Presentation
... of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. • In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continen ...
... of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. • In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continen ...
Chapter 7 Section 2 Pages 198-201
... of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. • In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continen ...
... of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. • In Wegener's mind, the drifting of continents after the break-up of Pangaea explained not only the matching fossil occurrences but also the evidence of dramatic climate changes on some continen ...
Story of the Red Centre
... Gondwana formed after breakup of Rodinia. Notice that the Australia/East Antarctica block (Mawson Block) has been together since Columbia. Gondwana mostly formed during the Neoproterozoic Era (colonial and soft-bodied multicellular aquatic organisms), with some of (4) during the early Cambrian (hard ...
... Gondwana formed after breakup of Rodinia. Notice that the Australia/East Antarctica block (Mawson Block) has been together since Columbia. Gondwana mostly formed during the Neoproterozoic Era (colonial and soft-bodied multicellular aquatic organisms), with some of (4) during the early Cambrian (hard ...
Earth Science - California Lutheran University
... Harry Hess, a Captain during WWII, gathered data while cruising from battle to battle ...
... Harry Hess, a Captain during WWII, gathered data while cruising from battle to battle ...
Unit 2 Study Notes
... 3. Sea-floor spreading occurs as oceanic plates are diverging from one another. Magma rises along a rift zone and spreads out at the surface, building new ocean floor. 4. At one time all continents were joined together to form one large landmass called Pangaea. South America and Africa show the most ...
... 3. Sea-floor spreading occurs as oceanic plates are diverging from one another. Magma rises along a rift zone and spreads out at the surface, building new ocean floor. 4. At one time all continents were joined together to form one large landmass called Pangaea. South America and Africa show the most ...
Plate Tectonics
... Wegener's body was found halfway between Eismitte and West camp. It had been buried (by Villumsen) with great care and a pair of skis marked the grave site. Wegener had been fifty years of age and a heavy smoker and it was believed that he had died of heart failure brought on by overexertion. His bo ...
... Wegener's body was found halfway between Eismitte and West camp. It had been buried (by Villumsen) with great care and a pair of skis marked the grave site. Wegener had been fifty years of age and a heavy smoker and it was believed that he had died of heart failure brought on by overexertion. His bo ...
KEY
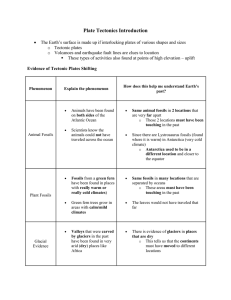
... 1. What early evidence suggested that Earth’s continents might be moving? Matching coastlines of continents on either side of the Atlantic Ocean 2. How do ancient glacial deposits in Africa, India, Australia, and South America support the idea of continental drift? The deposits indicate the continen ...
... 1. What early evidence suggested that Earth’s continents might be moving? Matching coastlines of continents on either side of the Atlantic Ocean 2. How do ancient glacial deposits in Africa, India, Australia, and South America support the idea of continental drift? The deposits indicate the continen ...
Lesson 2.1 Continental Drift
... Closed when India moved into Asia Panthalassic Ocean: Huge ocean surrounding Pangea Became the Pacific Atlantic Ocean: Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart ...
... Closed when India moved into Asia Panthalassic Ocean: Huge ocean surrounding Pangea Became the Pacific Atlantic Ocean: Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart ...
Plate Tectonics - River Mill Academy
... • Fossils of the same animals, rocks, plants, etc were found to correlate (match up to each other) in different parts of the globeparts that fit together like puzzle pieces. (Rainforest tree fossils found in the Arctic). ...
... • Fossils of the same animals, rocks, plants, etc were found to correlate (match up to each other) in different parts of the globeparts that fit together like puzzle pieces. (Rainforest tree fossils found in the Arctic). ...
Chapter 17 Vocabulary
... tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the seafloor. Rift Valley (p. 456) Long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary. Subduction (p. 457) Process by which one ...
... tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the seafloor. Rift Valley (p. 456) Long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary. Subduction (p. 457) Process by which one ...
Ocean Topography
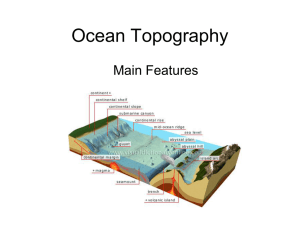
... known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
... known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
Plate Tectonics - Introduction and Evidence of Movement
... where it is warm) in Antarctica (very cold climate) o Antarctica used to be in a different location and closer to the equator ...
... where it is warm) in Antarctica (very cold climate) o Antarctica used to be in a different location and closer to the equator ...
Plate Tectonics – Study Guide
... 3. A ______ plant fossil found in a currently polar region is evidence that the _____ region was once tropical. 4. Identical fossils of species found on different continents may indicate those __________ were once joined. ...
... 3. A ______ plant fossil found in a currently polar region is evidence that the _____ region was once tropical. 4. Identical fossils of species found on different continents may indicate those __________ were once joined. ...
OCEAN BASINS, GEOGRAPHY AND GEOLOGY OF THE OCEANS
... Inner core –1200km, 4000oC or 7200oF - solid Outer core – 1300km - liquid Mantle – 2850 km thick, semi-solid but flows Continental crust or lithosphere – 100km thick Heat driven motion at the core creates convection currents and causes flowing and movement. HISTORY 200 million years ago – superconti ...
... Inner core –1200km, 4000oC or 7200oF - solid Outer core – 1300km - liquid Mantle – 2850 km thick, semi-solid but flows Continental crust or lithosphere – 100km thick Heat driven motion at the core creates convection currents and causes flowing and movement. HISTORY 200 million years ago – superconti ...
Geologic Setting and Evolution of Latin America
... Breakup of Gondwana produced Passive Margins on the flanks of the rifted continents - those facing the newly formed Atlantic Ocean ...
... Breakup of Gondwana produced Passive Margins on the flanks of the rifted continents - those facing the newly formed Atlantic Ocean ...
cenozoic1
... These strata were deformed and faulted by the great Alleghanian Orogeny, which shoved giant blocks westward for dozens of miles. These blocks are bounded by very large thrust faults. ...
... These strata were deformed and faulted by the great Alleghanian Orogeny, which shoved giant blocks westward for dozens of miles. These blocks are bounded by very large thrust faults. ...
How the Continents Move (910L)
... More clues are found in the rock formations along the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean. Rocks on Africa's Ivory Coast and in Brazil are alike. So are those in Scotland and in Labrador; on the island of Madagascar and in India. There are also similar fossils found along these coasts. It is unlikely that ...
... More clues are found in the rock formations along the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean. Rocks on Africa's Ivory Coast and in Brazil are alike. So are those in Scotland and in Labrador; on the island of Madagascar and in India. There are also similar fossils found along these coasts. It is unlikely that ...
6.4 NOTES What is plate tectonics? Objectives: Name some crustal
... Earth’s lithosphere is made up of crust and the solid upper mantle. The lithosphere is broken up into large pieces called tectonic plates. There are 7 large tectonic plates, and 14 smaller ones. Part of the mantle that has rock that flows like a liquid, is called the athenosphere. It is located just ...
... Earth’s lithosphere is made up of crust and the solid upper mantle. The lithosphere is broken up into large pieces called tectonic plates. There are 7 large tectonic plates, and 14 smaller ones. Part of the mantle that has rock that flows like a liquid, is called the athenosphere. It is located just ...
Name
... Mount Fuji is a dormant volcano in Japan. It is located on land, not in the ocean. What is most likely to have created Mount Fuji? ...
... Mount Fuji is a dormant volcano in Japan. It is located on land, not in the ocean. What is most likely to have created Mount Fuji? ...
Plate Tectonic Notes
... Scientists discovered Convection currents – movement of partly molten rock in the Asthenosphere, driven by, heated, rising material from mantle. The currents put friction on overlying layers of crust & cause plates to move. ...
... Scientists discovered Convection currents – movement of partly molten rock in the Asthenosphere, driven by, heated, rising material from mantle. The currents put friction on overlying layers of crust & cause plates to move. ...
Evidence of continental drift
... been joined as a single landmass that broke apart and sent the continents adrift. Wegner called the supercontinent Pangaea which means “all the earth” in Greek. Pangaea broke up 200 mya. The northern half of Pangaea was referred to as Laurasia and the southern portion is known as Gondwanaland. ...
... been joined as a single landmass that broke apart and sent the continents adrift. Wegner called the supercontinent Pangaea which means “all the earth” in Greek. Pangaea broke up 200 mya. The northern half of Pangaea was referred to as Laurasia and the southern portion is known as Gondwanaland. ...
Assembly and Breakup of Supercontinents
... Assembly and the subsequent breakup of the Pangea are not the only change that the earth's crust had undergone since it started forming, almost immediately after evolution of the planet about 4600 million-years ago. Very recently the earth-scientists have come forward with a novel idea of an older s ...
... Assembly and the subsequent breakup of the Pangea are not the only change that the earth's crust had undergone since it started forming, almost immediately after evolution of the planet about 4600 million-years ago. Very recently the earth-scientists have come forward with a novel idea of an older s ...
8.1 Earth has several layers
... matched rocks are found in different areas and different continents ...
... matched rocks are found in different areas and different continents ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.