Experiment 7 – Dehydration of Methylcyclohexanols
... The dehydration reaction will be run “neat” meaning no additional solvent is used. The alcohol acts as both the starting material and the solvent. Obtain 750 µL of the assigned alcohol using the provided pluringe (1- or 2-Methylcyclohexanol; the 2-methyl compound is a cis/trans mixture) and dispense ...
... The dehydration reaction will be run “neat” meaning no additional solvent is used. The alcohol acts as both the starting material and the solvent. Obtain 750 µL of the assigned alcohol using the provided pluringe (1- or 2-Methylcyclohexanol; the 2-methyl compound is a cis/trans mixture) and dispense ...
67 Preview of Carbonyl Chemistry Kinds of carbonyls 1. Aldehydes
... with α,β-unsaturated ketones; however, they also undergo direct addition to non-conjugated ketones (1,2-additions), aldehydes and will react with alkyl halides and tosylates, and epoxides Mechanism of conjugate addition by organocopper reagents is complex ...
... with α,β-unsaturated ketones; however, they also undergo direct addition to non-conjugated ketones (1,2-additions), aldehydes and will react with alkyl halides and tosylates, and epoxides Mechanism of conjugate addition by organocopper reagents is complex ...
Organic Chemistry - Snow College | It's SNOWing
... Ethers as Solvents • Ethers are relatively unreactive so they are frequently used as solvents – diethyl ether (ether) – tetrahydrofuran (THF) – 1,4-dioxane – 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME) – methyl t-butyl ether (MTBE) O O ...
... Ethers as Solvents • Ethers are relatively unreactive so they are frequently used as solvents – diethyl ether (ether) – tetrahydrofuran (THF) – 1,4-dioxane – 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME) – methyl t-butyl ether (MTBE) O O ...
Practice Questions for Chapters 1-8 CHEM 4000A
... In the first step, a relatively acidic site (pKa ~10) is deprotonated. The negative charge is delocalized onto two different oxygen atoms, stabilizing the anion shown. In the second step, the nucleophilic carbanion attacks the electrophilic carbon of the thioester. A tetrahedral intermediate is form ...
... In the first step, a relatively acidic site (pKa ~10) is deprotonated. The negative charge is delocalized onto two different oxygen atoms, stabilizing the anion shown. In the second step, the nucleophilic carbanion attacks the electrophilic carbon of the thioester. A tetrahedral intermediate is form ...
3.5 revision guide alcohols
... If the compound has an –OH group in addition to other functional groups that need a suffix ending then the OH can be named with the prefix hydroxy-): ...
... If the compound has an –OH group in addition to other functional groups that need a suffix ending then the OH can be named with the prefix hydroxy-): ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 1) Reduction reactions can be reversed to give the aldehydes or ketones 2) Oxidizing Reagent is Cr(VI) a) (Na2Cr2O7 or K2Cr2O7 or CrO3) and H2SO4 and H2O R' CH OH R ...
... 1) Reduction reactions can be reversed to give the aldehydes or ketones 2) Oxidizing Reagent is Cr(VI) a) (Na2Cr2O7 or K2Cr2O7 or CrO3) and H2SO4 and H2O R' CH OH R ...
Organometallic Catalysts
... the polymerization of ethylene at atmospheric pressure. Giulio Natta (1903-1979), an Italian chemist, extended the method to other olefins like propylene and developed variations of the Ziegler catalyst based on his findings on the mechanism of the polymerization reaction. The Ziegler-Natta catalyst ...
... the polymerization of ethylene at atmospheric pressure. Giulio Natta (1903-1979), an Italian chemist, extended the method to other olefins like propylene and developed variations of the Ziegler catalyst based on his findings on the mechanism of the polymerization reaction. The Ziegler-Natta catalyst ...
Chapter 20. Aldehydes and Ketones
... chemical yield would be high, our dedicated student prepared one mole of the Grignard reagent, added two moles of benzaldehyde, and, after working up the reaction, was delighted to obtain a good yield of a crystalline product. Unfortunately, the product that had been formed was benzophenone! On clos ...
... chemical yield would be high, our dedicated student prepared one mole of the Grignard reagent, added two moles of benzaldehyde, and, after working up the reaction, was delighted to obtain a good yield of a crystalline product. Unfortunately, the product that had been formed was benzophenone! On clos ...
MAIN GROUP ORGANOMETALLICS Dr. S. Draper 8 lecture course
... Reaction requires R' stabilisation of negative charge to be better than R. Hence good for formation of aryl Li which involves nucleophilic displacement of an sp2 C. Also reaction is good for X = I , Br occasionally Cl but not F. A volatile RX should be formed ButLi good starting material as ButI vol ...
... Reaction requires R' stabilisation of negative charge to be better than R. Hence good for formation of aryl Li which involves nucleophilic displacement of an sp2 C. Also reaction is good for X = I , Br occasionally Cl but not F. A volatile RX should be formed ButLi good starting material as ButI vol ...
Chapter 18 - people.vcu.edu
... Formation of imines o Overall: The nitrogen replaces the oxygen of the carbonyl, forming a carbonnitrogen double bond. It should be mildly acidic; pH between 4 and 5. NH3, H+ ...
... Formation of imines o Overall: The nitrogen replaces the oxygen of the carbonyl, forming a carbonnitrogen double bond. It should be mildly acidic; pH between 4 and 5. NH3, H+ ...
Alkenes - MsReenChemistry
... Electron deficient with positive or partial positive charges Examples NO2+, H+, ...
... Electron deficient with positive or partial positive charges Examples NO2+, H+, ...
Abbreviated Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... • The nitro group is a strongly deactivating group when considering its resonance forms. The nitrogen always has a formal positive charge. • Ortho or para addition will create an especially unstable ...
... • The nitro group is a strongly deactivating group when considering its resonance forms. The nitrogen always has a formal positive charge. • Ortho or para addition will create an especially unstable ...
EXPERIMENT 5: Oxidation of Alcohols: Solid
... Because the Cr is retained on the solid support it makes work-up of the reaction relatively simple, and it makes recovery of the heavy-metal Cr byproduct trivial. Because this resin can also be regenerated and reused, whereas the heavy metal products from the other simpler reactions are usually disc ...
... Because the Cr is retained on the solid support it makes work-up of the reaction relatively simple, and it makes recovery of the heavy-metal Cr byproduct trivial. Because this resin can also be regenerated and reused, whereas the heavy metal products from the other simpler reactions are usually disc ...
Instructor notes
... oxygens of two sulfate molecules, and another sulfate, along with a methane, coordinates to the Au(III) center through electrophilic substitution. The methyl group and bisulfate then combine and come off of the metal center, reducing the Au(III) to Au(I). An oxidative addition mechanism is also poss ...
... oxygens of two sulfate molecules, and another sulfate, along with a methane, coordinates to the Au(III) center through electrophilic substitution. The methyl group and bisulfate then combine and come off of the metal center, reducing the Au(III) to Au(I). An oxidative addition mechanism is also poss ...
Team In Toulouse
... Project: Molybdenum complexes containing chiral N,O-donor ligands. Catalytic applications: hydrosilylation and epoxidation of olefins. ...
... Project: Molybdenum complexes containing chiral N,O-donor ligands. Catalytic applications: hydrosilylation and epoxidation of olefins. ...
Slide 1
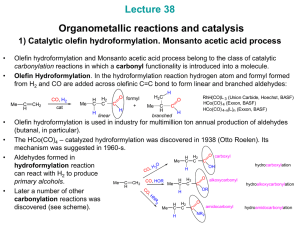
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
6-organic - fixurscore
... There is no further oxidation of the ketone under these conditions. Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised at all by potassium dichromate: This is because there is no hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon with the OH group Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones The fact that aldehydes can be furthe ...
... There is no further oxidation of the ketone under these conditions. Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidised at all by potassium dichromate: This is because there is no hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon with the OH group Distinguishing between Aldehydes and Ketones The fact that aldehydes can be furthe ...
ADDITION REACTIONS
... Grignard Addition - Preparation of Alcohols • Grignard reagents are prepared from the reaction of alkyl halides with magnesium in ether solvent. • The alkyl group assumes a negative character and is a nucleophile. • When presented with an aldehyde or ketone, the Grignard attacks the carbonyl carbon ...
... Grignard Addition - Preparation of Alcohols • Grignard reagents are prepared from the reaction of alkyl halides with magnesium in ether solvent. • The alkyl group assumes a negative character and is a nucleophile. • When presented with an aldehyde or ketone, the Grignard attacks the carbonyl carbon ...
proline catalyzed direct asymmetric aldol and mannich reactions
... enamine acceptors have also been investigated (Table 1, 21). 14 Interestingly, it was found that αbranched aldehydes are not good enolate donors, because these would lead to a β-hydroxyaldehyde with a quaternary α carbon (Table 1, 22). 15 Aldehyde cross-aldol reactions also have been shown to be eff ...
... enamine acceptors have also been investigated (Table 1, 21). 14 Interestingly, it was found that αbranched aldehydes are not good enolate donors, because these would lead to a β-hydroxyaldehyde with a quaternary α carbon (Table 1, 22). 15 Aldehyde cross-aldol reactions also have been shown to be eff ...
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I
... The transition state for this reaction has carbocation character Tertiary alcohols react the fastest because they have the most stable tertiary carbocation-like transition state in the second step Chapter 7 ...
... The transition state for this reaction has carbocation character Tertiary alcohols react the fastest because they have the most stable tertiary carbocation-like transition state in the second step Chapter 7 ...
Microsoft Word
... to amino group, or nucleophilic displacement. The resulting β-hydroxy nitro compounds have been used in various beneficial transformations to provide chiral β-amino alcohols and α-hydroxy carboxylic acids. Attention has recently been focused on the development of catalytic, asymmetric versions of th ...
... to amino group, or nucleophilic displacement. The resulting β-hydroxy nitro compounds have been used in various beneficial transformations to provide chiral β-amino alcohols and α-hydroxy carboxylic acids. Attention has recently been focused on the development of catalytic, asymmetric versions of th ...
Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
... water is slow • In the reverse direction there is also a barrier to the addition of the proton from water to enolate carbon ...
... water is slow • In the reverse direction there is also a barrier to the addition of the proton from water to enolate carbon ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.