* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 24
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
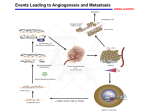
BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 24: Cancer Cells I. Uncontrolled Cell Proliferation A. Types of cancer Carcinomas Sarcomas Lymphomas & leukemias B. Unbalanced cell division vs. cell differentiation C. Characteristics of cancer cells Anchorage-independent Insensitive to population density D. Immortalization involves maintaining telomere length E. Defects in signaling pathways, cell cycle controls, apoptosis II. Spread of Cancer Cells A. Angiogenesis Angiogenesis-activating molecules – VEGF, FGF Angiogenesis-inhibiting molecules – angiostatin, endostatin B. Invasion & metastasis Invasion – growth of tumor into neighboring tissue Metastasis – tumor cells traveling through the blood to establish new tumors at distant sites C. Invasion – changes in cell adhesion, motility, proteases Reduced adhesion due to loss of E-cadherin Increased motility Protease production to break down basal lamina and other tissue Plasminogen activator produces plasmin Plasmin degrades ECM and activates matrix metalloproteinases D. Metastasis Tumor cells travel through lymphatic and/or blood vessels to new sites Blood flow patterns influence sites of metastasis Growth factor production by “target” organs can influence success of tumor metastasis E. Immune system response to cancer cells III. Causes of Cancer A. Epidemiological identification of carcinogens B. Metabolic activation of chemicals by liver Precarcinogens are activated by cytochrome P450 enzymes in liver C. DNA mutations by chemical carcinogens Ames test Incubation +/- liver extract D. Multistep process Initiation Promotion BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Tumor progression E. DNA mutation by ionizing & ultraviolet radiation F. Viruses trigger some cancers Rous sarcoma virus HPV – human papillomavirus IV. Cancer Genes – Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes A. Proto-oncogene conversion to oncogenes Point mutations Gene amplification Chromosomal translocation Local DNA rearrangements B. Oncogenes code for growth-signaling pathways Growth factors Receptors Plasma membrane GTP-binding proteins Nonreceptor protein kinases Transcription factors Cell cycle or cell death regulators C. Tumor suppressor genes D. RB tumor suppressor gene E. p53 tumor suppressor gene F. APC tumor suppressor gene G. Stepwise accumulation of mutations H. DNA repair or chromosome sorting I. Epigenetic alterations J. Summary of hallmarks of cancer Self-sufficiency in growth signals Insensitivity to antigrowth signals Evasion of apoptosis Limitless replicative potential Sustained angiogenesis Tissue invasion & metastasis V. Diagnosis, Screening & Treatment A. Microscopy B. Screening techniques for early detection C. Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy D. Immunotherapy E. Molecular targeting F. Molecular and genetic testing G. Anti-angiogenic therapies