BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 24
... Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Tumor progression E. DNA mutation by ionizing & ultraviolet radiation F. Viruses trigger some cancers Rous sarcoma virus HPV – human papillomavirus IV. Cancer Genes – Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes A. Proto-oncogene conversion to oncogenes Point mutations Gene ampli ...
... Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Tumor progression E. DNA mutation by ionizing & ultraviolet radiation F. Viruses trigger some cancers Rous sarcoma virus HPV – human papillomavirus IV. Cancer Genes – Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes A. Proto-oncogene conversion to oncogenes Point mutations Gene ampli ...
Document
... observations? If a scenario is not consistent, briefly explain why (i.e. what observation would be expected if that scenario were true?) Scenario I : The pGLO gene is present on a DNA segment that does not contain a ...
... observations? If a scenario is not consistent, briefly explain why (i.e. what observation would be expected if that scenario were true?) Scenario I : The pGLO gene is present on a DNA segment that does not contain a ...
Study Guide for Macromolecules
... 20 kinds of amino acid used in proteins, based on different R groups R groups can be charged (+ or -), uncharged but polar (hydrophilic), or non-polar (hydrophobic) Dehydration of the –OH in the carboxylic acid group and an –H in the amino group joins two amino acids in a peptide bond. Know the stru ...
... 20 kinds of amino acid used in proteins, based on different R groups R groups can be charged (+ or -), uncharged but polar (hydrophilic), or non-polar (hydrophobic) Dehydration of the –OH in the carboxylic acid group and an –H in the amino group joins two amino acids in a peptide bond. Know the stru ...
Review 1 - Allen ISD
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
nucleic acids
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
3.C.1 - The Bio Edge
... inherited and passed generation after generation • Somatic (body cells) mutations can not be inherited and thus die with the individual. ...
... inherited and passed generation after generation • Somatic (body cells) mutations can not be inherited and thus die with the individual. ...
Protein Function Follows Form: Small Changes may Cause Big
... students understand these properties before the next activities. ...
... students understand these properties before the next activities. ...
Topic guide 7.7: Genes and evolution
... now finding that silent mutations may be involved with certain genetic diseases, such as Marfan’s syndrome, if they occur in a regulatory portion of DNA and lead to changes in splicing or the structure of a regulatory length of RNA. If the base substitution changes the triplet making it code for a d ...
... now finding that silent mutations may be involved with certain genetic diseases, such as Marfan’s syndrome, if they occur in a regulatory portion of DNA and lead to changes in splicing or the structure of a regulatory length of RNA. If the base substitution changes the triplet making it code for a d ...
The Effects of Predictive Genetic Testing on the - Antioch Co-op
... of the double stranded DNA template into two single stranded molecules Annealing - The oligonucleotide primers anneal to or find their complementary sequences on the two single-stranded template strands of DNA. These act as primers for taq polymerase. All of this is done at 60℃ Extension - Taq polym ...
... of the double stranded DNA template into two single stranded molecules Annealing - The oligonucleotide primers anneal to or find their complementary sequences on the two single-stranded template strands of DNA. These act as primers for taq polymerase. All of this is done at 60℃ Extension - Taq polym ...
Document
... • Motivation for Alteration - Desire for an Intelligent Child – intelligent individuals lead ‘better’ lives, have successful careers, and are perceived as being ‘superior’ – with the seeming availability of the technology to do so, why not? ...
... • Motivation for Alteration - Desire for an Intelligent Child – intelligent individuals lead ‘better’ lives, have successful careers, and are perceived as being ‘superior’ – with the seeming availability of the technology to do so, why not? ...
13 4 (a) Genetic modification of organisms uses a
... Some of the enzymes and vectors that are important in genetic modification are given an identifying letter in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 enzymes ...
... Some of the enzymes and vectors that are important in genetic modification are given an identifying letter in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 enzymes ...
3-7-08 Transcription and Translation
... C) C pairs with G D) G pairs with C E) All of the above are true 19.3. DNA polymerase is different from the other enzymes we have talked about so far in that: A) it is not a protein B) is not soluble in water C) contains little or no carbon D) requires a template for its activity E) does not obey ei ...
... C) C pairs with G D) G pairs with C E) All of the above are true 19.3. DNA polymerase is different from the other enzymes we have talked about so far in that: A) it is not a protein B) is not soluble in water C) contains little or no carbon D) requires a template for its activity E) does not obey ei ...
S90 T4 Notes WEARING YOUR GENES p
... Our DNA can be changed by factors in the environment (mutagens), such as Xrays, UV rays, cosmic rays, and chemicals in the environment such as pollutants. Our DNA can also be changed simply by random errors in its duplication. These changes are called mutations. Mutations can cause cancer – the muta ...
... Our DNA can be changed by factors in the environment (mutagens), such as Xrays, UV rays, cosmic rays, and chemicals in the environment such as pollutants. Our DNA can also be changed simply by random errors in its duplication. These changes are called mutations. Mutations can cause cancer – the muta ...
Green Fluorescent Protein
... Add your bacteria cells and incubate for thirty Pick bacterial colonies or cells and add them to both the + and – tubes Vortex the tube and replace on ice To the + tube add plasmid DNA 10 ul of either green or blue 5ul of blue and green Do not add plasmid to the – DNA tube Check tips to make sure th ...
... Add your bacteria cells and incubate for thirty Pick bacterial colonies or cells and add them to both the + and – tubes Vortex the tube and replace on ice To the + tube add plasmid DNA 10 ul of either green or blue 5ul of blue and green Do not add plasmid to the – DNA tube Check tips to make sure th ...
The Great Divide
... 2. The smallest molecules that make up DNA are called _____. 3. Name the two pairs of nitrogen bases that make up the ‘rungs’ of DNA. 4. What gives each person a unique DNA code? 5. Describe two characteristics of a gene. 6. When DNA condenses before cell division what does it form? 7. Write the fol ...
... 2. The smallest molecules that make up DNA are called _____. 3. Name the two pairs of nitrogen bases that make up the ‘rungs’ of DNA. 4. What gives each person a unique DNA code? 5. Describe two characteristics of a gene. 6. When DNA condenses before cell division what does it form? 7. Write the fol ...
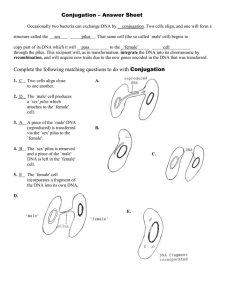
Conjugation Answer Sheet
... Conjugation – Answer Sheet Occasionally two bacteria can exchange DNA by structure called the ...
... Conjugation – Answer Sheet Occasionally two bacteria can exchange DNA by structure called the ...
Document
... amount of the remaining genome is transcribed into functioning but non-protein-coding RNAs, including a variety of small RNAs. ...
... amount of the remaining genome is transcribed into functioning but non-protein-coding RNAs, including a variety of small RNAs. ...
Test: Gene Regulation Free Response Questions It is known that
... transcriptase into host cells. The reverse transcriptase is use to make DNA from viral mRNA. Once a double stranded DNA is made, it embeds itself into the host genome and or uses host RNA polymerase to transcribe viral proteins and assembles new viruses, which can infect other cells and continue its ...
... transcriptase into host cells. The reverse transcriptase is use to make DNA from viral mRNA. Once a double stranded DNA is made, it embeds itself into the host genome and or uses host RNA polymerase to transcribe viral proteins and assembles new viruses, which can infect other cells and continue its ...
Document
... • A single C region gene encoded in the GERMLINE and separate from the V region genes • Multiple choices of V region genes available • A mechanism to rearrange V and C genes in the genome so that they can fuse to form a complete Immunoglobulin gene. ...
... • A single C region gene encoded in the GERMLINE and separate from the V region genes • Multiple choices of V region genes available • A mechanism to rearrange V and C genes in the genome so that they can fuse to form a complete Immunoglobulin gene. ...
Warm-up - Foothill Technology High School
... A change in the genetic material (DNA or RNA) of a cell – Somatic: If it occurs in body cells, it can’t be passed on to next generation – Germ-line: If it occurs in gametes, it can be passed on to next generation Back to Mutations ...
... A change in the genetic material (DNA or RNA) of a cell – Somatic: If it occurs in body cells, it can’t be passed on to next generation – Germ-line: If it occurs in gametes, it can be passed on to next generation Back to Mutations ...
Beyond Mendel
... A change in the genetic material (DNA or RNA) of a cell – Somatic: If it occurs in body cells, it can’t be passed on to next generation – Germ-line: If it occurs in gametes, it can be passed on to next generation Back to Mutations ...
... A change in the genetic material (DNA or RNA) of a cell – Somatic: If it occurs in body cells, it can’t be passed on to next generation – Germ-line: If it occurs in gametes, it can be passed on to next generation Back to Mutations ...
PowerPoint Slides
... CFBE41o- stable expression (planned) FRT(when cell lines created analyzed for 57 missense and 2 deletion mutations In vivo possible) ...
... CFBE41o- stable expression (planned) FRT(when cell lines created analyzed for 57 missense and 2 deletion mutations In vivo possible) ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.