse side To attain a grade of A on ...
How are Plant and Animal Cells Different Similar.indd
... Directions: Compare and contrast plant and animals cells by completing the Venn Diagram using the terms from the word bank. Then answer the questions. Cell Wall and Chloroplast 1. What does the plant cell have that the animal cell doesn’t? ____________________________ _______________________________ ...
... Directions: Compare and contrast plant and animals cells by completing the Venn Diagram using the terms from the word bank. Then answer the questions. Cell Wall and Chloroplast 1. What does the plant cell have that the animal cell doesn’t? ____________________________ _______________________________ ...
Introduction to Cellular Structure • All organisms are composed of
... • The cell is the structural and functional unit of life • Human adults are made up of ~100 trillion cells • Each cell has an outer boundary called the plasma (cell) membrane which isolates the fluid within the cell from the fluid that surrounds the cell ...
... • The cell is the structural and functional unit of life • Human adults are made up of ~100 trillion cells • Each cell has an outer boundary called the plasma (cell) membrane which isolates the fluid within the cell from the fluid that surrounds the cell ...
Ribosomes translate the genetic message from mRNA that
... They attach firmly to the phospholipids only drastic measure as using of detergent can release them. (2) Peripheral protein = are external to lipid bilayer. They are attached to the head by week bonds which easily break by changing PH Function: Participate in enzymatic activities. Maintain ionic ...
... They attach firmly to the phospholipids only drastic measure as using of detergent can release them. (2) Peripheral protein = are external to lipid bilayer. They are attached to the head by week bonds which easily break by changing PH Function: Participate in enzymatic activities. Maintain ionic ...
AS 1, Molecules and Cells
... Process by which substances taken into a cell cause the cell membrane to enclose the material in a vesicle Removal or secretion of substances from a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the cell membrane Movement of substances across a cell membrane from higher to lower concentration, using protein ...
... Process by which substances taken into a cell cause the cell membrane to enclose the material in a vesicle Removal or secretion of substances from a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the cell membrane Movement of substances across a cell membrane from higher to lower concentration, using protein ...
Introducing the Cell
... you must stay with that person until you are "recycled". (2) Ribsomes can only work on one protein at a time with the help of one mRNA molecule and the tRNA molecules. The tRNA molecules must stay near the table with amino acids unless they are delivering pieces. (3) Cell parts cannot run around the ...
... you must stay with that person until you are "recycled". (2) Ribsomes can only work on one protein at a time with the help of one mRNA molecule and the tRNA molecules. The tRNA molecules must stay near the table with amino acids unless they are delivering pieces. (3) Cell parts cannot run around the ...
Section 8.1 Summary – pages 195
... • Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • In a cell, water always moves to reach an equal concentration on both sides of the membrane. ...
... • Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • In a cell, water always moves to reach an equal concentration on both sides of the membrane. ...
LAB – HOW DO ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS DIFFER
... 1. Ask your teacher to put a drop of iodine stain on a slide. Gently scrape the agar plate for a bacterial colony. CAUTION: Do not scrape so hard that you cut into the agar. 2. Rub the toothpick in the stain and leave it there for 30 seconds. 3. Remove the tooth pick from the stain and coverslip. 4. ...
... 1. Ask your teacher to put a drop of iodine stain on a slide. Gently scrape the agar plate for a bacterial colony. CAUTION: Do not scrape so hard that you cut into the agar. 2. Rub the toothpick in the stain and leave it there for 30 seconds. 3. Remove the tooth pick from the stain and coverslip. 4. ...
Cell structure and functions
... molecules of protiens & phospholipids (certain types of fats). The cell membrane is seperating the contents of the cell from the outside world. It has the property of selective permiability: only certain substances may enter & leave the cell ...
... molecules of protiens & phospholipids (certain types of fats). The cell membrane is seperating the contents of the cell from the outside world. It has the property of selective permiability: only certain substances may enter & leave the cell ...
Exam 1 Study Guide
... 1. What is ATP? Explain its structure, the role it plays in cells, the type of energy it contains, and how it is produced. 2. What is protein folding? How does it contribute to protein’s functionality? Explain: What proteins are made of The four levels of protein folding The motifs found at ea ...
... 1. What is ATP? Explain its structure, the role it plays in cells, the type of energy it contains, and how it is produced. 2. What is protein folding? How does it contribute to protein’s functionality? Explain: What proteins are made of The four levels of protein folding The motifs found at ea ...
BIOL241StudyGuideExp1JUL2012
... (polysaccharides), lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. State the basic function(s) of each of these classes of (bio) molecules/macromolecules. 11. Define an enzyme. Describe the role of enzymes in metabolism. 12. Describe the properties of cell membranes including composition, structure, function, ...
... (polysaccharides), lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. State the basic function(s) of each of these classes of (bio) molecules/macromolecules. 11. Define an enzyme. Describe the role of enzymes in metabolism. 12. Describe the properties of cell membranes including composition, structure, function, ...
Cell Notes
... cell membrane and provides support to the cell. b. Cell Membrane- A phospholipid layer that covers a cells surface, acts as a barrier between the inside of a cell and the cell’s environment c. Cytoskeleton- web of proteins inside the cytoplasm, which acts as both a muscle and a skeleton d. Nucleus- ...
... cell membrane and provides support to the cell. b. Cell Membrane- A phospholipid layer that covers a cells surface, acts as a barrier between the inside of a cell and the cell’s environment c. Cytoskeleton- web of proteins inside the cytoplasm, which acts as both a muscle and a skeleton d. Nucleus- ...
Cell Theory
... Two types of cells • There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (you are made up of eukaryotic cells). • Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane bound organelles and have no nucleus. ...
... Two types of cells • There are two cell types: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (you are made up of eukaryotic cells). • Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane bound organelles and have no nucleus. ...
Is the reason that stem cells can be used to “produce” different types
... (organelle) of cells. They can exits either free in the cytoplasm or attached, via the ER, to the nuclear membrane. • Mitochondria: the energy producing organelle for the cell. They also contain there own set of DNA and are inherited from the female. So can be used to track the female linage of a sp ...
... (organelle) of cells. They can exits either free in the cytoplasm or attached, via the ER, to the nuclear membrane. • Mitochondria: the energy producing organelle for the cell. They also contain there own set of DNA and are inherited from the female. So can be used to track the female linage of a sp ...
LS. 2 Notes
... K. Vacuoles are the storage areas of the cell. L. Lysosomes are small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials of the cell. IV. Cellular Transport A. In endocytosis, the cell engulfs some of its extracellular fluid, including material dissolved or suspended in it. A p ...
... K. Vacuoles are the storage areas of the cell. L. Lysosomes are small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials of the cell. IV. Cellular Transport A. In endocytosis, the cell engulfs some of its extracellular fluid, including material dissolved or suspended in it. A p ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.























