(f) evaluate the role of plate tectonics with respect to long
... actual volume of the oceans continental mass decreases, increases or decreases and the continent may perhaps through glaciation, or “rebound”. No increase in glacier melting. oceanic volume, but sea-level “appears” to drop. Much of sea-level rise today is due to thermal expansion. As sea water warms ...
... actual volume of the oceans continental mass decreases, increases or decreases and the continent may perhaps through glaciation, or “rebound”. No increase in glacier melting. oceanic volume, but sea-level “appears” to drop. Much of sea-level rise today is due to thermal expansion. As sea water warms ...
Plate Tectonics and the changing earth ppt
... actual volume of the oceans continental mass decreases, increases or decreases and the continent may perhaps through glaciation, or “rebound”. No increase in glacier melting. oceanic volume, but sea-level “appears” to drop. Much of sea-level rise today is due to thermal expansion. As sea water warms ...
... actual volume of the oceans continental mass decreases, increases or decreases and the continent may perhaps through glaciation, or “rebound”. No increase in glacier melting. oceanic volume, but sea-level “appears” to drop. Much of sea-level rise today is due to thermal expansion. As sea water warms ...
Powerpoint
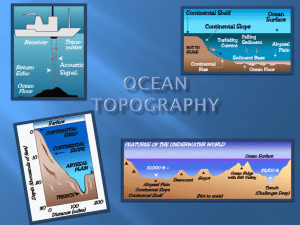
... Abyssal Plain – deep sea floor 3,000-5,000 meters Contains seamounts - underwater volcanoes with a pointy top Contains guyots (tablemounts) - flat topped seamounts that were once volcanic islands that eroded and sunk. Trenches – where the ocean plate descends into the continental plate. (subduction ...
... Abyssal Plain – deep sea floor 3,000-5,000 meters Contains seamounts - underwater volcanoes with a pointy top Contains guyots (tablemounts) - flat topped seamounts that were once volcanic islands that eroded and sunk. Trenches – where the ocean plate descends into the continental plate. (subduction ...
7th Grade Science Notes
... separated continents: Africa, South America, India, Australia, and Antarctica. Did these organisms develop independently, or did they somehow move across the ocean? The ancient climate of many of the continents had changed drastically over the past 300 million years. Glaciers once covered the warm l ...
... separated continents: Africa, South America, India, Australia, and Antarctica. Did these organisms develop independently, or did they somehow move across the ocean? The ancient climate of many of the continents had changed drastically over the past 300 million years. Glaciers once covered the warm l ...
The Floors of the Oceans
... development of a divergent plate boundary and new oceanic crust Atlantic is a mature ocean with passive edges ...
... development of a divergent plate boundary and new oceanic crust Atlantic is a mature ocean with passive edges ...
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
... • Alfred Wegener believed that the continents were once connected. • This large continent was called Pangea. • In 1915, he proposed his theory of Continental Drift. ...
... • Alfred Wegener believed that the continents were once connected. • This large continent was called Pangea. • In 1915, he proposed his theory of Continental Drift. ...
File
... its name • Color each legend and matching mountains or fossils • Cut out the continents • Piece the continents back ...
... its name • Color each legend and matching mountains or fossils • Cut out the continents • Piece the continents back ...
A historical overview of the work of Wegener
... In his spare time, follows an interest in the possibility that America and Africa had once been joined, and had subsequently drifted apart. (This is not a new idea; Flemish mapmaker Ortelius (in 1596) and English philosopher Frances Bacon (in 1620) recognised that the continents might have at one ti ...
... In his spare time, follows an interest in the possibility that America and Africa had once been joined, and had subsequently drifted apart. (This is not a new idea; Flemish mapmaker Ortelius (in 1596) and English philosopher Frances Bacon (in 1620) recognised that the continents might have at one ti ...
Earth`s Structure
... continents used to be one large continent. • He named his hypothesis the Continental Drift Theory. ...
... continents used to be one large continent. • He named his hypothesis the Continental Drift Theory. ...
Alfred Wegener - Colts Neck Township Schools
... America, Africa, India, and Australia –Coral reefs found in Northern Canada –Coal formation in North America ...
... America, Africa, India, and Australia –Coral reefs found in Northern Canada –Coal formation in North America ...
continental drift / plate tectonics test review
... 9. The scientist who developed the theory of how the continents move apart was ALFRED WEGENER 10. RIDGE-RIFT SYSTEMS are systems of underwater mountains that have a rift valley running through their centers. ...
... 9. The scientist who developed the theory of how the continents move apart was ALFRED WEGENER 10. RIDGE-RIFT SYSTEMS are systems of underwater mountains that have a rift valley running through their centers. ...
test review
... 9. The scientist who developed the theory of how the continents move apart was ALFRED WEGENER 10. RIDGE-RIFT SYSTEMS are systems of underwater mountains that have a rift valley running through their centers. ...
... 9. The scientist who developed the theory of how the continents move apart was ALFRED WEGENER 10. RIDGE-RIFT SYSTEMS are systems of underwater mountains that have a rift valley running through their centers. ...
Plate Tectonics - Mr. Brown`s Science Town
... The continents about 70 million years ago. Notice that the breakup of Pangaea formed the Atlantic Ocean. India’s eventual collision with Eurasia would form the Himalayan Mountains. ...
... The continents about 70 million years ago. Notice that the breakup of Pangaea formed the Atlantic Ocean. India’s eventual collision with Eurasia would form the Himalayan Mountains. ...
Geologic Time Webquest - Peoria Public Schools
... 12. What three eras make up the Phanerozoic Eon? What does each name mean? Start at the bottom of the geologic column and work your way up(start at Cambrian – and work to Quaternary) Quaternary ...
... 12. What three eras make up the Phanerozoic Eon? What does each name mean? Start at the bottom of the geologic column and work your way up(start at Cambrian – and work to Quaternary) Quaternary ...
Pangaea - SD43 Teacher Sites
... The name was coined by Alfred Wegener in 1915. When the continents first came together to form Pangaea about 300 MYA, mountains were formed, and some of these ranges still exist, such as the Appalachians, the Atlas Mountains, and the Urals. The vast ocean that surrounded Pang�a has been named Pantha ...
... The name was coined by Alfred Wegener in 1915. When the continents first came together to form Pangaea about 300 MYA, mountains were formed, and some of these ranges still exist, such as the Appalachians, the Atlas Mountains, and the Urals. The vast ocean that surrounded Pang�a has been named Pantha ...
Chapter 5 Test
... Who came up with the idea of Pangaea? What is not evidence to support Pangaea? Tectonic plates can be made up of what two types of crust? At a mid-ocean ridge, the two plates are____________________________? In seafloor spreading the oldest rocks are found where? The major lithospheric plate the con ...
... Who came up with the idea of Pangaea? What is not evidence to support Pangaea? Tectonic plates can be made up of what two types of crust? At a mid-ocean ridge, the two plates are____________________________? In seafloor spreading the oldest rocks are found where? The major lithospheric plate the con ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field
... __________ 1. According to the concepts of plate tectonics, the continents of Africa and South America are gradually approaching each other. __________ 2. Most geologists believe that continents are larger now than they were in the past. __________ 3. The size of the earth is gradually increasing o ...
... __________ 1. According to the concepts of plate tectonics, the continents of Africa and South America are gradually approaching each other. __________ 2. Most geologists believe that continents are larger now than they were in the past. __________ 3. The size of the earth is gradually increasing o ...
Ocean Topography
... Sediments: 4 kinds and how they are created Tectonic Plates: Features of Plate Boundaries -difference between Oceanic and Continental Crust-what they are made of (granite (cc)/Basalt (oc) 1. Convergent: Two plates colliding (Ocean-ocean, ocean-continent) Subductioncreates deep ocean trenches. Know h ...
... Sediments: 4 kinds and how they are created Tectonic Plates: Features of Plate Boundaries -difference between Oceanic and Continental Crust-what they are made of (granite (cc)/Basalt (oc) 1. Convergent: Two plates colliding (Ocean-ocean, ocean-continent) Subductioncreates deep ocean trenches. Know h ...
Extinction Hypothesis B – Continental Drift
... 2. Plate Tectonics: Major changes in the organization of the continental plates (continental drift) were occurring at the K-T boundary. The oceans (especially the Interior Seaway in North America) were experiencing a regression; they were receding from the land. A less mild climate would have been t ...
... 2. Plate Tectonics: Major changes in the organization of the continental plates (continental drift) were occurring at the K-T boundary. The oceans (especially the Interior Seaway in North America) were experiencing a regression; they were receding from the land. A less mild climate would have been t ...
Plate Tectonics Timeline
... mid-ocean ridges and spreads out laterally away from the ridges. The following year, geophysicist Robert S. Dietz named the phenomenon seafloor spreading. Hess and Dietz’s work played a pivotal role in the development of the modern theory of plate tectonics. British geologists Frederick J. Vine and ...
... mid-ocean ridges and spreads out laterally away from the ridges. The following year, geophysicist Robert S. Dietz named the phenomenon seafloor spreading. Hess and Dietz’s work played a pivotal role in the development of the modern theory of plate tectonics. British geologists Frederick J. Vine and ...
Answers to pgs. 125 - 128 wks.
... 14. The continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations because of a. tectonic drift. b. plate tectonics. c. continental drift. d. continental tectonics. 15. As a continent moves across Earth’s surface, a. it carries oceans with it. b. it carries rocks and ...
... 14. The continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations because of a. tectonic drift. b. plate tectonics. c. continental drift. d. continental tectonics. 15. As a continent moves across Earth’s surface, a. it carries oceans with it. b. it carries rocks and ...
Lithosphere
... • Wegener also found fossils of the same animals in very distant countries – There was no way the same animal could have evolved in two places! – There was also no way that it swam across the ocean ...
... • Wegener also found fossils of the same animals in very distant countries – There was no way the same animal could have evolved in two places! – There was also no way that it swam across the ocean ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.