Protons and how they are transported by proton pumps
... pathway. Arg655 is suggested to play a key role in proton release and proton pumping against high membrane potentials [25]. The positive charge of Arg655, now approaching Asp684, will favor proton release from Asp684 and at the same time inhibit reprotonation of Asp684 with an extracellular proton, ...
... pathway. Arg655 is suggested to play a key role in proton release and proton pumping against high membrane potentials [25]. The positive charge of Arg655, now approaching Asp684, will favor proton release from Asp684 and at the same time inhibit reprotonation of Asp684 with an extracellular proton, ...
Normal placentae of domestic mammals
... and is lost in the lochia, usually by day 12 postpartum (PP). Reepithelialization occurs in about 21 days PP. Because the outer part of the caruncle is lost anyway, it can be sampled without damage to the future reproductive capacity of the cow. Such sampling is recommended when there is no placenta ...
... and is lost in the lochia, usually by day 12 postpartum (PP). Reepithelialization occurs in about 21 days PP. Because the outer part of the caruncle is lost anyway, it can be sampled without damage to the future reproductive capacity of the cow. Such sampling is recommended when there is no placenta ...
Reversible translocation of cytidylyltransferase between cytosol and
... 12-myristate 13-acetate, indicating that hydrolysis can be a rapid process [21]. Since the existence of a phosphatidylcholine cycle was recently proposed [22], it seemed conceivable that, for an efficient regulation of cell metabolism, resynthesis should be regulated in the same range of time as hyd ...
... 12-myristate 13-acetate, indicating that hydrolysis can be a rapid process [21]. Since the existence of a phosphatidylcholine cycle was recently proposed [22], it seemed conceivable that, for an efficient regulation of cell metabolism, resynthesis should be regulated in the same range of time as hyd ...
Role of the ABC Transporter Ste6 in Cell Fusion during Yeast
... The p G A L - H O plasmid (URA3 ÷) was then cured by growth on 5-fluoroorotic acid medium (34). The resulting M A T s I M A T a CEF1/cefl strain mated efficiently as a M A T a strain indicating that ceil was recessive. The ceil gene was cloned by complementation of the mating defect of the ceil stra ...
... The p G A L - H O plasmid (URA3 ÷) was then cured by growth on 5-fluoroorotic acid medium (34). The resulting M A T s I M A T a CEF1/cefl strain mated efficiently as a M A T a strain indicating that ceil was recessive. The ceil gene was cloned by complementation of the mating defect of the ceil stra ...
Detergent-Insoluble Membrane Compartment CD20 Required for Its
... D20 is a B cell molecule capable of transducing cell cycle progression signals in resting B cells upon Ab ligation (1–5). Recently, we demonstrated that Ab binding to the CD20 extracellular domain causes rapid redistribution of a large majority of CD20 molecules to a low density, detergentinsoluble ...
... D20 is a B cell molecule capable of transducing cell cycle progression signals in resting B cells upon Ab ligation (1–5). Recently, we demonstrated that Ab binding to the CD20 extracellular domain causes rapid redistribution of a large majority of CD20 molecules to a low density, detergentinsoluble ...
Localization of polysaccharides in isolated and intact cuticles of
... hydroxide. Concerning cellulase, 1 ml of the Au solution was mixed with 20 µl of a 0.2% solution of the enzymatic mixture. A 2.5:1 colloidal Au:enzyme ratio was selected for preventing the flocculation of the Au colloid in the final solution [22]. After 5 min stirring of the Au-enzyme solution, 100 ...
... hydroxide. Concerning cellulase, 1 ml of the Au solution was mixed with 20 µl of a 0.2% solution of the enzymatic mixture. A 2.5:1 colloidal Au:enzyme ratio was selected for preventing the flocculation of the Au colloid in the final solution [22]. After 5 min stirring of the Au-enzyme solution, 100 ...
Light Control of Plasma Membrane Recruitment Using
... of the supernatant, and pool together the “invisible” pellets for infection. ...
... of the supernatant, and pool together the “invisible” pellets for infection. ...
Metabolite transport across the peroxisomal membrane
... membrane protein of 47 kDa (PMP47). Although its function was unclear at the time, it was soon recognized on the basis of primary sequence homology to be a member of the MCF (mitochondrial carrier family) (SLC25) [28]. Since then, orthologues have been identified in A. thaliana (PMP38) [29], humans ...
... membrane protein of 47 kDa (PMP47). Although its function was unclear at the time, it was soon recognized on the basis of primary sequence homology to be a member of the MCF (mitochondrial carrier family) (SLC25) [28]. Since then, orthologues have been identified in A. thaliana (PMP38) [29], humans ...
Structure and Organelles
... Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins. • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
... Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins. • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
Chapter 94: Larynx - Anatomy
... its function in the earliest animal forms was quite different. The beginnings of a larynx appeared first in primitive lungfish as a few sphincter muscle fibers to protect the air sac from water. Only later in the evolutionary scheme did the larynx begin to function for the purpose of phonation (Negu ...
... its function in the earliest animal forms was quite different. The beginnings of a larynx appeared first in primitive lungfish as a few sphincter muscle fibers to protect the air sac from water. Only later in the evolutionary scheme did the larynx begin to function for the purpose of phonation (Negu ...
Full PDF - British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery
... the lax interosseous membrane allows dislocation of the head of the radius as the forearm is pronated ...
... the lax interosseous membrane allows dislocation of the head of the radius as the forearm is pronated ...
PDF Datastream - Brown Digital Repository
... RsaA- using Q-TOF or LTQ-Orbitrap……………………...............................................81 Figure 3.8: Functional classification of total 91 putative surface-exposed proteins identified using both Q-TOF and LTQ-Orbitrap method..................................................82 Figure 3.9: Distribu ...
... RsaA- using Q-TOF or LTQ-Orbitrap……………………...............................................81 Figure 3.8: Functional classification of total 91 putative surface-exposed proteins identified using both Q-TOF and LTQ-Orbitrap method..................................................82 Figure 3.9: Distribu ...
Regulators of Lysosome Function and Dynamics in Caenorhabditis
... al. 2012). Primary lysosomes that are formed are thought to undergo cycles of homotypic fusion with each other using the HOPS complex and SNARES, and fission reactions that yield mature lysosomes that can fuse with late endosomes (WARD et al. 2000; WANG et al. 2003). In addition to all of these memb ...
... al. 2012). Primary lysosomes that are formed are thought to undergo cycles of homotypic fusion with each other using the HOPS complex and SNARES, and fission reactions that yield mature lysosomes that can fuse with late endosomes (WARD et al. 2000; WANG et al. 2003). In addition to all of these memb ...
Myosin-Powered Membrane Compartment Drives Cytoplasmic
... Plant cells present an ultimate case of perpetual and rapid cytoplasmic streaming, which reaches maximal velocities of up to 4 μm/sec in Arabidopsis [18] and over 50 μm/sec in a filamentous alga Chara corallina [19], compared to 0.4 μm/sec in Drosophila oocytes [14]. Numerous studies over decades ha ...
... Plant cells present an ultimate case of perpetual and rapid cytoplasmic streaming, which reaches maximal velocities of up to 4 μm/sec in Arabidopsis [18] and over 50 μm/sec in a filamentous alga Chara corallina [19], compared to 0.4 μm/sec in Drosophila oocytes [14]. Numerous studies over decades ha ...
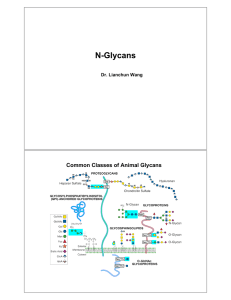
N-Glycans
... ER. Following transfer of the 14-sugar Glc3Man9GlcNAc2 glycan to protein, glucosidases in the ER remove the three glucose residues, and ER mannosidase removes a mannose residue. These reactions are intimately associated with the folding of the glycoprotein assisted by the lectins calnexin and calret ...
... ER. Following transfer of the 14-sugar Glc3Man9GlcNAc2 glycan to protein, glucosidases in the ER remove the three glucose residues, and ER mannosidase removes a mannose residue. These reactions are intimately associated with the folding of the glycoprotein assisted by the lectins calnexin and calret ...
Unraveling the complex network of cuticular structure and function
... The cuticle is involved in several different functions; for example, it inhibits the uncontrolled permeation of water, solutes and gases and the deposition of advertive substances, and it protects the plant against UV irradiation, mechanical damage, phythopathogens and herbivorous insects [4,10]. Po ...
... The cuticle is involved in several different functions; for example, it inhibits the uncontrolled permeation of water, solutes and gases and the deposition of advertive substances, and it protects the plant against UV irradiation, mechanical damage, phythopathogens and herbivorous insects [4,10]. Po ...
Distinct cathepsins control necrotic cell death
... believed to be a non-regulated process caused by trauma or environmental insults.17 However, recent studies indicate that necrotic cell death is, like apoptosis, controlled by inducer-specific cellular factors and susceptible to distinct inhibitors.5,8,28,41,55 In contrast to a multistep cascade dri ...
... believed to be a non-regulated process caused by trauma or environmental insults.17 However, recent studies indicate that necrotic cell death is, like apoptosis, controlled by inducer-specific cellular factors and susceptible to distinct inhibitors.5,8,28,41,55 In contrast to a multistep cascade dri ...
Molecular Cloning of CD68, a Human Macrophage
... of CD68 transcripts in uninduced U937 cells (Fig. 2B). yInterferon (y-IFN) did not significantly upregulate CD68 expression whereas the expression of ICAM- 1 was induced (Fig 2B). CD68 transcripts were absent from resting KG1 cells (myeloblastic leukemia) and CEM (T lymphoblastic leukemia) and prese ...
... of CD68 transcripts in uninduced U937 cells (Fig. 2B). yInterferon (y-IFN) did not significantly upregulate CD68 expression whereas the expression of ICAM- 1 was induced (Fig 2B). CD68 transcripts were absent from resting KG1 cells (myeloblastic leukemia) and CEM (T lymphoblastic leukemia) and prese ...
Bile Formation: a Concerted Action of Membrane
... Transporters in Hepatocytes and Cholangiocytes Akos Zsembery, Theresia Thalhammer, and Jürg Graf A large number of membrane transport mechanisms in hepatocytes and cholangiocytes serves for the secretion of bile acids, various other organic anions, organic cations, lipids, and electrolytes. After th ...
... Transporters in Hepatocytes and Cholangiocytes Akos Zsembery, Theresia Thalhammer, and Jürg Graf A large number of membrane transport mechanisms in hepatocytes and cholangiocytes serves for the secretion of bile acids, various other organic anions, organic cations, lipids, and electrolytes. After th ...
4T, 3T AND 3T1D DRAM CELL DESIGN ON 32 NM
... Manufacturing process introduces variations in devices characteristic parameters, such as threshold voltage and physical dimensions (length and width) of transistors. These variations can be classified depending on their statistics as systematic (inter die and intra-die systematic) or random (intra- ...
... Manufacturing process introduces variations in devices characteristic parameters, such as threshold voltage and physical dimensions (length and width) of transistors. These variations can be classified depending on their statistics as systematic (inter die and intra-die systematic) or random (intra- ...
Lysosomal Function and Dysfunction
... conditions and the role of lysosomal dysfunction in pathological conditions. With the exception of erythrocytes, lysosomes are found in all eukaryotic cell types. However, not all lysosomes are alike and some have acquired specific functions in given cell types, such as melanosomes and lytic granule ...
... conditions and the role of lysosomal dysfunction in pathological conditions. With the exception of erythrocytes, lysosomes are found in all eukaryotic cell types. However, not all lysosomes are alike and some have acquired specific functions in given cell types, such as melanosomes and lytic granule ...
Bacterial toxins modifying the actin cytoskeleton
... which is closely related to ToxB (88% amino acid sequence identity and immunological cross reactions between the two toxins) and a hemorrhagic toxin (HT). C. novyi is an etiological agent of gangrene with major edema. The main toxin produced is the alpha toxin. The large clostridial toxins have a co ...
... which is closely related to ToxB (88% amino acid sequence identity and immunological cross reactions between the two toxins) and a hemorrhagic toxin (HT). C. novyi is an etiological agent of gangrene with major edema. The main toxin produced is the alpha toxin. The large clostridial toxins have a co ...
Sphingolipid homeostasis in the web of metabolic routes
... human diseases generated by the defects in these pathways [3]. 2.3. Regulation of sphingolipid synthesis Although SLs are essential players in cell homeostasis the regulatory mechanisms controlling this pathway have only recently begun to emerge. The initial advances in the network of enzymatic cont ...
... human diseases generated by the defects in these pathways [3]. 2.3. Regulation of sphingolipid synthesis Although SLs are essential players in cell homeostasis the regulatory mechanisms controlling this pathway have only recently begun to emerge. The initial advances in the network of enzymatic cont ...
Influenza virus assembly and budding
... 1960). Indeed, the two most widely used laboratory spherical strains, A/WSN/33 and A/PR/8, have been passaged extensively in eggs. Thus, the loss of filament-forming ability may be an adaptation to growth in eggs and not specifically applicable to human infection, although it should be noted that even ...
... 1960). Indeed, the two most widely used laboratory spherical strains, A/WSN/33 and A/PR/8, have been passaged extensively in eggs. Thus, the loss of filament-forming ability may be an adaptation to growth in eggs and not specifically applicable to human infection, although it should be noted that even ...
Introduction to Biology Pacing Guide
... of the bond types (e.g., ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds) to chemical activity and explain how this is relevant to biological activity. (DOK 2) ...
... of the bond types (e.g., ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds) to chemical activity and explain how this is relevant to biological activity. (DOK 2) ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.