Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides - City University of New York
... Attack of nucleophile on the carbonyl Followed by transfer of proton from weak acid to strong base. Protonation of –OH to establish leaving group. Leaving group departs, double bond forms. ...
... Attack of nucleophile on the carbonyl Followed by transfer of proton from weak acid to strong base. Protonation of –OH to establish leaving group. Leaving group departs, double bond forms. ...
Remodeling of the natural product fumagillol
... Further optimization using La(OTf)3 and Zn(OTf)2 catalysts was next pursued. The transformations were robust and did not require inert atmosphere, nor special precautions for anhydrous solvent. Other nonpolar solvents provided similar regioselectivity, though toluene proved to be optimal, in which c ...
... Further optimization using La(OTf)3 and Zn(OTf)2 catalysts was next pursued. The transformations were robust and did not require inert atmosphere, nor special precautions for anhydrous solvent. Other nonpolar solvents provided similar regioselectivity, though toluene proved to be optimal, in which c ...
haloalkanes - Knockhardy
... This form of nucleophilic substitution is known as SN2; it is a bimolecular process. An alternative method involves the initial breaking of the C-X bond to form a carbocation, or carbonium ion, (a unimolecular process - SN1 mechanism), which is then attacked by the nucleophile. SN1 is favoured for t ...
... This form of nucleophilic substitution is known as SN2; it is a bimolecular process. An alternative method involves the initial breaking of the C-X bond to form a carbocation, or carbonium ion, (a unimolecular process - SN1 mechanism), which is then attacked by the nucleophile. SN1 is favoured for t ...
Organic molecules with functional groups containing oxygen
... • The arrows are double headed in this case, indicating the movement of a pair of electrons • The arrows begin at a definite pair of electrons - a bond or a lone pair – and move towards a positive charge • If they move into the space between two atoms, a bond is formed • If they move out of the spac ...
... • The arrows are double headed in this case, indicating the movement of a pair of electrons • The arrows begin at a definite pair of electrons - a bond or a lone pair – and move towards a positive charge • If they move into the space between two atoms, a bond is formed • If they move out of the spac ...
Document
... Halogenoalkanes are not soluble in the concentrated halide acid Therefore, the product solution is cloudy ...
... Halogenoalkanes are not soluble in the concentrated halide acid Therefore, the product solution is cloudy ...
reactions.html Reaction 1. Electrophilic addition of
... Mechanistic details positively charged electrophile adds to the aromatic ring in the rate-limiting step; the resulting carbocation reverts to aromaticity by the loss of proton the relative reactivity and regiochemistry of the reaction on substituted benzene derivatives is governed by the nature of t ...
... Mechanistic details positively charged electrophile adds to the aromatic ring in the rate-limiting step; the resulting carbocation reverts to aromaticity by the loss of proton the relative reactivity and regiochemistry of the reaction on substituted benzene derivatives is governed by the nature of t ...
Catalytic asymmetric carbonyl addition reactions catalysed by group
... Catalytic asymmetric carbonyl addition reactions catalysed by group 10 metals The addition of a nucleophilic species to the carbonyl group is one of the most important methodology for carbon-carbon bond construction and various solutions have been offered to achieve an asymmetric version. ...
... Catalytic asymmetric carbonyl addition reactions catalysed by group 10 metals The addition of a nucleophilic species to the carbonyl group is one of the most important methodology for carbon-carbon bond construction and various solutions have been offered to achieve an asymmetric version. ...
Synthesis of n-Butyl Acetate via Esterification
... In a 5-mL short-necked round-bottomed flask, place 0.2 g of Dowex 50X2-l00 ion-exchange resin [Note: The Dowex resin as received should be washed with water by decantation to remove much of the yellow color. It is then collected by vacuum filtration on a Buchner funnel before use], 0.61 g (0.58 mL) ...
... In a 5-mL short-necked round-bottomed flask, place 0.2 g of Dowex 50X2-l00 ion-exchange resin [Note: The Dowex resin as received should be washed with water by decantation to remove much of the yellow color. It is then collected by vacuum filtration on a Buchner funnel before use], 0.61 g (0.58 mL) ...
Ch. 16: Solutions - Quynh Nguyen Official Website
... They tend to have much lower bps than alcohols, because alcohols are much more polar Aldehydes and ketones of 5 C atoms or less are soluble in water ...
... They tend to have much lower bps than alcohols, because alcohols are much more polar Aldehydes and ketones of 5 C atoms or less are soluble in water ...
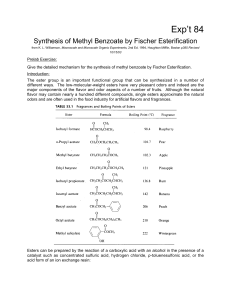
Synthesis of Methyl Benzoate by Fisher Esterification
... For primary alcohols reacting with unhindered carboxylic acids, Keq ~4. If equal quantities of 1butanol and acetic acid are allowed to react, the theoretical yield of ester is only 67% at equilibrium. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either ...
... For primary alcohols reacting with unhindered carboxylic acids, Keq ~4. If equal quantities of 1butanol and acetic acid are allowed to react, the theoretical yield of ester is only 67% at equilibrium. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either ...
WRL0437.tmp
... Alkyl halides are most commonly synthesized from alcohols by replacing the hydroxyl group with a halide substituent. This is an example of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution, which is part of a very important group of reactions. The overall reaction is the same, but the mechanism varies depending o ...
... Alkyl halides are most commonly synthesized from alcohols by replacing the hydroxyl group with a halide substituent. This is an example of nucleophilic aliphatic substitution, which is part of a very important group of reactions. The overall reaction is the same, but the mechanism varies depending o ...
Spring 2015 CH 421 Name ________________________________________ Section ___________ Post‐lab 3: The Grignard Reaction: Preparation of an Alcohol
... 4) Aldehydes undergo reaction with a Grignard reagent to provide an alcohol product. Many aldehydes are prone to air oxidation. For instance, a bottle of benzaldehyde will turn from a clear liquid to a white solid if left open over time. What is the oxidation produ ...
... 4) Aldehydes undergo reaction with a Grignard reagent to provide an alcohol product. Many aldehydes are prone to air oxidation. For instance, a bottle of benzaldehyde will turn from a clear liquid to a white solid if left open over time. What is the oxidation produ ...
Microwave-Enhanced Sulphated Zirconia and SZ/MCM
... There is a noticeable growing interest in obtaining solid catalysts that should be able to replace those commonly used, such as concentrated H2SO4, HCl and triflates, among others, for chemical transformations because they can be recovered, reused, and are generally innocuous to the environment. Sul ...
... There is a noticeable growing interest in obtaining solid catalysts that should be able to replace those commonly used, such as concentrated H2SO4, HCl and triflates, among others, for chemical transformations because they can be recovered, reused, and are generally innocuous to the environment. Sul ...
Synthesis of Chiral C2-symmetric Palladium and Rhodium SCS
... separate stages; (1) treatment of an excess amount of the terminal acetylene with diethylzinc in refluxing toluene; (2) stepwise addition of (R)-BINOL, Ti(OiPr)4, a second solvent (CH2Cl2), and finally the aromatic dialdehyde 2. The first stage probably generated the alkynyl(ethyl)zinc intermediate, ...
... separate stages; (1) treatment of an excess amount of the terminal acetylene with diethylzinc in refluxing toluene; (2) stepwise addition of (R)-BINOL, Ti(OiPr)4, a second solvent (CH2Cl2), and finally the aromatic dialdehyde 2. The first stage probably generated the alkynyl(ethyl)zinc intermediate, ...
Programme
... initially explored. Particular attention was paid to 3(hydroxymethyl)benzophenone, which upon photolysis in acidic aqueous media undergoes an intramolecular photoredox reaction to produce 3-formylbenzhydrol. Extensive investigation into the mechanistic behaviour of 3-(hydroxymethyl)benzophenone prod ...
... initially explored. Particular attention was paid to 3(hydroxymethyl)benzophenone, which upon photolysis in acidic aqueous media undergoes an intramolecular photoredox reaction to produce 3-formylbenzhydrol. Extensive investigation into the mechanistic behaviour of 3-(hydroxymethyl)benzophenone prod ...
New L-Serine Derivative Ligands as Cocatalysts for Diels
... pharmaceutical interest [1, 2]. The most efficient and widely used method for the preparation of bicyclic compounds is the Diels-Alder reaction. Generally, activation by an electronwithdrawing group and a Lewis acid is required in order to achieve good conversion rates. The acid catalyzed Diels-Alde ...
... pharmaceutical interest [1, 2]. The most efficient and widely used method for the preparation of bicyclic compounds is the Diels-Alder reaction. Generally, activation by an electronwithdrawing group and a Lewis acid is required in order to achieve good conversion rates. The acid catalyzed Diels-Alde ...
communication - Kyushu University Library
... near hydroxy group of the ammonium cation. Furthermore, it was reported that BH4– anion of the N-9-anthracenylmethyl cinchonidinium tetrahydroborate salt prefers to be located near the 9-hydroxy group in the literature.[14] These facts suggest that OH– is located near the 9-hydroxy group of the ammo ...
... near hydroxy group of the ammonium cation. Furthermore, it was reported that BH4– anion of the N-9-anthracenylmethyl cinchonidinium tetrahydroborate salt prefers to be located near the 9-hydroxy group in the literature.[14] These facts suggest that OH– is located near the 9-hydroxy group of the ammo ...
Chapter 1 Organoaluminum Reagents for Selective Organic
... Reactions of dialkyl phosphates of a variety of terpene alcohols were exposed to organoaluminum reagents. After careful investigation of these systems, Yamamoto achieved biomimetic synthesis of many terpenes with this technology [34]. ...
... Reactions of dialkyl phosphates of a variety of terpene alcohols were exposed to organoaluminum reagents. After careful investigation of these systems, Yamamoto achieved biomimetic synthesis of many terpenes with this technology [34]. ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes Calculating a Molecule’s Degree of Unsaturation Naming Alkenes Electronic Structure of Alkenes Cis-Trans Isomerism in Alkenes Sequence Rules: The E,Z Designation Alkene Stability Electrophilic Addition of HX to Alkenes Orientation of Electrophilic Addition: ...
... Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes Calculating a Molecule’s Degree of Unsaturation Naming Alkenes Electronic Structure of Alkenes Cis-Trans Isomerism in Alkenes Sequence Rules: The E,Z Designation Alkene Stability Electrophilic Addition of HX to Alkenes Orientation of Electrophilic Addition: ...
Experiment 4- Alkene
... (ii) Reactions of Alkenes Alkenes, containing a site of unsaturation, undergo electrophilic addition reactions with several reagents such as halogens, oxidizing agents, and sulfuric, halogen, and hypohalous acids. In particular, bromine and oxidizing agents such as permanganate are widely used in qu ...
... (ii) Reactions of Alkenes Alkenes, containing a site of unsaturation, undergo electrophilic addition reactions with several reagents such as halogens, oxidizing agents, and sulfuric, halogen, and hypohalous acids. In particular, bromine and oxidizing agents such as permanganate are widely used in qu ...
A Biocatalytic Henry Reaction-The Hydroxynitrile Lyase from Hevea
... ethene, was detected as the only by-product. By comparing optical rotation data of the product with literature values the absolute configuration of the product was determined to be S,[5] which is in agreement with the known stereopreference of HbHNL in cyanohydrin reactions. Although the nitroaldol ...
... ethene, was detected as the only by-product. By comparing optical rotation data of the product with literature values the absolute configuration of the product was determined to be S,[5] which is in agreement with the known stereopreference of HbHNL in cyanohydrin reactions. Although the nitroaldol ...
Contents - Personal WWW Pages
... 1.2 Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysis. It was Sabatier who, in 1927, published the first classification of catalysts and used the terms homogeneous and heterogeneous. A heterogeneous catalyst exists in a separate phase to the reaction medium (most commonly as a solid in either a liquid or gaseo ...
... 1.2 Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysis. It was Sabatier who, in 1927, published the first classification of catalysts and used the terms homogeneous and heterogeneous. A heterogeneous catalyst exists in a separate phase to the reaction medium (most commonly as a solid in either a liquid or gaseo ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.