Phenols Like alcohols, phenols are starting materials for a wide
... Cannot readily replace the halide of aryl halides by -OH, since aryl halides are inert. The reaction can be performed in industry under high pressure and temperature: OH ...
... Cannot readily replace the halide of aryl halides by -OH, since aryl halides are inert. The reaction can be performed in industry under high pressure and temperature: OH ...
THIOALCOHOLS AND DISULFIDES:
... Reaction of aldehyde and ketones with alcohols: Alcohols add to the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones to form hemiacetals and hemiketals respectively. Hemiacetals contain both an alcohol and ether functional group in the same carbon. The two groups are so close to each other that they modify e ...
... Reaction of aldehyde and ketones with alcohols: Alcohols add to the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones to form hemiacetals and hemiketals respectively. Hemiacetals contain both an alcohol and ether functional group in the same carbon. The two groups are so close to each other that they modify e ...
Poly(ethylene glycol)-supported a,a,a
... amino acids and their derivatives2,3 and naturally occurring alkaloids.4 These catalysts have been found to be effective in Baylis–Hillman,5 Strecker,6 and anhydride desymmetrization7 reactions. Another class of useful organic catalysts are dioxirane compounds, derived from the oxidation of ketones w ...
... amino acids and their derivatives2,3 and naturally occurring alkaloids.4 These catalysts have been found to be effective in Baylis–Hillman,5 Strecker,6 and anhydride desymmetrization7 reactions. Another class of useful organic catalysts are dioxirane compounds, derived from the oxidation of ketones w ...
Chapter 3. The Concept of Protecting Functional Groups
... Acid-catalyzed acetalization of α,β-unsaturated ketone may result in double bond migration. ...
... Acid-catalyzed acetalization of α,β-unsaturated ketone may result in double bond migration. ...
Organic Chemistry HL
... Using water as the nucleophile would produce an alcohol but the reaction is much slower than with hydroxide ions as the hydroxide ions have a negative charge so are attracted more strongly to the d+ on the C atom. ...
... Using water as the nucleophile would produce an alcohol but the reaction is much slower than with hydroxide ions as the hydroxide ions have a negative charge so are attracted more strongly to the d+ on the C atom. ...
Discussion Worksheet #10 Formation of Alcohols Skill 1: Functional
... Skill 1: Functional group transformations for alcohols ...
... Skill 1: Functional group transformations for alcohols ...
Organic Halides
... hemiacetal, and its acetal all exist in solution. Hemiacetal results from addition of the alcohol’s hydroxyl group to the carbon in the C=O bond. A cetals are products of substitution reactions catalyzed by acid. The presence of acid improves the leaving capacity of the hydroxyl group and enables it ...
... hemiacetal, and its acetal all exist in solution. Hemiacetal results from addition of the alcohol’s hydroxyl group to the carbon in the C=O bond. A cetals are products of substitution reactions catalyzed by acid. The presence of acid improves the leaving capacity of the hydroxyl group and enables it ...
asymmetric alkyne addition to aldehydes
... Chiral propargylic alcohols are important compounds, as this structural motif is often found in pharmaceutical compounds as well as natural products and can also serve as versatile synthetic intermediates.1 Although there are many methods available for the preparation of these compounds (e.g. asymme ...
... Chiral propargylic alcohols are important compounds, as this structural motif is often found in pharmaceutical compounds as well as natural products and can also serve as versatile synthetic intermediates.1 Although there are many methods available for the preparation of these compounds (e.g. asymme ...
Lewis base-assisted Lewis acid-catalyzed selective
... to concomitantly extend the knowledge of this relatively simple reaction to the dehydration of complex alcohol substrates re‐ quires a separate model reaction. Therefore, the requirement remains to develop an efficient liquid‐phase system for 1‐arylethylene production thro ...
... to concomitantly extend the knowledge of this relatively simple reaction to the dehydration of complex alcohol substrates re‐ quires a separate model reaction. Therefore, the requirement remains to develop an efficient liquid‐phase system for 1‐arylethylene production thro ...
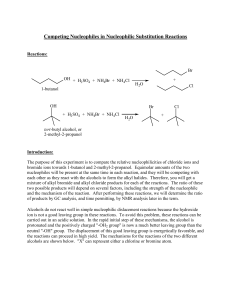
Competing Nucleophiles in Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... The sulfuric acid, ammonium bromide, and ammonium chloride will be provided to you as a solvent-nucleophile medium. One mL of this solution contains 0.42 mL of sulfuric acid, 0.1056 g of ammonium chloride, and 0.1944 g of ammonium bromide. From this information, you will be able to calculate the act ...
... The sulfuric acid, ammonium bromide, and ammonium chloride will be provided to you as a solvent-nucleophile medium. One mL of this solution contains 0.42 mL of sulfuric acid, 0.1056 g of ammonium chloride, and 0.1944 g of ammonium bromide. From this information, you will be able to calculate the act ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
... group around the carbonyl carbon and it is easier for the nucleophile to attack the carbonyl carbon as compared to ketones. Electronically, aldehyde is also more reactive than ketone because the presence of two alkyl groups in ketones will reduce the electrophilicity (partial positive charge ) of th ...
... group around the carbonyl carbon and it is easier for the nucleophile to attack the carbonyl carbon as compared to ketones. Electronically, aldehyde is also more reactive than ketone because the presence of two alkyl groups in ketones will reduce the electrophilicity (partial positive charge ) of th ...
Experiments
... two layers, green and ochre. Upon the addition of water (removing the H+ from the HSO3- group), there is a milky ppt. A solution of fuming sulphuric acid is used here to provide the attacking molecule, SO3. Refluxing for several hours is sometimes necessary with benzene, though not with methyl or ...
... two layers, green and ochre. Upon the addition of water (removing the H+ from the HSO3- group), there is a milky ppt. A solution of fuming sulphuric acid is used here to provide the attacking molecule, SO3. Refluxing for several hours is sometimes necessary with benzene, though not with methyl or ...
Oxidation of alcohols
... During the reaction, the orange potassium dichromate(VI) solution changes to a green solution that contains chromium(III) ions. ...
... During the reaction, the orange potassium dichromate(VI) solution changes to a green solution that contains chromium(III) ions. ...
CHEM 203 Topics Discussed on Nov. 20 Principle: protonation of
... Electrophilic character of the above reagents and facile reaction thereof with nucleophiles Principle: the above reagents rely on the nucleophilic properties of the OH group to achieve conversion of alcohols into alkyl halides Principle: only primary and secondary alcohols are sufficiently nucleophi ...
... Electrophilic character of the above reagents and facile reaction thereof with nucleophiles Principle: the above reagents rely on the nucleophilic properties of the OH group to achieve conversion of alcohols into alkyl halides Principle: only primary and secondary alcohols are sufficiently nucleophi ...
File - TGHS Level 3 Chemistry
... secondary alcohols present because they can be oxidised also Benedict’s solution: This blue solution (Cu2+) turns red/orange (Cu2O) when boiled with aldehydes (but not with alcohols) Tollen’s (silver mirror) test: This colourless (Ag(NH3)2+) solution turns the test tube silver (Ag) when aldehydes ar ...
... secondary alcohols present because they can be oxidised also Benedict’s solution: This blue solution (Cu2+) turns red/orange (Cu2O) when boiled with aldehydes (but not with alcohols) Tollen’s (silver mirror) test: This colourless (Ag(NH3)2+) solution turns the test tube silver (Ag) when aldehydes ar ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... mechanism must equal the overall reaction equation. The reaction is a substitution reaction in which the nucleophile chloride takes the place of the OH. Thus, it is known as an SN reaction. ...
... mechanism must equal the overall reaction equation. The reaction is a substitution reaction in which the nucleophile chloride takes the place of the OH. Thus, it is known as an SN reaction. ...
Chem 3.5 #3 Alcohols 1
... Explain why the lower molecular weight alcohols are soluble in water while the higher ones are not. ...
... Explain why the lower molecular weight alcohols are soluble in water while the higher ones are not. ...
Stockholm University
... the transient allylboronates with aldehyde and imine electrophiles. In a typical reaction the diboronate 1, the allylacetate 2, the appropriate electrophile (3 or 4) and catalytic amounts of Pd2(dba)3 [dba = (dibenzylidene)acetone] were mixed in DMSO and after the allotted reaction time (Table 1) th ...
... the transient allylboronates with aldehyde and imine electrophiles. In a typical reaction the diboronate 1, the allylacetate 2, the appropriate electrophile (3 or 4) and catalytic amounts of Pd2(dba)3 [dba = (dibenzylidene)acetone] were mixed in DMSO and after the allotted reaction time (Table 1) th ...
organic revision nots
... directs the substituents to Ortho and para positions in benzene ring. 3. The –OH group in phenols is more strongly held as compared to –OH group in alcohols. 4. Phenol does not undergo protonation easily. 5. Nitration is an example of aromatic electrophonic substitution and its rate depends upon the ...
... directs the substituents to Ortho and para positions in benzene ring. 3. The –OH group in phenols is more strongly held as compared to –OH group in alcohols. 4. Phenol does not undergo protonation easily. 5. Nitration is an example of aromatic electrophonic substitution and its rate depends upon the ...
reactions of alcohols
... ammonia and silver nitrate. The active substance is the complex ion of [Ag(NH3)2]+ . • Conditions: heat gently • Reaction: aldehydes only are oxidised by Tollen’s reagent into a carboxylic acid and the silver(I) ions are reduced to silver atoms coating the inside of the test tube . The silver coatin ...
... ammonia and silver nitrate. The active substance is the complex ion of [Ag(NH3)2]+ . • Conditions: heat gently • Reaction: aldehydes only are oxidised by Tollen’s reagent into a carboxylic acid and the silver(I) ions are reduced to silver atoms coating the inside of the test tube . The silver coatin ...
EXPERIMENT 3: The Grignard Reaction: Synthesis of
... The reactions involved in the synthesis of complex organic molecules can commonly be categorized into either functional group interconversions or skeleton building reactions. The latter category, primarily those involving carbon-carbon bond formations, is most important in anabolic organic synthesis ...
... The reactions involved in the synthesis of complex organic molecules can commonly be categorized into either functional group interconversions or skeleton building reactions. The latter category, primarily those involving carbon-carbon bond formations, is most important in anabolic organic synthesis ...
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the
... The carbonyl p electrons shift to oxygen to give the alkoxide The carbonyl carbon changes from trigonal planar to tetrahedral ...
... The carbonyl p electrons shift to oxygen to give the alkoxide The carbonyl carbon changes from trigonal planar to tetrahedral ...
Summer Scholar Report
... then added with 30 mL of THF. The reaction was stirred for 4 hours at 40°C, 1.5 mL (3.42 g, 0.024 moles, double excess) of methyl iodide was added to the reaction and then the reaction was stirred for 2 hours. Once the reaction was complete the reaction solution transferred to a separatory funnel an ...
... then added with 30 mL of THF. The reaction was stirred for 4 hours at 40°C, 1.5 mL (3.42 g, 0.024 moles, double excess) of methyl iodide was added to the reaction and then the reaction was stirred for 2 hours. Once the reaction was complete the reaction solution transferred to a separatory funnel an ...
Rates of Hydrolysis of Some Halogeno-compounds
... the preparation of alcohols, ethers, esters, nitrides and amines when substitution occurs with by —OH, —OR, —OOCCH3, —CN and —NH2 groups respectively. ...
... the preparation of alcohols, ethers, esters, nitrides and amines when substitution occurs with by —OH, —OR, —OOCCH3, —CN and —NH2 groups respectively. ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.