Genetics Glossary
... Panel: Also known as “next generation sequencing,” a panel is a cost and time-effective method of analyzing multiple genes at the same time. Polyp: Abnormal growths of tissue that can be found in any organ and can be either benign or precancerous Positive: One of three possible results one can recei ...
... Panel: Also known as “next generation sequencing,” a panel is a cost and time-effective method of analyzing multiple genes at the same time. Polyp: Abnormal growths of tissue that can be found in any organ and can be either benign or precancerous Positive: One of three possible results one can recei ...
Model organisms and mutants
... • Mus Musculus • Specific fragments of DNA can be inserted into the genome of mice – E.g. the jellyfish gene for green fluorescent protein ...
... • Mus Musculus • Specific fragments of DNA can be inserted into the genome of mice – E.g. the jellyfish gene for green fluorescent protein ...
Definitions
... characteristics that allow them to be well adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce and pass on their genes to the next generation The study of fossils Inherited factors are controlled by pairs of factors. These factors separate from each other at gamete formation with only one member ...
... characteristics that allow them to be well adapted to their environment will survive and reproduce and pass on their genes to the next generation The study of fossils Inherited factors are controlled by pairs of factors. These factors separate from each other at gamete formation with only one member ...
DNA
... glands in the skin, digestive enzyme secreting cells of the pancreas, etc. The CFTR protein is actually a glycoprotein, that is, it is a protein that has been modified to by the addition of several monosaccharides. a. Trace the pathway of the normal CFTR protein from the organelle where CFTR is made ...
... glands in the skin, digestive enzyme secreting cells of the pancreas, etc. The CFTR protein is actually a glycoprotein, that is, it is a protein that has been modified to by the addition of several monosaccharides. a. Trace the pathway of the normal CFTR protein from the organelle where CFTR is made ...
Science Hand Out 6 - Literacy Action Network
... Most of the cells in a human contain two copies of each of 22 different chromosomes. In addition, there is a pair of chromosomes that determine sex. Changes in DNA (mutations) occur spontaneously at low rates. Where on the DNA chain are instructions for specifying characteristics located? What is th ...
... Most of the cells in a human contain two copies of each of 22 different chromosomes. In addition, there is a pair of chromosomes that determine sex. Changes in DNA (mutations) occur spontaneously at low rates. Where on the DNA chain are instructions for specifying characteristics located? What is th ...
protein synthesis
... contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the nitrogenous base uracil for thymine. • An RNA molecules almost always consists of a single ...
... contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the nitrogenous base uracil for thymine. • An RNA molecules almost always consists of a single ...
CH 3 RG 2014 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... 9. Do you remember we said, “To change the structure will change the function”? Explain how this principle applies to sickle–cell disease. Why is the structure changed? ...
... 9. Do you remember we said, “To change the structure will change the function”? Explain how this principle applies to sickle–cell disease. Why is the structure changed? ...
15-Work-Experience - College Admissions Strategies
... summer I seized an opportunity to further my interests in molecular biology through a program concentrating on the genetic mutations that cause Pompe’s Disease, an autosomal recessive disorder resulting in rapid muscle degeneration. At Bellevue Hospital’s Muscle Rehabilitation Unit, I assisted a res ...
... summer I seized an opportunity to further my interests in molecular biology through a program concentrating on the genetic mutations that cause Pompe’s Disease, an autosomal recessive disorder resulting in rapid muscle degeneration. At Bellevue Hospital’s Muscle Rehabilitation Unit, I assisted a res ...
Discovery of DNA
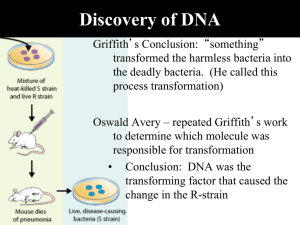
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
Molecular diagnostics in congenital adrenal hyperplasia
... complement direct mutation analysis studies. These and our other in-house flanking and physically mapped STR markers provide >99% accuracy in linkage analysis situations. Please consult with Celtek when linkage studies are being considered. We are often asked about genotype/phenotype correlations. T ...
... complement direct mutation analysis studies. These and our other in-house flanking and physically mapped STR markers provide >99% accuracy in linkage analysis situations. Please consult with Celtek when linkage studies are being considered. We are often asked about genotype/phenotype correlations. T ...
Presentation
... Biology of Cancer Oncogene- cancer-causing genes Proto-oncogene- normal cellular genes How does a proto-oncogene become an oncogene? movement of DNA; chromosome fragments that have rejoined incorrectly amplification; increases the number of copies of proto-oncogenes point mutation; prot ...
... Biology of Cancer Oncogene- cancer-causing genes Proto-oncogene- normal cellular genes How does a proto-oncogene become an oncogene? movement of DNA; chromosome fragments that have rejoined incorrectly amplification; increases the number of copies of proto-oncogenes point mutation; prot ...
EOC Study Guide (2) - Duplin County Schools
... ______ 60. Mutations can be random and spontaneous. ______ 61. Radiation can cause mutations. ______ 62. Mutations are always bad. ______ 63. Chemical exposure can cause mutations. ______ 64. Mutations are caused by a change in the amino acid sequence. 65. Sickle Cell anemia is linked to what diseas ...
... ______ 60. Mutations can be random and spontaneous. ______ 61. Radiation can cause mutations. ______ 62. Mutations are always bad. ______ 63. Chemical exposure can cause mutations. ______ 64. Mutations are caused by a change in the amino acid sequence. 65. Sickle Cell anemia is linked to what diseas ...
Modelling_evolution - the Department of Statistics
... First, it is assumed that the matrix Q is reversible – This means that watching the process forwards in time is equivalent to watching it back in time – Consequently, summing over ancestral states is equivalent to treating one of the two sequences as ancestral ...
... First, it is assumed that the matrix Q is reversible – This means that watching the process forwards in time is equivalent to watching it back in time – Consequently, summing over ancestral states is equivalent to treating one of the two sequences as ancestral ...
Mutations in Paternity
... Unlike the RFLP case, the formula will depend on the actual alleles and possible patterns of sharing. Instead of trying to give a general treatise, I'll just illustrate with one typical example. Suppose the mother is PP, the child is PQ, and the man is Q'R, where Q' is s=l or 2 steps smaller (or lar ...
... Unlike the RFLP case, the formula will depend on the actual alleles and possible patterns of sharing. Instead of trying to give a general treatise, I'll just illustrate with one typical example. Suppose the mother is PP, the child is PQ, and the man is Q'R, where Q' is s=l or 2 steps smaller (or lar ...
Slide 1
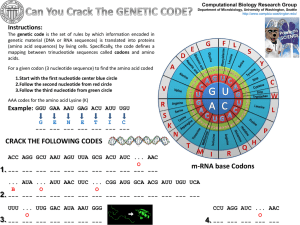
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
BIOLOGY - San Marcos Unified School District
... • PACKAGES PROTEINS (inside vesicles) so they can be shipped out of the cell! ER Golgi Vesicles to Cell Membrane ...
... • PACKAGES PROTEINS (inside vesicles) so they can be shipped out of the cell! ER Golgi Vesicles to Cell Membrane ...
Updated BioI_Unit3_Voc
... 1 uncontrolled growth of cells that can invade other parts of the body 2 any substance that can induce or promote cancer 3 type of tumor that grow in the skin & tissues lining the organs of the body 4 development of cells into such that have specialized functions 5 sequences of DNA, although distant ...
... 1 uncontrolled growth of cells that can invade other parts of the body 2 any substance that can induce or promote cancer 3 type of tumor that grow in the skin & tissues lining the organs of the body 4 development of cells into such that have specialized functions 5 sequences of DNA, although distant ...
EMS-treated culture
... • Untreated culture Do a serial dilution of the untreated wildtype E. coli culture: Fill 7 tubes with 4.5 ml of sterile saline. Transfer 0.5 ml of the undiluted culture to one of the tubes. This is a 10-1 dilution. Next make serial dilutions of 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6 and 10-7. Always change pi ...
... • Untreated culture Do a serial dilution of the untreated wildtype E. coli culture: Fill 7 tubes with 4.5 ml of sterile saline. Transfer 0.5 ml of the undiluted culture to one of the tubes. This is a 10-1 dilution. Next make serial dilutions of 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6 and 10-7. Always change pi ...
Epigenetics ppt
... The study of the mechanisms by which genes bring about their phenotypic effects ...
... The study of the mechanisms by which genes bring about their phenotypic effects ...
Heredity in One Page - Lakewood City Schools
... Some proteins are structural like muscle and skin; others are chemical like enzymes and hormones. To make a protein (protein synthesis), a gene makes a copy of its DNA code. The copy is called messenger RNA, (m-RNA). Other RNA called transfer RNA (t-RNA) brings amino acids to the m-RNA. The amino ac ...
... Some proteins are structural like muscle and skin; others are chemical like enzymes and hormones. To make a protein (protein synthesis), a gene makes a copy of its DNA code. The copy is called messenger RNA, (m-RNA). Other RNA called transfer RNA (t-RNA) brings amino acids to the m-RNA. The amino ac ...
Chapter 4 - HCC Learning Web
... corresponding protein. Since protein structure is controlled by genes… ...
... corresponding protein. Since protein structure is controlled by genes… ...
Biology Concepts at a Glance
... Recognize phases from diagrams Step 1 Transcription – DNA to RNA – “make copy of recipe in the library” o Helicase splits DNA down the middle o RNA polymerase adds bases to both sides to form mRNA o mRNA leaves nucleus to go to cytoplasm, DNA closes back up unchanged Step 2 Translation – RNA to prot ...
... Recognize phases from diagrams Step 1 Transcription – DNA to RNA – “make copy of recipe in the library” o Helicase splits DNA down the middle o RNA polymerase adds bases to both sides to form mRNA o mRNA leaves nucleus to go to cytoplasm, DNA closes back up unchanged Step 2 Translation – RNA to prot ...
Genotyping and Copy Number Variation
... Each person has enough DNA to go to the sun and back 500 times ...
... Each person has enough DNA to go to the sun and back 500 times ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.