Biofilm formation by staphylococci and streptococci: structural
... et al., 2000; Otto, 2013). Initially the bacteria must adhere to a surface or host tissue (primary attachment phase) before they proliferate to form multicellular aggregates (accumulation phase). During the maturation stage, channels and mushroom-shaped structures are created to allow nutrients to p ...
... et al., 2000; Otto, 2013). Initially the bacteria must adhere to a surface or host tissue (primary attachment phase) before they proliferate to form multicellular aggregates (accumulation phase). During the maturation stage, channels and mushroom-shaped structures are created to allow nutrients to p ...
The lysosome as a command-and-control center for cellular
... and other building blocks that can be subsequently released on demand. Because of the high conservation of lysosomal enzymes and permeases between yeast and mammals, it is likely that the mammalian lysosome has a similar ability for selective retention and release of metabolic building blocks. Throu ...
... and other building blocks that can be subsequently released on demand. Because of the high conservation of lysosomal enzymes and permeases between yeast and mammals, it is likely that the mammalian lysosome has a similar ability for selective retention and release of metabolic building blocks. Throu ...
Intraflagellar transport and the generation of dynamic, structurally
... cilia from most cell types, including liver, pancreas, kidney, olfactory epithelia, oviduct, respiratory tissue, and in rod or cone photoreceptors [24–29]. A bipartite axoneme consisting of microtubule doublets followed by singlets therefore represents an evolutionarily conserved feature of motile a ...
... cilia from most cell types, including liver, pancreas, kidney, olfactory epithelia, oviduct, respiratory tissue, and in rod or cone photoreceptors [24–29]. A bipartite axoneme consisting of microtubule doublets followed by singlets therefore represents an evolutionarily conserved feature of motile a ...
Microfluidic devices for drug discovery and analysis
... be the new approach in identification of drug targets and it has reduced the use of living organisms and living tissues (Terstappen et al., 2007). Drug targets, which may be a cellular receptor, an ion channel, nucleic acids, DNA or RNA, enzymes, polysaccharides and lipids, are chemically well-defin ...
... be the new approach in identification of drug targets and it has reduced the use of living organisms and living tissues (Terstappen et al., 2007). Drug targets, which may be a cellular receptor, an ion channel, nucleic acids, DNA or RNA, enzymes, polysaccharides and lipids, are chemically well-defin ...
Etude in vitro de la stéatose hépatique induite par la - HAL
... the core protein from the ER (Figure 1). This cleaved core protein remains associated with the cytoplasmic monolayer of the ER membrane via a hydrophobic domain located between aa 120 and aa 175 [17, 49]. This enables it to move along this monolayer towards the surface of the lipid droplets [48]. Th ...
... the core protein from the ER (Figure 1). This cleaved core protein remains associated with the cytoplasmic monolayer of the ER membrane via a hydrophobic domain located between aa 120 and aa 175 [17, 49]. This enables it to move along this monolayer towards the surface of the lipid droplets [48]. Th ...
The lysosome as a command-and-control center for cellular
... and other building blocks that can be subsequently released on demand. Because of the high conservation of lysosomal enzymes and permeases between yeast and mammals, it is likely that the mammalian lysosome has a similar ability for selective retention and release of metabolic building blocks. Throu ...
... and other building blocks that can be subsequently released on demand. Because of the high conservation of lysosomal enzymes and permeases between yeast and mammals, it is likely that the mammalian lysosome has a similar ability for selective retention and release of metabolic building blocks. Throu ...
Recent developments in the cell and molecular biology of root hairs
... these vesicles contain pectic polysaccharides and cell wall precursors. For example, Sherrier and VandenBosch (1994) have shown that vesicles in Vicia villosa root hairs contain xyloglucan and methyl-esterified polygalacturonic acid, both cell wall matrix polysaccharides. Vesicles are found mostly i ...
... these vesicles contain pectic polysaccharides and cell wall precursors. For example, Sherrier and VandenBosch (1994) have shown that vesicles in Vicia villosa root hairs contain xyloglucan and methyl-esterified polygalacturonic acid, both cell wall matrix polysaccharides. Vesicles are found mostly i ...
Dynamics of the Cell Cycle: Checkpoints, Sizers, and Timers
... illuminate the workings of the cell cycle, based on various dynamical mechanisms including limit cycle oscillation (Goldbeter, 1991; Hatzimanikatis et al., 1999; Obeyesekere et al., 1997), bistability (Chen et al., 2000; Sveiczer et al., 2000; Thron, 1997; Tyson et al., 2001; Tyson and Novak, 2001), ...
... illuminate the workings of the cell cycle, based on various dynamical mechanisms including limit cycle oscillation (Goldbeter, 1991; Hatzimanikatis et al., 1999; Obeyesekere et al., 1997), bistability (Chen et al., 2000; Sveiczer et al., 2000; Thron, 1997; Tyson et al., 2001; Tyson and Novak, 2001), ...
pdf
... A review of the anatomy and biomechanics of the clivus and the craniocervical junction will help us understand the etiology of retroclival hematoma. The clivus (Figure 1) is a shallow depression behind the dorsum sellae formed by the wedge-shaped body of the sphenoid bone (basisphenoid) and the basi ...
... A review of the anatomy and biomechanics of the clivus and the craniocervical junction will help us understand the etiology of retroclival hematoma. The clivus (Figure 1) is a shallow depression behind the dorsum sellae formed by the wedge-shaped body of the sphenoid bone (basisphenoid) and the basi ...
Endoplasmic reticulum potassium–hydrogen exchanger and small
... effect in GT1-7 neurons (supplementary material Fig. S3A,B). Similarly, activators of SKCa channels, DC-EBIO (50 mM) and NS309 (50 mM), had no strong effect on Ca2+ uptake (supplementary material Fig. S3C,D). These data suggest that SKCa but not KATP channels control the K+ fluxes required for effic ...
... effect in GT1-7 neurons (supplementary material Fig. S3A,B). Similarly, activators of SKCa channels, DC-EBIO (50 mM) and NS309 (50 mM), had no strong effect on Ca2+ uptake (supplementary material Fig. S3C,D). These data suggest that SKCa but not KATP channels control the K+ fluxes required for effic ...
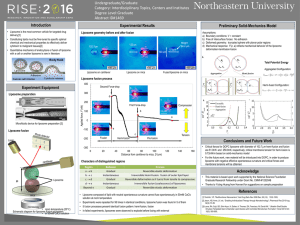
Undergraduate/Graduate Category: Interdisciplinary Topics, Centers and Institutes Degree Level:Graduate
... • Liposome composed of lipid with neutral spontaneous curvature cannot fuse spontaneously in 50mM CaCl 2 solution at room temperature • Experiments were repeated for 56 times in identical conditions, liposome fusion was found in 5 of them ...
... • Liposome composed of lipid with neutral spontaneous curvature cannot fuse spontaneously in 50mM CaCl 2 solution at room temperature • Experiments were repeated for 56 times in identical conditions, liposome fusion was found in 5 of them ...
FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein associates
... valuable reagent in segregating the p70S6K regulatory signals (5). NTCT-p70S6K is sensitive to kinase-directed signals initiated by mitogens and growth factors, but it is insensitive to signals that pass through the FRAP-regulated phosphatase. NTCT-p70S6K is unable to interact with this phosphatase. ...
... valuable reagent in segregating the p70S6K regulatory signals (5). NTCT-p70S6K is sensitive to kinase-directed signals initiated by mitogens and growth factors, but it is insensitive to signals that pass through the FRAP-regulated phosphatase. NTCT-p70S6K is unable to interact with this phosphatase. ...
Physical and Chemical Basis of Cytoplasmic Streaming
... movementsof the slime mold was made by Kobatake and his associates (47, 153-155). Threshold concentrations for the recognition of attractants (glucose, galactose, phosphates, pyrophosphates, ATP, cAMP)and of repel- ...
... movementsof the slime mold was made by Kobatake and his associates (47, 153-155). Threshold concentrations for the recognition of attractants (glucose, galactose, phosphates, pyrophosphates, ATP, cAMP)and of repel- ...
Relationship of Net Chloride Flow across the Human Erythrocyte
... Blood was obtained from apparently healthy adults with heparin as an anticoagulant. The cells were washed three times in 160 mM NaCl and 5 mM HEPES at room temperature and the white cells were removed by aspiration . ...
... Blood was obtained from apparently healthy adults with heparin as an anticoagulant. The cells were washed three times in 160 mM NaCl and 5 mM HEPES at room temperature and the white cells were removed by aspiration . ...
In the prevailing view Conducitn is usually considered to act as a
... conductin depends on the respective DIX-DIX domain interactions. A bioinformatical analysis predicted ten amino acids likely to be required for specificity of DIX domain interactions (Ehebauer and Arias, 2009). Four of these amino acids differ between axin and conductin and may mediate differential ...
... conductin depends on the respective DIX-DIX domain interactions. A bioinformatical analysis predicted ten amino acids likely to be required for specificity of DIX domain interactions (Ehebauer and Arias, 2009). Four of these amino acids differ between axin and conductin and may mediate differential ...
distribution of microtubules in the golgi apparatus of euglena gracilis
... (1 %) for 2 h. The cells were then rinsed in several changes of distilled water and post-stained in 05 % uranyl acetate for about 18 h. All steps were carried out in the cold (about 1—2 °C), except for the first 15 min of the aldehyde fixation, which was at room temperature. The cells were dehydrate ...
... (1 %) for 2 h. The cells were then rinsed in several changes of distilled water and post-stained in 05 % uranyl acetate for about 18 h. All steps were carried out in the cold (about 1—2 °C), except for the first 15 min of the aldehyde fixation, which was at room temperature. The cells were dehydrate ...
- Wiley Online Library
... mitochondria, part of the regulation involves the Miro and Milton proteins (8,9). Mitochondrial positioning in processes is crucial, as they may locally buffer calcium transients (10), and also produce ATP needed for multiple cellular activities, including formation of de novo synapses during develo ...
... mitochondria, part of the regulation involves the Miro and Milton proteins (8,9). Mitochondrial positioning in processes is crucial, as they may locally buffer calcium transients (10), and also produce ATP needed for multiple cellular activities, including formation of de novo synapses during develo ...
(2009). Age determination and growth in the male South African fur
... study of ion transport and bioenergetics of vacuoles of Kalanchoedaigremontiana. Gave a series of lectures to post-graduate students on ion transport in 1989 and 1990. 1991 to 1992. Research Associate for Dr Rosalind Hinde (The University of Sydney, NSW) working on glycerol transport by the symbioti ...
... study of ion transport and bioenergetics of vacuoles of Kalanchoedaigremontiana. Gave a series of lectures to post-graduate students on ion transport in 1989 and 1990. 1991 to 1992. Research Associate for Dr Rosalind Hinde (The University of Sydney, NSW) working on glycerol transport by the symbioti ...
Dispersal of Golgi matrix proteins during mitotic Golgi
... 15 for interphase and 40 for metaphase cells, were taken at a step size of 0.3 µm. Images were deconvolved using SoftWorx (Applied Precision). Deconvolved manually cropped sections were assembled into a 3D image using Matlab (Mathworks, Natick, MA, USA). The background value subtracted from each vox ...
... 15 for interphase and 40 for metaphase cells, were taken at a step size of 0.3 µm. Images were deconvolved using SoftWorx (Applied Precision). Deconvolved manually cropped sections were assembled into a 3D image using Matlab (Mathworks, Natick, MA, USA). The background value subtracted from each vox ...
Golgi-targeting sequence of p230 - Journal of Cell Science
... of GFP-p230-C98aa fusion protein, endogenous p230 was no longer associated with Golgi membranes, suggesting that the GFP fusion protein and endogenous p230 may compete for the same membrane target structures. The Golgi binding of GFP-p230-C98aa is brefeldin A-sensitive and is regulated by G proteins ...
... of GFP-p230-C98aa fusion protein, endogenous p230 was no longer associated with Golgi membranes, suggesting that the GFP fusion protein and endogenous p230 may compete for the same membrane target structures. The Golgi binding of GFP-p230-C98aa is brefeldin A-sensitive and is regulated by G proteins ...
Divalent Cation-Dependent Formation of
... is no clustering. Thus we obtain the boundaries of the parameter region that lead to domain formation (shaded in the phase diagram). Fig. 1 a shows AFM images of the transferred samples. These images show a clear distinction between conditions that lead to domain formation (panels a 2 and a 3) and c ...
... is no clustering. Thus we obtain the boundaries of the parameter region that lead to domain formation (shaded in the phase diagram). Fig. 1 a shows AFM images of the transferred samples. These images show a clear distinction between conditions that lead to domain formation (panels a 2 and a 3) and c ...
Multiple Roles of the Cytoskeleton in Bacterial Autophagy
... In humans there are six ATG8 orthologues belonging to the light chain 3 (LC3) or c-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein (GABARAP) subfamilies, and by interacting with an extensive repertoire of proteins, they have important roles in mediating membrane-remodelling processes. Autophagy can be ...
... In humans there are six ATG8 orthologues belonging to the light chain 3 (LC3) or c-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein (GABARAP) subfamilies, and by interacting with an extensive repertoire of proteins, they have important roles in mediating membrane-remodelling processes. Autophagy can be ...
Subcellular trafficking kinetics of GLUT4 mutated at the N
... intracellular retention. These results are also considered in terms of a consecutive intracellular pool model in which GLUT4 targeting domains alter the distribution between recycling endosomes and a slowly recycling compartment. In this case the more rapid apparent exocytosis of the mutated GLUT4s ...
... intracellular retention. These results are also considered in terms of a consecutive intracellular pool model in which GLUT4 targeting domains alter the distribution between recycling endosomes and a slowly recycling compartment. In this case the more rapid apparent exocytosis of the mutated GLUT4s ...
original version
... phospholipids appears to change as cells pass from exponential growth into stationary phase [51,52] and recent work shows that depletion of cellular acidic phospholipids leads to under initiation of replication from oriC during the cell-cycle [39]. Acidic phospholipids, particularly CL, are present ...
... phospholipids appears to change as cells pass from exponential growth into stationary phase [51,52] and recent work shows that depletion of cellular acidic phospholipids leads to under initiation of replication from oriC during the cell-cycle [39]. Acidic phospholipids, particularly CL, are present ...
Full-Text PDF
... phospholipids appears to change as cells pass from exponential growth into stationary phase [51,52] and recent work shows that depletion of cellular acidic phospholipids leads to under initiation of replication from oriC during the cell-cycle [39]. Acidic phospholipids, particularly CL, are present ...
... phospholipids appears to change as cells pass from exponential growth into stationary phase [51,52] and recent work shows that depletion of cellular acidic phospholipids leads to under initiation of replication from oriC during the cell-cycle [39]. Acidic phospholipids, particularly CL, are present ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.