Highly Enantioselective Cyclocarbonylation of Allylic
... Recently, we have achieved high enantioselectivity in a number of Rh-BICP and Ru-BICP catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation reactions.7 These results demonstrated that the BICP ligand is an excellent chiral motif for group VIII transition metal-catalyzed reactions. To optimize the steric and electronic ...
... Recently, we have achieved high enantioselectivity in a number of Rh-BICP and Ru-BICP catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation reactions.7 These results demonstrated that the BICP ligand is an excellent chiral motif for group VIII transition metal-catalyzed reactions. To optimize the steric and electronic ...
aldehyde ketone
... attached that might stabilize anions and act as leaving groups Due to the polarity of the C=O bond, a permanent dipole moment exists in aldehydes and ketones (dipole-dipole forces). Thus, the MP/BP of aldehydes and ketones is mid-range – higher than that of alkanes or alkenes (London forces) but low ...
... attached that might stabilize anions and act as leaving groups Due to the polarity of the C=O bond, a permanent dipole moment exists in aldehydes and ketones (dipole-dipole forces). Thus, the MP/BP of aldehydes and ketones is mid-range – higher than that of alkanes or alkenes (London forces) but low ...
Chapter 21 aldehydes and ketones
... Hydrolysis of Imines and Enamines • Because imines and enamines are formed by a reversible set of reactions, both can be converted back to carbonyl compounds by hydrolysis with mild acid. • The mechanism of hydrolysis is the exact reverse of the mechanism written for formation of imines and enamine ...
... Hydrolysis of Imines and Enamines • Because imines and enamines are formed by a reversible set of reactions, both can be converted back to carbonyl compounds by hydrolysis with mild acid. • The mechanism of hydrolysis is the exact reverse of the mechanism written for formation of imines and enamine ...
A-level Chemistry Question paper Unit 4 - Further Physical
... (i) Calculate the number of moles of iodine and the number of moles of hydrogen iodide in the equilibrium mixture. Number of moles of iodine ....................................................................................... Number of moles of hydrogen iodide .................................... ...
... (i) Calculate the number of moles of iodine and the number of moles of hydrogen iodide in the equilibrium mixture. Number of moles of iodine ....................................................................................... Number of moles of hydrogen iodide .................................... ...
Substitution Rxns-a-Sn2-12-quesx
... Fig. 2. (A to D) Center-of-mass images of the I- reaction product velocity from the reaction of Cl- with ...
... Fig. 2. (A to D) Center-of-mass images of the I- reaction product velocity from the reaction of Cl- with ...
Lecture 8a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • Fluorides are usually not suitable due to the high C-F bond strength • Iodides constitute the most reactive class of reagents but they are also very expensive and labile (often they are sensitive towards light, decompose at room temperature and upon exposure to air) • Bromides are most commonly us ...
... • Fluorides are usually not suitable due to the high C-F bond strength • Iodides constitute the most reactive class of reagents but they are also very expensive and labile (often they are sensitive towards light, decompose at room temperature and upon exposure to air) • Bromides are most commonly us ...
Esters are reduced by hydride reagents to give alcohols or aldehydes.
... Esters form enolates that can be alkylated. Treatment of esters with a strong base at low temperatures produces ester enolates (acidic -hydrogens). These enolates react like ketone enolates, undergoing alkylations. ...
... Esters form enolates that can be alkylated. Treatment of esters with a strong base at low temperatures produces ester enolates (acidic -hydrogens). These enolates react like ketone enolates, undergoing alkylations. ...
Give reasons for the following.(one mark each)
... 26. Use of DDT is banned . 27. Tertiary alcohols react much faster than secondary & primary with lucas reagent. 28. Optically active 2-iodobutane on treatment with NaI in acetone gives a product which does not show optical activity. 29. Vinyl chloride is hydrolysed more slowly than ethyl chloride. 3 ...
... 26. Use of DDT is banned . 27. Tertiary alcohols react much faster than secondary & primary with lucas reagent. 28. Optically active 2-iodobutane on treatment with NaI in acetone gives a product which does not show optical activity. 29. Vinyl chloride is hydrolysed more slowly than ethyl chloride. 3 ...
Experiment #9 – Identification of Aldehydes and Ketones
... are different enough to be considered different classes of compounds. This situation is similar to that of alcohols and phenols which both share the -OH group. Aldehydes and ketones both undergo a reaction type known as nucleophilic addition. Under less acidic conditions, in this type of reaction a ...
... are different enough to be considered different classes of compounds. This situation is similar to that of alcohols and phenols which both share the -OH group. Aldehydes and ketones both undergo a reaction type known as nucleophilic addition. Under less acidic conditions, in this type of reaction a ...
Document
... addition of FBSM to chalcones using cinchona-based phase transfer catalysts. Michael addition between nitromethane and chalcone with high ee and chemical yields using cinchona alkaloid-derived chiral bifunctional thiourea asan effective organocatalyst. ...
... addition of FBSM to chalcones using cinchona-based phase transfer catalysts. Michael addition between nitromethane and chalcone with high ee and chemical yields using cinchona alkaloid-derived chiral bifunctional thiourea asan effective organocatalyst. ...
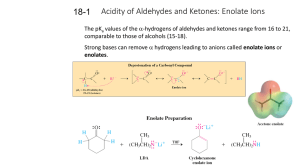
18-1 Enolates (PPT)
... Either equilibration is fast and reversible in solution in the presence of the required catalyst. ...
... Either equilibration is fast and reversible in solution in the presence of the required catalyst. ...
Chemistry Name Mr. Reger Review Guide – Ch. 9
... 3 Cl2(g) + 6 NaOH(aq) 5 NaCl(aq) + NaClO3(aq) + 3 H2O(l) 11. Use the equation in the question above to answer the following: a) What is the theoretical yield of NaClO3 if 4.0mol Cl2 is reacted with excess NaOH? b) If 94.2g NaClO3 is obtained, what is the % yield? c) A different student performs th ...
... 3 Cl2(g) + 6 NaOH(aq) 5 NaCl(aq) + NaClO3(aq) + 3 H2O(l) 11. Use the equation in the question above to answer the following: a) What is the theoretical yield of NaClO3 if 4.0mol Cl2 is reacted with excess NaOH? b) If 94.2g NaClO3 is obtained, what is the % yield? c) A different student performs th ...
Identification of Ketones and Aldehydes
... Preparation of 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazone (DNPH) Derivatives - This derivative will be prepared simultaneously on three carbonyl compounds: benzaldehyde, methyl ethyl ketone, and your unknown. Place 3 drops of each compound into separate, labeled test tubes and add 8 ml of CH3OH to each. To each tub ...
... Preparation of 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazone (DNPH) Derivatives - This derivative will be prepared simultaneously on three carbonyl compounds: benzaldehyde, methyl ethyl ketone, and your unknown. Place 3 drops of each compound into separate, labeled test tubes and add 8 ml of CH3OH to each. To each tub ...
Pd presentation
... •Buchwald-Hartwig- between aryl halide & amine or aryl alcohol •Tsuji-Trost- between alkene & a nucleophile •Heck- between alkenes & alkyl halides This presentation was created as part of the requirements for Chemistry 165 "Organometallics" at Harvey Mudd College during the fall semester 2009. The a ...
... •Buchwald-Hartwig- between aryl halide & amine or aryl alcohol •Tsuji-Trost- between alkene & a nucleophile •Heck- between alkenes & alkyl halides This presentation was created as part of the requirements for Chemistry 165 "Organometallics" at Harvey Mudd College during the fall semester 2009. The a ...
Acetal Formation
... The acetal is a functional group in which a carbon atom is bonded to two –OR groups Acetal formation is a condensation reaction between two hydroxyl groups and a ketone or aldehyde in which water is lost. Vocabulary Acetal Hemiacetal Diol Students should be able to: Identify the acetal a ...
... The acetal is a functional group in which a carbon atom is bonded to two –OR groups Acetal formation is a condensation reaction between two hydroxyl groups and a ketone or aldehyde in which water is lost. Vocabulary Acetal Hemiacetal Diol Students should be able to: Identify the acetal a ...
10 bioenergetics 03
... • In the presence of hydrogen methanol is only used as electron acceptor → methyl – respiration. H2 + CH3OH → CH4 + H2O ...
... • In the presence of hydrogen methanol is only used as electron acceptor → methyl – respiration. H2 + CH3OH → CH4 + H2O ...
Protecting Groups Introduction to Carbonyl
... Reagents; Oxidation and Reduction Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is ...
... Reagents; Oxidation and Reduction Protecting Groups Solving this problem requires a three-step strategy: [1] Convert the OH group into another functional group that does not interfere with the desired reaction. This new blocking group is called a protecting group, and the reaction that creates it is ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... Attack of nucleophile on the carbonyl Followed by transfer of proton from weak acid to strong base. Protonation of –OH to establish leaving group. Leaving group departs, double bond forms. ...
... Attack of nucleophile on the carbonyl Followed by transfer of proton from weak acid to strong base. Protonation of –OH to establish leaving group. Leaving group departs, double bond forms. ...
aldehydes and ketones
... any hydrogen atoms bonded to the oxygen atom, so it cannot hydrogen bond between molecules. ...
... any hydrogen atoms bonded to the oxygen atom, so it cannot hydrogen bond between molecules. ...
Chapter_Sixteen_lecture
... ketones by loss of alcohol and establish an equilibrium with the aldehyde or ketone. – When equilibrium is reached, very little hemiacetal is present. ...
... ketones by loss of alcohol and establish an equilibrium with the aldehyde or ketone. – When equilibrium is reached, very little hemiacetal is present. ...
Full answers
... to represent atomic orbitals, account for this property in compounds of Co2+. Co2+ has a 3d7 configuration: ...
... to represent atomic orbitals, account for this property in compounds of Co2+. Co2+ has a 3d7 configuration: ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides - City University of New York
... Attack of nucleophile on the carbonyl Followed by transfer of proton from weak acid to strong base. Protonation of –OH to establish leaving group. Leaving group departs, double bond forms. ...
... Attack of nucleophile on the carbonyl Followed by transfer of proton from weak acid to strong base. Protonation of –OH to establish leaving group. Leaving group departs, double bond forms. ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.