Exocytosis Precedes and Predicts the Increase in
... 50 s (Pierson et al., 1996; Cárdenas et al., 2008). Additionally, many of the underlying processes also oscillate with the same period, but usually with a different phase than the growth rate (Holdaway-Clarke and Hepler, 2003; Chebli and Geitmann, 2007; Moreno et al., 2007). Thus, growth emerges as ...
... 50 s (Pierson et al., 1996; Cárdenas et al., 2008). Additionally, many of the underlying processes also oscillate with the same period, but usually with a different phase than the growth rate (Holdaway-Clarke and Hepler, 2003; Chebli and Geitmann, 2007; Moreno et al., 2007). Thus, growth emerges as ...
Exocytosis Precedes and Predicts the Increase in Growth in
... 50 s (Pierson et al., 1996; Cárdenas et al., 2008). Additionally, many of the underlying processes also oscillate with the same period, but usually with a different phase than the growth rate (Holdaway-Clarke and Hepler, 2003; Chebli and Geitmann, 2007; Moreno et al., 2007). Thus, growth emerges as ...
... 50 s (Pierson et al., 1996; Cárdenas et al., 2008). Additionally, many of the underlying processes also oscillate with the same period, but usually with a different phase than the growth rate (Holdaway-Clarke and Hepler, 2003; Chebli and Geitmann, 2007; Moreno et al., 2007). Thus, growth emerges as ...
Regulation of Chlamydomonas flagella and ependymal cell motile
... most of the algae were still motile and swimSEM, n = 3, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). ming toward light. By 15 h, only the algae not exposed to myriocin were fully motile RESULTS (Figure 3A). This was confirmed both by cell counting with a hemoChlamydomonas expresses se ...
... most of the algae were still motile and swimSEM, n = 3, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). ming toward light. By 15 h, only the algae not exposed to myriocin were fully motile RESULTS (Figure 3A). This was confirmed both by cell counting with a hemoChlamydomonas expresses se ...
Plasma membrane HATPase regulation is required for auxin
... (Supplementary Fig S2). Finally, concomitant apoplast acidification and basification on opposing sides enhanced the gradients observed in the acidification-only scenario (Fig 2A). Topological parameters strongly modulate gradient formation Cellular topology has the potential to contribute to the for ...
... (Supplementary Fig S2). Finally, concomitant apoplast acidification and basification on opposing sides enhanced the gradients observed in the acidification-only scenario (Fig 2A). Topological parameters strongly modulate gradient formation Cellular topology has the potential to contribute to the for ...
Sensory TRP Channel Interactions with Endogenous Lipids and
... intercellular transmitters are recently being raised; (c) Lipid modulators would alter the plasma membrane structure, leading to changes in TRP channel gating. ...
... intercellular transmitters are recently being raised; (c) Lipid modulators would alter the plasma membrane structure, leading to changes in TRP channel gating. ...
M6PRs are found in a subset of PC12 cell ISGs
... Fig. 1. Subcellular fractionation reveals that both the CI- and the CDM6PR are found in fractions which contain ISGs but not MSGs. (A) Fractions from a velocity sucrose gradient of a post-nuclear supernatant obtained from PC12 cells were immunoblotted with antibodies to the CI- and CD-M6PRs. The loc ...
... Fig. 1. Subcellular fractionation reveals that both the CI- and the CDM6PR are found in fractions which contain ISGs but not MSGs. (A) Fractions from a velocity sucrose gradient of a post-nuclear supernatant obtained from PC12 cells were immunoblotted with antibodies to the CI- and CD-M6PRs. The loc ...
Mitochondrial Dynamics
... localizes to the inner surface of the cell membrane at division sites, where it forms a ring structure (Z ring) that enables constriction and scission of the parent into two daughter cells. FtsZ is a GTPase, which can hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate to provide a source of energy. However, it is tho ...
... localizes to the inner surface of the cell membrane at division sites, where it forms a ring structure (Z ring) that enables constriction and scission of the parent into two daughter cells. FtsZ is a GTPase, which can hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate to provide a source of energy. However, it is tho ...
Cell adhesion and cell mechanics during zebrafish
... and share related duties. Strikingly, as soon as differentiation starts, the constituting cells change their properties and as a result eventually separate from each other, ending up in different compartments to perform specific functions. Such positional changes normally take place by cell migratio ...
... and share related duties. Strikingly, as soon as differentiation starts, the constituting cells change their properties and as a result eventually separate from each other, ending up in different compartments to perform specific functions. Such positional changes normally take place by cell migratio ...
Cell behaviour and cleft palate in the mutant mouse
... 12-5 days, when they appear as a pair of parallel ridges growing down from either side of the roof of the buccal cavity (Fig. 1 a). That these are ridges can be seen at their posterior end where the knife has cut a glancing transverse section through the tissue. By the 14th day of development (14-5 ...
... 12-5 days, when they appear as a pair of parallel ridges growing down from either side of the roof of the buccal cavity (Fig. 1 a). That these are ridges can be seen at their posterior end where the knife has cut a glancing transverse section through the tissue. By the 14th day of development (14-5 ...
Vancomycin
... Vancomycin is effective against gram-positive organisms. It has been lifesaving in the treatment of MRSA and methicillin-resistant Staphylo coccus epidermidis (MRSE) infections as well as enterococcal infections. With the emergence of resistant strains, it is important to curtail the increase in van ...
... Vancomycin is effective against gram-positive organisms. It has been lifesaving in the treatment of MRSA and methicillin-resistant Staphylo coccus epidermidis (MRSE) infections as well as enterococcal infections. With the emergence of resistant strains, it is important to curtail the increase in van ...
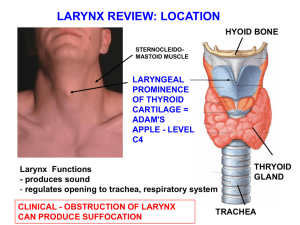
Larynx_mini_review_2012f
... 1) Superior Laryngeal N. a) Internal Laryngeal N. Visceral Sensory (GVA) to Larynx Above (true vocal folds) b) External Laryngeal N. Branchial motor (SVE) to Cricothyroid 2) Recurrent Laryngeal n. - Visceral Sensory (GVA) to Larynx Below True Vocal Folds - Branchial motor (SVE) to all other Muscles ...
... 1) Superior Laryngeal N. a) Internal Laryngeal N. Visceral Sensory (GVA) to Larynx Above (true vocal folds) b) External Laryngeal N. Branchial motor (SVE) to Cricothyroid 2) Recurrent Laryngeal n. - Visceral Sensory (GVA) to Larynx Below True Vocal Folds - Branchial motor (SVE) to all other Muscles ...
Facing extremes: archaeal surface-layer (glyco)proteins
... in which these micro-organisms exist, manages to maintain its structural integrity. In most cases, a surface (S)-layer, generally formed from identical protein subunits arranged into a monolayer of simple and repetitive patterns, serves as the envelope of the archaeal cell. Research into the biogene ...
... in which these micro-organisms exist, manages to maintain its structural integrity. In most cases, a surface (S)-layer, generally formed from identical protein subunits arranged into a monolayer of simple and repetitive patterns, serves as the envelope of the archaeal cell. Research into the biogene ...
CASK (LIN2) interacts with Cx43 in wounded skin and their
... transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blocked and then incubated with a 32P-labeled GST–Cx43CT (amino acids 236–382) probe. After washing, a band corresponding to CASK (approximately 120 kDa) but no LIN7 band was observed (Fig. 1A), suggesting that the direct interaction between ...
... transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blocked and then incubated with a 32P-labeled GST–Cx43CT (amino acids 236–382) probe. After washing, a band corresponding to CASK (approximately 120 kDa) but no LIN7 band was observed (Fig. 1A), suggesting that the direct interaction between ...
PowerPoint
... MANY STRUCTURES ARE FROM BRANCHIAL ARCHES 1. BRANCHIAL ARCHESStructures which develop in foregut (pharynx) and are similar to gills of fish - Gill = Branchial - Gills of fish are composed of cartilage and have muscles, nerves, ...
... MANY STRUCTURES ARE FROM BRANCHIAL ARCHES 1. BRANCHIAL ARCHESStructures which develop in foregut (pharynx) and are similar to gills of fish - Gill = Branchial - Gills of fish are composed of cartilage and have muscles, nerves, ...
Facing extremes: archaeal surface-layer (glyco)proteins
... in which these micro-organisms exist, manages to maintain its structural integrity. In most cases, a surface (S)-layer, generally formed from identical protein subunits arranged into a monolayer of simple and repetitive patterns, serves as the envelope of the archaeal cell. Research into the biogene ...
... in which these micro-organisms exist, manages to maintain its structural integrity. In most cases, a surface (S)-layer, generally formed from identical protein subunits arranged into a monolayer of simple and repetitive patterns, serves as the envelope of the archaeal cell. Research into the biogene ...
View Full Text-PDF
... vegetal extracts tested present potential antimicrobial activity with efficient properties in the inhibition of Salmonella, especially vegetal extracts from the Myrtaceae family. ...
... vegetal extracts tested present potential antimicrobial activity with efficient properties in the inhibition of Salmonella, especially vegetal extracts from the Myrtaceae family. ...
Cleavage furrow formation and ingression during animal cytokinesis
... Cytokinesis is the final act of cell division. In a typical animal mitosis, a cleavage furrow forms at the equatorial cortex after anaphase. This furrow then advances inwards to separate the two daughter cells. Since the early studies of Rappaport more than forty years ago (Rappaport, 1961), it has ...
... Cytokinesis is the final act of cell division. In a typical animal mitosis, a cleavage furrow forms at the equatorial cortex after anaphase. This furrow then advances inwards to separate the two daughter cells. Since the early studies of Rappaport more than forty years ago (Rappaport, 1961), it has ...
Identification and localization of the multiple bacterial
... metabolism, to anabolic processes, such as nitrogen fixation (Brune & Stingl, 2005; Ohkuma, 2008). Another function, shown in some cases, is the involvement of ectosymbiotic bacteria in motility, with the flagella of the symbionts propelling their eukaryotic host (Cleveland & Grimstone, 1964; Tamm, ...
... metabolism, to anabolic processes, such as nitrogen fixation (Brune & Stingl, 2005; Ohkuma, 2008). Another function, shown in some cases, is the involvement of ectosymbiotic bacteria in motility, with the flagella of the symbionts propelling their eukaryotic host (Cleveland & Grimstone, 1964; Tamm, ...
Nanoscale Architecture of Endoplasmic Reticulum Export Sites and
... preserve these membrane systems in their natural state for electron microscope (EM) analysis requires fixation methods that can stabilize cellular structures in a fraction of a second and processing techniques that can preserve the stabilized structures until they have been immobilized in polymerize ...
... preserve these membrane systems in their natural state for electron microscope (EM) analysis requires fixation methods that can stabilize cellular structures in a fraction of a second and processing techniques that can preserve the stabilized structures until they have been immobilized in polymerize ...
Identification of A Novel, N-ethylmaleimide
... purified and characterized an N-ethylmaleimide (NEM)sensitive protein, termed NSF (NEM-sensitive fusion protein), that is required for intra-Golgi transport in vitro (Glick and Rothman, 1987; Block et al., 1988). NSF is also required for ER--'Golgi transport (Beckers and Balch, 1989), as well as end ...
... purified and characterized an N-ethylmaleimide (NEM)sensitive protein, termed NSF (NEM-sensitive fusion protein), that is required for intra-Golgi transport in vitro (Glick and Rothman, 1987; Block et al., 1988). NSF is also required for ER--'Golgi transport (Beckers and Balch, 1989), as well as end ...
Comparison of Methods for Estimating Unbound Intracellular
... with the unbound fraction in liver homogenates (fT,homogenate) measured by equilibrium dialysis using human liver samples. The Kp,uu,ss obtained were then compared with Kp,uu,V0 in both rat and human hepatocytes. The difference between Kp,uu,ss or Kp,uu,V0 and true Kp,uu (Kp,uu,true) is discussed in ...
... with the unbound fraction in liver homogenates (fT,homogenate) measured by equilibrium dialysis using human liver samples. The Kp,uu,ss obtained were then compared with Kp,uu,V0 in both rat and human hepatocytes. The difference between Kp,uu,ss or Kp,uu,V0 and true Kp,uu (Kp,uu,true) is discussed in ...
atlas of dengue viruses morphology and morphogenesis
... Electron microscopy has been used as a very efficient tool to study virus particle morphology (Ackermann & Berthiaume, 1995; Doane & Anderson, 1987; Madeley & Field, 1988), as the unique technique for direct visualization of morphological structures. Virus infected tissues can also be analyzed by th ...
... Electron microscopy has been used as a very efficient tool to study virus particle morphology (Ackermann & Berthiaume, 1995; Doane & Anderson, 1987; Madeley & Field, 1988), as the unique technique for direct visualization of morphological structures. Virus infected tissues can also be analyzed by th ...
LIU-THESIS - eCommons@USASK
... stress. As the temperature is lowered, the more serious cell dehydration becomes (Pearce and Ashworth, 1992). However, dehydration resulting from extracellular freezing can help cells to avoid intracellular freezing and increase survival at very low, even liquid-nitrogen temperatures (Sakai and Larc ...
... stress. As the temperature is lowered, the more serious cell dehydration becomes (Pearce and Ashworth, 1992). However, dehydration resulting from extracellular freezing can help cells to avoid intracellular freezing and increase survival at very low, even liquid-nitrogen temperatures (Sakai and Larc ...
Biofilm formation by staphylococci and streptococci
... et al., 2000; Otto, 2013). Initially the bacteria must adhere to a surface or host tissue (primary attachment phase) before they proliferate to form multicellular aggregates (accumulation phase). During the maturation stage, channels and mushroom-shaped structures are created to allow nutrients to p ...
... et al., 2000; Otto, 2013). Initially the bacteria must adhere to a surface or host tissue (primary attachment phase) before they proliferate to form multicellular aggregates (accumulation phase). During the maturation stage, channels and mushroom-shaped structures are created to allow nutrients to p ...
Biofilm formation by staphylococci and streptococci: structural
... et al., 2000; Otto, 2013). Initially the bacteria must adhere to a surface or host tissue (primary attachment phase) before they proliferate to form multicellular aggregates (accumulation phase). During the maturation stage, channels and mushroom-shaped structures are created to allow nutrients to p ...
... et al., 2000; Otto, 2013). Initially the bacteria must adhere to a surface or host tissue (primary attachment phase) before they proliferate to form multicellular aggregates (accumulation phase). During the maturation stage, channels and mushroom-shaped structures are created to allow nutrients to p ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.