γ-Secretase Gene Mutations in Familial Acne Inversa BREVIA
... family 3), a guanine-to-adenine transition at the invariant +1 position of the donor site of intron 13 (c.1551+1G>A, family 5), and a cytosine-tothymine transition (c.349C>T, family 6) (Fig. 1 and fig. S3). The single-base deletion in PSEN1 would result in a frameshift and premature termination codo ...
... family 3), a guanine-to-adenine transition at the invariant +1 position of the donor site of intron 13 (c.1551+1G>A, family 5), and a cytosine-tothymine transition (c.349C>T, family 6) (Fig. 1 and fig. S3). The single-base deletion in PSEN1 would result in a frameshift and premature termination codo ...
RNA
... The genetic code is read in three-letter groupings called codons. (a group of three nucleotide bases in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid) ...
... The genetic code is read in three-letter groupings called codons. (a group of three nucleotide bases in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid) ...
Ch5-Genetics - Medical School Pathology
... • Because of a DELETION, this cannot be detected by standard karyotyping and needs FISH • Cardiac defects, DiGeorge syndrome, velocardiofacial, CATCH* ...
... • Because of a DELETION, this cannot be detected by standard karyotyping and needs FISH • Cardiac defects, DiGeorge syndrome, velocardiofacial, CATCH* ...
Lecture 7
... Although insects have shorter generation times that mammals and many more numbers of replication, number of mutations appear to be independent of the number of generations but dependent upon time ...
... Although insects have shorter generation times that mammals and many more numbers of replication, number of mutations appear to be independent of the number of generations but dependent upon time ...
Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
... 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung. 3. The virus uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and the cell returns to normal. ...
... 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung. 3. The virus uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and the cell returns to normal. ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS SYNTHESIS
... 44. What is the reason for so many different proteins existing, when there are only 20 amino acids? -Each protein is made from a different combination and number of amino acids. ...
... 44. What is the reason for so many different proteins existing, when there are only 20 amino acids? -Each protein is made from a different combination and number of amino acids. ...
Popular scientific report
... for example, wind or insects. The insect pollination was an evolutionary success, because less pollen is produced by the plant and the fertilization rate is higher than for wind pollination. In nature, the phenomenon of adaptive radiation is quite common. The adaptive radiation means that where spec ...
... for example, wind or insects. The insect pollination was an evolutionary success, because less pollen is produced by the plant and the fertilization rate is higher than for wind pollination. In nature, the phenomenon of adaptive radiation is quite common. The adaptive radiation means that where spec ...
Question 1: Mr. Kohn is tired of having to turn on the lights at night
... Question 1: Mr. Kohn is tired of having to turn on the lights at night when he wants a glass of milk. Mr. Kohn knows of jelly fish that produce proteins that glow in the dark. Explain how Mr. Kohn could create genetically engineered cows that could produce these glowing proteins in their milk. Part ...
... Question 1: Mr. Kohn is tired of having to turn on the lights at night when he wants a glass of milk. Mr. Kohn knows of jelly fish that produce proteins that glow in the dark. Explain how Mr. Kohn could create genetically engineered cows that could produce these glowing proteins in their milk. Part ...
Pre/Post Test
... B. Bacterial cells contain the same organelles as human cells. C. The basic components of DNA are the same in humans and bacteria. D. Bacterial cells and human cells contain the same kind of chromosomes ...
... B. Bacterial cells contain the same organelles as human cells. C. The basic components of DNA are the same in humans and bacteria. D. Bacterial cells and human cells contain the same kind of chromosomes ...
Penelitian biologi molekular
... • Only RT-PCR can reliably detect aberrant splicing – Sometimes hard to predict from a DNA sequence change – May be caused by activation of a cryptic splice site deep within an intron ...
... • Only RT-PCR can reliably detect aberrant splicing – Sometimes hard to predict from a DNA sequence change – May be caused by activation of a cryptic splice site deep within an intron ...
Data visualization in the post
... – expanding protein diversity – generating proteins with subtle or opposing functional roles – enabling an organism to respond to environmental pressures ...
... – expanding protein diversity – generating proteins with subtle or opposing functional roles – enabling an organism to respond to environmental pressures ...
Chapter 14 Outline
... Determine this by complementation test. Cross mutants together so resulting organism has one copy of each mutant allele. If the phenotype is wild type, the mutations are in different genes (they complement each other). If the phenotype is mutant, the mutations are in the same gene and form part of t ...
... Determine this by complementation test. Cross mutants together so resulting organism has one copy of each mutant allele. If the phenotype is wild type, the mutations are in different genes (they complement each other). If the phenotype is mutant, the mutations are in the same gene and form part of t ...
Final Exam Review (Spring 09)
... 3. Tell how DNA codes for protein (DNA mRNA construction of a protein). 4. Describe the history of how DNA was discovered and studied, including the names of the scientists and what year its structure was identified. 5. Construct a chain of DNA (12 bases), and then translate the message into a ...
... 3. Tell how DNA codes for protein (DNA mRNA construction of a protein). 4. Describe the history of how DNA was discovered and studied, including the names of the scientists and what year its structure was identified. 5. Construct a chain of DNA (12 bases), and then translate the message into a ...
Bis2A 8.2 The Flow of Genetic Information
... In bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes, the primary role of DNA is store heritable information that is required for encoding the organism in question. Understanding all of the ways in which information is encoded in a genome is still an area of active research - while we have gotten much better at qui ...
... In bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes, the primary role of DNA is store heritable information that is required for encoding the organism in question. Understanding all of the ways in which information is encoded in a genome is still an area of active research - while we have gotten much better at qui ...
common to all organisms
... 1. Fill out the COMPLIMENTARY DNA strands on each strip! 2. Cut all the pictures and gene segments apart from one another. 3. The human DNA strand is: ATG-TAC-AAC-GGA-CAG. Glue this one at the top of your notebook page! 4. Put the images in order from most to least related to human in your ...
... 1. Fill out the COMPLIMENTARY DNA strands on each strip! 2. Cut all the pictures and gene segments apart from one another. 3. The human DNA strand is: ATG-TAC-AAC-GGA-CAG. Glue this one at the top of your notebook page! 4. Put the images in order from most to least related to human in your ...
Chapter 3-1 • Definitions: - Genetics: the scientific study of heredity
... • Chromosome Theory of Inheritance: genes are passed from parent to offspring on the chromosomes. ...
... • Chromosome Theory of Inheritance: genes are passed from parent to offspring on the chromosomes. ...
File - Chereese Langley
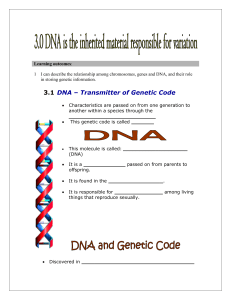
... Deoxyribonucleic acid contains genetic information. Also known as DNA. The double helix is in the DNA molecule. The double helix is a pair of parallel helices intertwined about a common axis. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine are a compound that is one of the four constituent bases of nucleic ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid contains genetic information. Also known as DNA. The double helix is in the DNA molecule. The double helix is a pair of parallel helices intertwined about a common axis. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine are a compound that is one of the four constituent bases of nucleic ...
DNA & Heredity
... mRNA- is grabbed onto by a ribosome. So that the ribosome can hold it in place for the tRNA. The tRNA then comes and hooks onto the mRNA and bring the amino acid. When a bunch of amino acids are hooked together it makes something called a polypeptide chain (protein). ...
... mRNA- is grabbed onto by a ribosome. So that the ribosome can hold it in place for the tRNA. The tRNA then comes and hooks onto the mRNA and bring the amino acid. When a bunch of amino acids are hooked together it makes something called a polypeptide chain (protein). ...
Genetic Mutations
... 20. All cells have DNA errors due to the mistakes that occur each time DNA is replicated prior to cell division. There are proofreading enzymes in cells that correct many of these mistakes, but on average, 3 – 5 errors are found in DNA after each replication. a. If each cell has multiple mutation ...
... 20. All cells have DNA errors due to the mistakes that occur each time DNA is replicated prior to cell division. There are proofreading enzymes in cells that correct many of these mistakes, but on average, 3 – 5 errors are found in DNA after each replication. a. If each cell has multiple mutation ...
ACT - Genetic Mutations-S
... 16. As a group, describe the range of changes in the amino acid sequence that can result from this type of mutation. 13. All of the DNA and mRNA sequences in Model 1 have ellipses (…) on one or both ends of the sequences shown. Propose an explanation for this use of this symbol in that context. ...
... 16. As a group, describe the range of changes in the amino acid sequence that can result from this type of mutation. 13. All of the DNA and mRNA sequences in Model 1 have ellipses (…) on one or both ends of the sequences shown. Propose an explanation for this use of this symbol in that context. ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 12. What are the functions of primase? DNA polymerase? Ligase? 13. What is the difference between the 5’ and 3’ ends of the DNA molecule? Where are the 5’ and 3’ ends on opposite strands of the double helix? 14. What is the difference between the leading and lagging strand during replication? Why ar ...
... 12. What are the functions of primase? DNA polymerase? Ligase? 13. What is the difference between the 5’ and 3’ ends of the DNA molecule? Where are the 5’ and 3’ ends on opposite strands of the double helix? 14. What is the difference between the leading and lagging strand during replication? Why ar ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... Genes are located in the chromosomes Each chromosome has numerous gene locations Genes come in ____ Both genes in a pair carry DNA instructions for the same thing Specific characteristic genes occupy ...
... Genes are located in the chromosomes Each chromosome has numerous gene locations Genes come in ____ Both genes in a pair carry DNA instructions for the same thing Specific characteristic genes occupy ...
set 3
... The table below represents the DNA sequence of a short region within a gene, the sequence of the RNA transcript, the anticodon sequences of the tRNA’s that decode the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of the protein product. The identities of some nucleotides and amino acid/s are given, but most boxe ...
... The table below represents the DNA sequence of a short region within a gene, the sequence of the RNA transcript, the anticodon sequences of the tRNA’s that decode the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of the protein product. The identities of some nucleotides and amino acid/s are given, but most boxe ...
Webquest
... happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/ . Use the tabs at the top of the page and answer the following questions: a. What is DNA? b. What does “DNA” stand for? ...
... happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/ . Use the tabs at the top of the page and answer the following questions: a. What is DNA? b. What does “DNA” stand for? ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.