B - Uplift Education
... The theory of plate tectonics explains that earth’s lithosphere moves due to the unbalanced forces occurring within the mantle. Alfred Wegner was one of the first scientists to collect scientific evidence in an effort to prove that earth’s tectonic plates drifted. Which of the following pieces of ...
... The theory of plate tectonics explains that earth’s lithosphere moves due to the unbalanced forces occurring within the mantle. Alfred Wegner was one of the first scientists to collect scientific evidence in an effort to prove that earth’s tectonic plates drifted. Which of the following pieces of ...
Plate Tectonics
... • continents are made and deformed by plate motion • continents are (in general) older than ocean rocks ...
... • continents are made and deformed by plate motion • continents are (in general) older than ocean rocks ...
3 Paleozoic Geology Homework c
... 28) All of the following landforms are associated with the Ancestral Rockies EXCEPT: a) the Front Range. b) the Catskill Mountains. c) the Uncompahgre Plateau. 29) Sediments in the stratigraphic record of North America primarily record: a) sedimentary sequences of regression away from the cratonic i ...
... 28) All of the following landforms are associated with the Ancestral Rockies EXCEPT: a) the Front Range. b) the Catskill Mountains. c) the Uncompahgre Plateau. 29) Sediments in the stratigraphic record of North America primarily record: a) sedimentary sequences of regression away from the cratonic i ...
Unit 5: Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics
... a seamount with a flat top created by wave action when the seamount was at sea level ...
... a seamount with a flat top created by wave action when the seamount was at sea level ...
File
... and the Pacific Ocean will be much smaller. North and South America will have moved farther west (California moving north) while Greenland will be located farther west but also farther north. The western part of Africa will rotate clockwise and crash into Europe causing great mountain building, ...
... and the Pacific Ocean will be much smaller. North and South America will have moved farther west (California moving north) while Greenland will be located farther west but also farther north. The western part of Africa will rotate clockwise and crash into Europe causing great mountain building, ...
Cycles of the Lithosphere
... - 1910 – German geologist theorized the continents once fit together as one giant super continent called PANGAEA - 200 million years ago it broke into 2 pieces GONDWANALAND and LAURASIA - They split again - Over millions of years they drifted apart “Continental drift.’ - Based this on outlines of co ...
... - 1910 – German geologist theorized the continents once fit together as one giant super continent called PANGAEA - 200 million years ago it broke into 2 pieces GONDWANALAND and LAURASIA - They split again - Over millions of years they drifted apart “Continental drift.’ - Based this on outlines of co ...
study-guide-test-on-plate
... The plates of the lithosphere float on the asthenosphere The results of plate movements can be seen at plate boundaries The Himalaya mountains are the result of a collision between the indo-Australian plate and Eurasian plate The presence of the same fossils and same rocks found on different contine ...
... The plates of the lithosphere float on the asthenosphere The results of plate movements can be seen at plate boundaries The Himalaya mountains are the result of a collision between the indo-Australian plate and Eurasian plate The presence of the same fossils and same rocks found on different contine ...
File
... Geologists think Earth’s land masses formed a single gigantic continent called Pangaea at that time. ...
... Geologists think Earth’s land masses formed a single gigantic continent called Pangaea at that time. ...
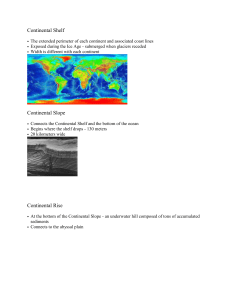
Continental Shelf • The extended perimeter of each continent and
... • The extended perimeter of each continent and associated coast lines • Exposed during the Ice Age - submerged when glaciers receded • Width is different with each continent ...
... • The extended perimeter of each continent and associated coast lines • Exposed during the Ice Age - submerged when glaciers receded • Width is different with each continent ...
Atlas Scavenger Hunt
... Africa including Sudan, Ethiopia and Egypt? The _________ 17. The world is made up of many different ecosystems and environments. What is the name given to the common ecosystem of North Africa that is sand and stones with very little vegetation (plants)? _____ 18. What is the name given to the highe ...
... Africa including Sudan, Ethiopia and Egypt? The _________ 17. The world is made up of many different ecosystems and environments. What is the name given to the common ecosystem of North Africa that is sand and stones with very little vegetation (plants)? _____ 18. What is the name given to the highe ...
plate tec article and ques from ed helper
... their own plate. For example there is a North American plate, which includes all of North America and extends out into the ocean on both sides. Europe and Asia share a plate, the Eurasian Plate. There are also plates that are mostly under the oceans. Plate tectonics show us powerful forces at work w ...
... their own plate. For example there is a North American plate, which includes all of North America and extends out into the ocean on both sides. Europe and Asia share a plate, the Eurasian Plate. There are also plates that are mostly under the oceans. Plate tectonics show us powerful forces at work w ...
Overhead: Continental Drift / Plate Tectonics
... • About 300 million years ago all the earth’s land masses were joined together into one supercontinent called Pangaea • About 200 million years ago Pangaea began to break up, with each tectonic plate moving in a different direction. ...
... • About 300 million years ago all the earth’s land masses were joined together into one supercontinent called Pangaea • About 200 million years ago Pangaea began to break up, with each tectonic plate moving in a different direction. ...
Growing and Shrinking Oceans
... the result of two tectonic plates that are pulling apart. When this happens under the ocean, magma comes up to the surface, cools, hardens, and forms new rock along the ocean floor. Older rock gets pushed further and further away. This is called “seafloor spreading” and it causes oceans to get bigge ...
... the result of two tectonic plates that are pulling apart. When this happens under the ocean, magma comes up to the surface, cools, hardens, and forms new rock along the ocean floor. Older rock gets pushed further and further away. This is called “seafloor spreading” and it causes oceans to get bigge ...
The plate tectonic revolution part II.
... years ago, the Atlantic ocean began to form Continued spreading has produced the current configuration of continents ...
... years ago, the Atlantic ocean began to form Continued spreading has produced the current configuration of continents ...
WATERS Mini Lesson
... Plate Tectonics – the theory of continental drift. The lesson includes the discussion of Pangaea, the supercontinent of 250 million years ago. We will show a video that depicts evidence that supports continental drift, such as fossil evidence, and climatic evidence (ice sheet in Africa near equator) ...
... Plate Tectonics – the theory of continental drift. The lesson includes the discussion of Pangaea, the supercontinent of 250 million years ago. We will show a video that depicts evidence that supports continental drift, such as fossil evidence, and climatic evidence (ice sheet in Africa near equator) ...
Ch. 10 Section 3 Power Point
... – EX: Geologic evidence shows that ice once covered most of Earth’s continental surfaces. As continents began to drift around the globe, however, global temperatures changed and much of the ice sheet melted. 2. As continents rift or as mountains form, populations of organisms are separated. When pop ...
... – EX: Geologic evidence shows that ice once covered most of Earth’s continental surfaces. As continents began to drift around the globe, however, global temperatures changed and much of the ice sheet melted. 2. As continents rift or as mountains form, populations of organisms are separated. When pop ...
Earth: An Ever changing planet
... 3.5 to 3.9 Billion years ago (13% of Earth’s history) • Archean: Earth with only bacteria like cells 3.9 to 2.5 Billion years ago (28% of Earth’s history) • Proterozoic: Multicellular life forms 2.5 BYA to 540 MYA (48% of Earth’s history) • Phanerozoic: Dinosaurs to now • 540 MYA – present day (11% ...
... 3.5 to 3.9 Billion years ago (13% of Earth’s history) • Archean: Earth with only bacteria like cells 3.9 to 2.5 Billion years ago (28% of Earth’s history) • Proterozoic: Multicellular life forms 2.5 BYA to 540 MYA (48% of Earth’s history) • Phanerozoic: Dinosaurs to now • 540 MYA – present day (11% ...
Chapter 2
... slide past each other Faults are formed from this process Earthquakes are produced from this process ...
... slide past each other Faults are formed from this process Earthquakes are produced from this process ...
Evidence of continental drift
... been joined as a single landmass that broke apart and sent the continents adrift. Wegner called the supercontinent Pangaea which means “all the earth” in Greek. Pangaea broke up 200 mya. The northern half of Pangaea was referred to as Laurasia and the southern portion is known as Gondwanaland. ...
... been joined as a single landmass that broke apart and sent the continents adrift. Wegner called the supercontinent Pangaea which means “all the earth” in Greek. Pangaea broke up 200 mya. The northern half of Pangaea was referred to as Laurasia and the southern portion is known as Gondwanaland. ...
Chapter 19
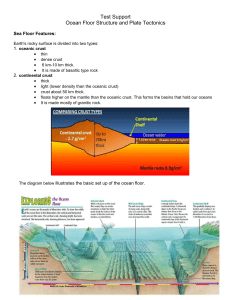
... called guyots (waves cut their tops off when sea level was lower). The continental margin consists of a gentle continental shelf, a steep continental slope, and at the base of the slope the continental rise. The youngest part of the ocean basins are at divergent boundaries called spreading centers. ...
... called guyots (waves cut their tops off when sea level was lower). The continental margin consists of a gentle continental shelf, a steep continental slope, and at the base of the slope the continental rise. The youngest part of the ocean basins are at divergent boundaries called spreading centers. ...
Planet Earth - Topic 4 (ANSWERS)
... Rocks: they found similarities of rocks on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean (different mountain ranges contained the same type of rock) Geological: in order for coal to be formed, it must have a tropical environment. Coal is found in many places where there is no tropical weather (Ex: Alberta). Most ...
... Rocks: they found similarities of rocks on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean (different mountain ranges contained the same type of rock) Geological: in order for coal to be formed, it must have a tropical environment. Coal is found in many places where there is no tropical weather (Ex: Alberta). Most ...
teachnm6
... When does the North Atlantic rift open? When does the South Atlantic rift open? When does India collide with Eurasia? When does Arabia rift away from Africa? ...
... When does the North Atlantic rift open? When does the South Atlantic rift open? When does India collide with Eurasia? When does Arabia rift away from Africa? ...
Editorial – Alfred Wegener`s Theory By: Kelrin Li
... But how exactly and why do plates move? In 1948, a scientist named Ewing discovered a large group of islands in the Atlantic Ocean that were the highest points along a mountain range hidden below sea level; he named this the Mid Atlantic Ridge. He discovered that there were similar rocks on either ...
... But how exactly and why do plates move? In 1948, a scientist named Ewing discovered a large group of islands in the Atlantic Ocean that were the highest points along a mountain range hidden below sea level; he named this the Mid Atlantic Ridge. He discovered that there were similar rocks on either ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.