
SBI 3CI Diagnostic Quiz October 10, 2014 – Microbiology Name
... It’s an immunity where the body make its own antibodies. A cell with no internal membrane bound structures like a nucleus The process of asexual reproduction in bacteria The outer coating on a virus It is an organism that would initiate antibody production A symbiotic relationship where one benefits ...
... It’s an immunity where the body make its own antibodies. A cell with no internal membrane bound structures like a nucleus The process of asexual reproduction in bacteria The outer coating on a virus It is an organism that would initiate antibody production A symbiotic relationship where one benefits ...
anth-260-midterm-review-sheet-2016
... • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False • All of the following are true of the relationship between DNA and proteins EXCEPT: a. a sequence of three DNA base-pairs codes for one amino acid b. a single codon codes fo ...
... • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False • All of the following are true of the relationship between DNA and proteins EXCEPT: a. a sequence of three DNA base-pairs codes for one amino acid b. a single codon codes fo ...
Directed Reading B
... b. genetic engineering c. genetics d. transfer RNA 24. What is an organism that has an exact copy of another’s DNA called? a. a twin b. a brother or sister c. a clone d. a child ...
... b. genetic engineering c. genetics d. transfer RNA 24. What is an organism that has an exact copy of another’s DNA called? a. a twin b. a brother or sister c. a clone d. a child ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... • Uneven distribution of morphogens plays a role in establishing these axes. ...
... • Uneven distribution of morphogens plays a role in establishing these axes. ...
New gene link to Glaucoma
... Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide, affecting more than 65 million people. Prof David Mackey, genetic researcher and Managing Director of the Lions Eye Institute, is a member of the consortium that have identified three new gene mutations associated with an increased s ...
... Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide, affecting more than 65 million people. Prof David Mackey, genetic researcher and Managing Director of the Lions Eye Institute, is a member of the consortium that have identified three new gene mutations associated with an increased s ...
1 BI 112 Instructor: Waite Final Unit Practice Exam 1) Which of the
... 16) Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder. A child with cystic fibrosis is born to two healthy individuals. Which of the following statements must be true? a) The mother, but not the father, must be a carrier b) Only one parent is a carrier, but it is impossible to say which one c) Both ...
... 16) Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder. A child with cystic fibrosis is born to two healthy individuals. Which of the following statements must be true? a) The mother, but not the father, must be a carrier b) Only one parent is a carrier, but it is impossible to say which one c) Both ...
2015 Midterm Study Guide
... Significance of using operons - Why have bacteria that have operons continue to remain in existence What genes are always turned on? (examples) Eukaryotic Gene Expression Why are there multiple points of gene regulation? Why is it essential that multicellular organisms have tightly regulated gene ex ...
... Significance of using operons - Why have bacteria that have operons continue to remain in existence What genes are always turned on? (examples) Eukaryotic Gene Expression Why are there multiple points of gene regulation? Why is it essential that multicellular organisms have tightly regulated gene ex ...
Genetics Vocabulary List
... DNA: The genetic material found in all living cells Chromosomes: The physical structure in the cell that contains the cell’s genetic material Genome: The full DNA sequence of an organism Mutation: Any change made in DNA Genetic Engineering: The process used by scientists to intentionally manipulate ...
... DNA: The genetic material found in all living cells Chromosomes: The physical structure in the cell that contains the cell’s genetic material Genome: The full DNA sequence of an organism Mutation: Any change made in DNA Genetic Engineering: The process used by scientists to intentionally manipulate ...
Affymetrix Resequencing Arrays
... Autosomal recessive disorders are a major cause of infant morbidity and mortality Significantly higher in WM than rest of country (Bundy report, 1990) Clinical phenotypes can be caused by mutations in one of several genes or different mutated genes can cause very similar clinical phenotype Genes are ...
... Autosomal recessive disorders are a major cause of infant morbidity and mortality Significantly higher in WM than rest of country (Bundy report, 1990) Clinical phenotypes can be caused by mutations in one of several genes or different mutated genes can cause very similar clinical phenotype Genes are ...
Big Idea #3
... to these sites and either block or increase gene activity. Poly A tail and a 5’cap are added to an RNA message before it leaves the nucleus. Sometimes, these end caps can be removed to reduce gene activity. Alternative splicing: occurs when dif ferent introns (noncoding regions of DNA) are splic ...
... to these sites and either block or increase gene activity. Poly A tail and a 5’cap are added to an RNA message before it leaves the nucleus. Sometimes, these end caps can be removed to reduce gene activity. Alternative splicing: occurs when dif ferent introns (noncoding regions of DNA) are splic ...
Chapter 15
... Types of Mutations in Genes 1. Point mutation- alteration in a single base pair in a coding sequence. • Base substitution- one base for another. Ex: C instead of T • Missense mutation- substitution that changes an amino acid in a protein • Nonsense mutation- base is changed such that the transcribed ...
... Types of Mutations in Genes 1. Point mutation- alteration in a single base pair in a coding sequence. • Base substitution- one base for another. Ex: C instead of T • Missense mutation- substitution that changes an amino acid in a protein • Nonsense mutation- base is changed such that the transcribed ...
Introduction to the biology and technology of DNA microarrays
... The genetic code • DNA: sequence of four different nucleotides. • Proteins: sequence of twenty different amino acids. • The correspondence between DNA's four-letter alphabet and a protein's twenty-letter alphabet is specified by the genetic code, which relates nucleotide triplets or codons to amino ...
... The genetic code • DNA: sequence of four different nucleotides. • Proteins: sequence of twenty different amino acids. • The correspondence between DNA's four-letter alphabet and a protein's twenty-letter alphabet is specified by the genetic code, which relates nucleotide triplets or codons to amino ...
DNA WebQuest - kruegerscience
... 19. What are the three regions of a gene? ______________________________ 20. What does RNA polymerase do? _________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 21. Describe the transcription process in terms of the three regions of the gene. ________ ______________ ...
... 19. What are the three regions of a gene? ______________________________ 20. What does RNA polymerase do? _________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 21. Describe the transcription process in terms of the three regions of the gene. ________ ______________ ...
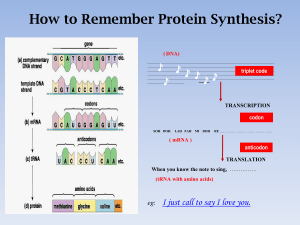
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
Chapter 3 Section 1
... Involved in what type of reproduction Type of cells which undergo the process Reason for this process to occur Stages involves (list all of the stages) Number of cells produced Number of chromosomes in the resulting ...
... Involved in what type of reproduction Type of cells which undergo the process Reason for this process to occur Stages involves (list all of the stages) Number of cells produced Number of chromosomes in the resulting ...
Natural Selection - This area is password protected
... likely to survive and reproduce, meaning that their genes are less likely to be passed to the next generation S Given enough time, a species will gradually evolve… ...
... likely to survive and reproduce, meaning that their genes are less likely to be passed to the next generation S Given enough time, a species will gradually evolve… ...
Study guide: Ch 4: Due Thursday (Test Friday)
... 18:What is the purpose of the Human genome project? Identify DNA sequence of each gene. 19:What is a genome? DNA in one cell 20:How do police use DNA fingerprinting to solve the crimes? Comparing suspect’s DNA with the evidence. 22:What is a Karyotype? 23:What factors can affect a person’s height? G ...
... 18:What is the purpose of the Human genome project? Identify DNA sequence of each gene. 19:What is a genome? DNA in one cell 20:How do police use DNA fingerprinting to solve the crimes? Comparing suspect’s DNA with the evidence. 22:What is a Karyotype? 23:What factors can affect a person’s height? G ...
Section 4.3 – DNA
... Stored in cells that have a nucleus 1952 – Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is 2 chains in a spiral -‐ 1953 – Watson and Crick made a DNA model o DNA is made of deoxyribose (sugar) ...
... Stored in cells that have a nucleus 1952 – Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is 2 chains in a spiral -‐ 1953 – Watson and Crick made a DNA model o DNA is made of deoxyribose (sugar) ...
4.1. Genetics as a Tool in Anthropology
... Statistical approach to link changes in gene structure to history of a population Gene structure can change randomly during replication or by chemical or radiation impact. The causes a change in base sequence ⇒ Mutation. Mutation can be a replacement of a base or base addition/deletion. Only a mutat ...
... Statistical approach to link changes in gene structure to history of a population Gene structure can change randomly during replication or by chemical or radiation impact. The causes a change in base sequence ⇒ Mutation. Mutation can be a replacement of a base or base addition/deletion. Only a mutat ...
GENETICS 310-PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY
... EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answers can be accessed via the internet at: Genetics 310 TAMU . GRADES: Your grade will be determined by your performance on 3 in-class exams, a comprehensive final, and an outside paper on a re ...
... EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answers can be accessed via the internet at: Genetics 310 TAMU . GRADES: Your grade will be determined by your performance on 3 in-class exams, a comprehensive final, and an outside paper on a re ...
Mutations—1 [1] Mutations [2] To understand what mutations are
... [2] To understand what mutations are, how they happen, and why they are important, we need to know about two kinds of cell division that happen inside of living organisms. / One kind of cell division is called mitosis--a highly complex process that happens all the time / as your body continually mak ...
... [2] To understand what mutations are, how they happen, and why they are important, we need to know about two kinds of cell division that happen inside of living organisms. / One kind of cell division is called mitosis--a highly complex process that happens all the time / as your body continually mak ...
The phenomenon of incomplete The mRNA-counting analysis of penetrance — whereby organisms
... The phenomenon of incomplete penetrance — whereby organisms with genetically identical alleles can develop distinct phenotypes — has been known for 80 years, and several mechanisms have been proposed to explain it. A paper now provides a quantitative description of the effect of an incompletely pene ...
... The phenomenon of incomplete penetrance — whereby organisms with genetically identical alleles can develop distinct phenotypes — has been known for 80 years, and several mechanisms have been proposed to explain it. A paper now provides a quantitative description of the effect of an incompletely pene ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.



















![Mutations—1 [1] Mutations [2] To understand what mutations are](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002828601_1-86318c7047d168e9c4500928cbbe6885-300x300.png)


