info
... i. NaBH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, or acid chloride to the corresponding alcohol. It will not reduce an acid or an ester. ii. LiAlH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, acid, or ester to the corresponding alcohol. iii. LiAlH(OtBu)3 will reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde. iv. DIBAL will ...
... i. NaBH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, or acid chloride to the corresponding alcohol. It will not reduce an acid or an ester. ii. LiAlH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, acid, or ester to the corresponding alcohol. iii. LiAlH(OtBu)3 will reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde. iv. DIBAL will ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 14. a) Write the mechanism for the reduction of CH3COOC2H5 by LAH. b) How will you prepare isobutyl alcohol using a Grignard reagent? 15. An amide(A) having molecular formula C3H7ON on hydrolysis gives an acid C3H6O2(B) which upon chlorination in the presence of red phosphorus produces a chloroacid( ...
... 14. a) Write the mechanism for the reduction of CH3COOC2H5 by LAH. b) How will you prepare isobutyl alcohol using a Grignard reagent? 15. An amide(A) having molecular formula C3H7ON on hydrolysis gives an acid C3H6O2(B) which upon chlorination in the presence of red phosphorus produces a chloroacid( ...
acidic site
... have its own transition state (which is *not* drawn as part of the mechanism). In addition, a multi-step mechanism will have intermediates. (the products of all elementary processes except the last one). Intermediates are semi-stable molecules or ions that often exist long enough to be observed. An ...
... have its own transition state (which is *not* drawn as part of the mechanism). In addition, a multi-step mechanism will have intermediates. (the products of all elementary processes except the last one). Intermediates are semi-stable molecules or ions that often exist long enough to be observed. An ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... 2. Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon double bond by Ozone: Oxidative cleavage of an alkene breaks both the σ and π bonds of the double bond to form two carbonyl groups. Depending on the number of R groups bonded to the double bond, oxidative cleavage yields either ketones or aldehydes. ...
... 2. Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon double bond by Ozone: Oxidative cleavage of an alkene breaks both the σ and π bonds of the double bond to form two carbonyl groups. Depending on the number of R groups bonded to the double bond, oxidative cleavage yields either ketones or aldehydes. ...
14. The Direct and Enantioselective Organocatalytic -Oxidation of Aldehydes
... nitrogen atom should partition the addition toward the desired, O-addition manifold. Direct formation of highly versatile aldehyde products without preactivation via an enol derivative is attractive from operational, atom-9 and step-economy standpoints. Moreover, the facile conversion to terminal 1, ...
... nitrogen atom should partition the addition toward the desired, O-addition manifold. Direct formation of highly versatile aldehyde products without preactivation via an enol derivative is attractive from operational, atom-9 and step-economy standpoints. Moreover, the facile conversion to terminal 1, ...
Study_guide_2010-01
... Conjugate reductions and selectivity Hard vs. Soft nucleophiles and electrophiles: understanding polarizability by considering electronegativity, electron screening, and delocalization Other nucleophiles for conjugate additions: organocuprates, thiols Conjugate additions of enolates: Michael reactio ...
... Conjugate reductions and selectivity Hard vs. Soft nucleophiles and electrophiles: understanding polarizability by considering electronegativity, electron screening, and delocalization Other nucleophiles for conjugate additions: organocuprates, thiols Conjugate additions of enolates: Michael reactio ...
CBSE Guess Papers Chemistry Class XII(12th) 2006
... 9. Draw the structures of optically active unsaturated compound having molecular formula C5H9Br, that after addition of H2 becomes either optically inactive or shows optical activity. ...
... 9. Draw the structures of optically active unsaturated compound having molecular formula C5H9Br, that after addition of H2 becomes either optically inactive or shows optical activity. ...
Study guide/lecture topics
... Conjugate reductions and selectivity Hard vs. Soft nucleophiles and electrophiles: understanding polarizability by considering electronegativity, electron screening, and delocalization Other nucleophiles for conjugate additions: organocuprates, thiols Conjugate additions of enolates: Michael reactio ...
... Conjugate reductions and selectivity Hard vs. Soft nucleophiles and electrophiles: understanding polarizability by considering electronegativity, electron screening, and delocalization Other nucleophiles for conjugate additions: organocuprates, thiols Conjugate additions of enolates: Michael reactio ...
Addition/elimination under acidic conditions
... 2. Although the stability of the starting materials and products are about the same in the reaction above, the equilibrium lies far to the right. Explain how this is possible. How could this reaction be forced back to the left? (Hint: What is the byproduct of the reaction?) ...
... 2. Although the stability of the starting materials and products are about the same in the reaction above, the equilibrium lies far to the right. Explain how this is possible. How could this reaction be forced back to the left? (Hint: What is the byproduct of the reaction?) ...
This is the first exam with targeted syntheses that you
... forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to form triphenylphosphine oxide and an alkene product to complete the process. If the nucleophile is a weaker base than t ...
... forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to form triphenylphosphine oxide and an alkene product to complete the process. If the nucleophile is a weaker base than t ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... 1. Why is the bond dissociation energy of fluorine molecule less than that of chlorine molecule? 2. What is meant by shape selective catalysis? 3. Write the IUPAC name of CH3CO CH2CH=CH COOH. 4. Is optical isomerism possible in tetrahedral complex? Why? 5. What do you mean by order of reaction? 6. H ...
... 1. Why is the bond dissociation energy of fluorine molecule less than that of chlorine molecule? 2. What is meant by shape selective catalysis? 3. Write the IUPAC name of CH3CO CH2CH=CH COOH. 4. Is optical isomerism possible in tetrahedral complex? Why? 5. What do you mean by order of reaction? 6. H ...
Esterification
... Homework • Describe and explain the formation of phenyl benzoate from benzyl chloride and phenol including a detailed explanation of recrystallization. ...
... Homework • Describe and explain the formation of phenyl benzoate from benzyl chloride and phenol including a detailed explanation of recrystallization. ...
Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
... conjugated enone as it is formed, especially if reaction conditions are pushed, eg high temperature. Mixed or "crossed" Aldol Reactions — If two different carbonyl compounds are allowed to react in an aldol reaction four products usually result; each carbonyl compound forms an enolate and each enola ...
... conjugated enone as it is formed, especially if reaction conditions are pushed, eg high temperature. Mixed or "crossed" Aldol Reactions — If two different carbonyl compounds are allowed to react in an aldol reaction four products usually result; each carbonyl compound forms an enolate and each enola ...
Synthesis of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds1i2 A simple new
... Preparation of %nitrooctane from b-iodo~ctane.~2-Iodooctane (71.2 g., 0.30 mole) was poured into a stirred solution of 225 ml. dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 36 g. of sodium nitrite (0.52 mole) contained in a 500 ml. flask immersed in a water bath held a t room temperature. Stirring was continued for ...
... Preparation of %nitrooctane from b-iodo~ctane.~2-Iodooctane (71.2 g., 0.30 mole) was poured into a stirred solution of 225 ml. dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 36 g. of sodium nitrite (0.52 mole) contained in a 500 ml. flask immersed in a water bath held a t room temperature. Stirring was continued for ...
Organic Reactions
... – Diatomic gas has two atoms – both add to opposite sides of the double bond (and opposite sides of the molecule) – Uses: Chlorine + ethane 1,2-dichloroethane: used as starting material for PVC – Uses: Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish- ...
... – Diatomic gas has two atoms – both add to opposite sides of the double bond (and opposite sides of the molecule) – Uses: Chlorine + ethane 1,2-dichloroethane: used as starting material for PVC – Uses: Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish- ...
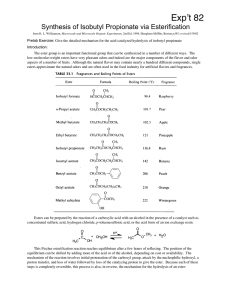
Synthesis of Isobutyl Propionate via Esterification
... Assemble a microscale chromatography column (see Lab Guide for review), being sure it is clamped in a vertical position. Close the valve, and fill the column with dichloromethane to the bottom of the funnel. Prepare a slurry of 1 g of silica gel in 4 mL of dichloromethane in a small beaker. Stir the ...
... Assemble a microscale chromatography column (see Lab Guide for review), being sure it is clamped in a vertical position. Close the valve, and fill the column with dichloromethane to the bottom of the funnel. Prepare a slurry of 1 g of silica gel in 4 mL of dichloromethane in a small beaker. Stir the ...
Microsoft Word - Final Exam Study Guide
... rearrangements, Grignard, hydride reduction, epoxides) Answer questions based on mechanisms ~1/3 reagents, reactions Predict the major product with stereochemistry and regiochemistry Provide the correct reagents Multistep synthesis ~1/3 miscellaneous concepts from list of major topics ** The exam is ...
... rearrangements, Grignard, hydride reduction, epoxides) Answer questions based on mechanisms ~1/3 reagents, reactions Predict the major product with stereochemistry and regiochemistry Provide the correct reagents Multistep synthesis ~1/3 miscellaneous concepts from list of major topics ** The exam is ...
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol – Preparation of an Alkene
... generate an alkyl halide. This reaction occurred through the SN2 pathway. In this experiment you will react an alcohol (cyclohexanol) utilizing an acid catalyst (sulfuric acid) to “dehydrate” the alcohol and form an alkene (cyclohexene). Alcohols are frequently converted into the desired alkene usin ...
... generate an alkyl halide. This reaction occurred through the SN2 pathway. In this experiment you will react an alcohol (cyclohexanol) utilizing an acid catalyst (sulfuric acid) to “dehydrate” the alcohol and form an alkene (cyclohexene). Alcohols are frequently converted into the desired alkene usin ...
Physical Organic Chemistry
... nucleophiles in normal condition, but will react while benzyne intermediate form. ...
... nucleophiles in normal condition, but will react while benzyne intermediate form. ...
Chapter 18 Reactions of aromatics
... carbocations are too hard to form) • Will not work with rings containing an amino group substituent or a strongly electron-withdrawing group ...
... carbocations are too hard to form) • Will not work with rings containing an amino group substituent or a strongly electron-withdrawing group ...
Abstracts - Thieme Verlag
... Nitromethane readily adds to carbonyl derivatives in a process known as the nitroaldol or Henry reaction. The enantioselective addition onto prochiral carbonyl groups can be carried out under asymmetric catalysis, mainly using copper and zinc complexes. Organocatalytic methods find only limited appl ...
... Nitromethane readily adds to carbonyl derivatives in a process known as the nitroaldol or Henry reaction. The enantioselective addition onto prochiral carbonyl groups can be carried out under asymmetric catalysis, mainly using copper and zinc complexes. Organocatalytic methods find only limited appl ...
Esters
... Ester hydrolysis Breakdown of an ester by water. Process sped up by catalysis Can use an acid to catalyse (H2SO4) Alkali catalysts (e.g. sodium hydroxide) can also be used but instead of producing carboxylic acid a carboxylate salt is formed. Alkaline hydrolysis goes to completion & hence is u ...
... Ester hydrolysis Breakdown of an ester by water. Process sped up by catalysis Can use an acid to catalyse (H2SO4) Alkali catalysts (e.g. sodium hydroxide) can also be used but instead of producing carboxylic acid a carboxylate salt is formed. Alkaline hydrolysis goes to completion & hence is u ...
11.Unit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes.
... For C4H9Br, four isomeric compounds are possible out of which one(sec-butyl bromide) can show enantiomerism. For C5H11Br, eight isomeric compounds are possible out of which three can exhibit enantiomerism. Alcohols can be converted into chlorides by reaction with (i)HCl/ZnCl2 (ii)PCl5 (iii)PCl3 (iv) ...
... For C4H9Br, four isomeric compounds are possible out of which one(sec-butyl bromide) can show enantiomerism. For C5H11Br, eight isomeric compounds are possible out of which three can exhibit enantiomerism. Alcohols can be converted into chlorides by reaction with (i)HCl/ZnCl2 (ii)PCl5 (iii)PCl3 (iv) ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.