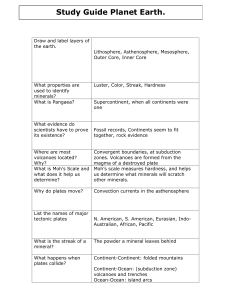
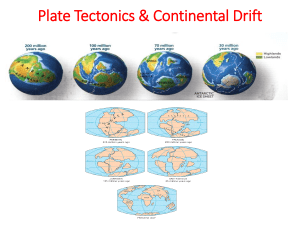
Continental Drift
... People couldn’t imagine how the earth could be millions of years old People couldn’t imagine a force great enough to move the continents ...
... People couldn’t imagine how the earth could be millions of years old People couldn’t imagine a force great enough to move the continents ...
Plate Tectonics
... Believed continents were once all combined into one landmass he called Pangaea meaning “All Earth” Continents seemed to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle Explained why fossils of the same plants and animals are found on the coast of Africa and South America ...
... Believed continents were once all combined into one landmass he called Pangaea meaning “All Earth” Continents seemed to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle Explained why fossils of the same plants and animals are found on the coast of Africa and South America ...
Plate-Study-Guide-11-12
... Sea floor spreading A. In sea floor spreading, molten material forms new rock along the midocean ridge, which was mapped by _____________in the mid-1900’s. B. In______________, the ocean floor sinks back to the mantle beneath the deep ocean trenches. C. Molten Material erupts at the _______________ ...
... Sea floor spreading A. In sea floor spreading, molten material forms new rock along the midocean ridge, which was mapped by _____________in the mid-1900’s. B. In______________, the ocean floor sinks back to the mantle beneath the deep ocean trenches. C. Molten Material erupts at the _______________ ...
Geologic Time PowerPoint
... nickel. The lighter elements made their way to the surface as lava from the interior. Scientists believe the crust was formed by 2.5 billion years ago. The oldest rocks on earth are called Precambrian shield and the one in North America is called the Canadian shield. Two early collisions of continen ...
... nickel. The lighter elements made their way to the surface as lava from the interior. Scientists believe the crust was formed by 2.5 billion years ago. The oldest rocks on earth are called Precambrian shield and the one in North America is called the Canadian shield. Two early collisions of continen ...
Chap-4-Sec-2-Evidence-Supporting-Continental
... refers to large rigid blocks of the Earth's surface which appear to move as a unit. These plates may include both oceans and continents. When the plates move, the continents and ocean floor above them move as well. Continential Drift occurs when the continents change position in relation to each oth ...
... refers to large rigid blocks of the Earth's surface which appear to move as a unit. These plates may include both oceans and continents. When the plates move, the continents and ocean floor above them move as well. Continential Drift occurs when the continents change position in relation to each oth ...
ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL
... MANTLE- Thick layer of really hot rocks & semi-melted rocks called Magma CORE- Solid, superhot ball of iron ...
... MANTLE- Thick layer of really hot rocks & semi-melted rocks called Magma CORE- Solid, superhot ball of iron ...
Earth`s Moving Plates
... of oceans, which are usually found on the edges of continents and islands. Deepest part of the ocean ...
... of oceans, which are usually found on the edges of continents and islands. Deepest part of the ocean ...
Plate Tectonics - Historical Development
... How he got started: •The first clue Wegener had was the matching coast lines • he said they were almost like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle •Then noticed that other continents seemed to fit together to ...
... How he got started: •The first clue Wegener had was the matching coast lines • he said they were almost like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle •Then noticed that other continents seemed to fit together to ...
Chapter 13
... The history of the Earth can be subdivided into various time intervals using the geologic time scale. Precambrian time includes crustal rocks that range in age between 4.6 billion years to 570 million years. The Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras include crustal rocks that range in age from 570 t ...
... The history of the Earth can be subdivided into various time intervals using the geologic time scale. Precambrian time includes crustal rocks that range in age between 4.6 billion years to 570 million years. The Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras include crustal rocks that range in age from 570 t ...
Continental_Drift_and_Plate_Boundaries_
... Wegener - 1915 • Continents started as a single landmass and split apart 200 million years ago • Not accepted by scientists as a valid theory ...
... Wegener - 1915 • Continents started as a single landmass and split apart 200 million years ago • Not accepted by scientists as a valid theory ...
North American History Powerpoint
... collisions of small things – island arcs, continental fragments – builds the NA continent wider • Orogenies: Antler, Sevier • Accreted terranes have ophiolites in between them ...
... collisions of small things – island arcs, continental fragments – builds the NA continent wider • Orogenies: Antler, Sevier • Accreted terranes have ophiolites in between them ...
Chapter 10 * Plate Tectonics
... a single landmass called a supercontinent. According to Wegener, this supercontinent began breaking up into smaller continents during the Mesozoic Era (250 million years ago). It has taken millions of years for these continents to drift to their present locations. Some mountains may be the result of ...
... a single landmass called a supercontinent. According to Wegener, this supercontinent began breaking up into smaller continents during the Mesozoic Era (250 million years ago). It has taken millions of years for these continents to drift to their present locations. Some mountains may be the result of ...
to the PDF
... generally unstable, with frequent earthquakes, tsunamis and often volcanoes. All the mountain ranges have resulted from colliding plates, where one slides past, or under the other and crumples it along the edge. The mountains of Central Thailand were probably formed at an early stage before the brea ...
... generally unstable, with frequent earthquakes, tsunamis and often volcanoes. All the mountain ranges have resulted from colliding plates, where one slides past, or under the other and crumples it along the edge. The mountains of Central Thailand were probably formed at an early stage before the brea ...
Science Background Information
... Background Science Information Plate Tectonics The current theory of Plate Tectonics has been developing over the last century beginning with the theory of continental drift first developed by German astronomer, meteorologist, and climatologist Alfred L. Wegener. He was one of several geologists fro ...
... Background Science Information Plate Tectonics The current theory of Plate Tectonics has been developing over the last century beginning with the theory of continental drift first developed by German astronomer, meteorologist, and climatologist Alfred L. Wegener. He was one of several geologists fro ...
Timeline for Core Geology
... 1862 - Lord Kelvin attempts to find the age of the Earth by examining its cooling time and estimates that the Earth is between 20 - 400 million years old 1903 - George Darwin and John Joly claim that radioactivity is partially responsible for the Earth's heat 1907 - Bertram Boltwood proposes that th ...
... 1862 - Lord Kelvin attempts to find the age of the Earth by examining its cooling time and estimates that the Earth is between 20 - 400 million years old 1903 - George Darwin and John Joly claim that radioactivity is partially responsible for the Earth's heat 1907 - Bertram Boltwood proposes that th ...
Video: Colliding Continents - National Geographic Name: https
... dives down into the mantle. 26. The world’s last supercontinent is known as _____________________. 27. Because much of the land is located far from the sea, the climate of the interior changes radically from _____________to ________________ - it gets very hot in the summer, and extremely cold in the ...
... dives down into the mantle. 26. The world’s last supercontinent is known as _____________________. 27. Because much of the land is located far from the sea, the climate of the interior changes radically from _____________to ________________ - it gets very hot in the summer, and extremely cold in the ...
Theory of Continental Drift
... • In the early 1960’s Harry Hess proposed seafloor spreading. • He believed that molten rock rises from the mantle along mid ocean ridges, forcing the crust to move in opposite directions and creating a new seafloor in the process. • He also believed that crust was being destroyed as it sinks into d ...
... • In the early 1960’s Harry Hess proposed seafloor spreading. • He believed that molten rock rises from the mantle along mid ocean ridges, forcing the crust to move in opposite directions and creating a new seafloor in the process. • He also believed that crust was being destroyed as it sinks into d ...
download soal
... A revolution in our understanding of the Earth is reaching its climax as evidence accumulates that the continents of today are not venerable landmasses but amalgams of other lands repeatedly broken up, juggled, rotated, scattered far and wide, then crunched together into new configurations like ice ...
... A revolution in our understanding of the Earth is reaching its climax as evidence accumulates that the continents of today are not venerable landmasses but amalgams of other lands repeatedly broken up, juggled, rotated, scattered far and wide, then crunched together into new configurations like ice ...
EarthViewer Questions
... 20. Name two (2) supercontinents. ____________________________________________ and ___________________________________________ 21. According to the diagram, where is new plate material formed? _____________________________________________________ ...
... 20. Name two (2) supercontinents. ____________________________________________ and ___________________________________________ 21. According to the diagram, where is new plate material formed? _____________________________________________________ ...
Continental Drift - Frost Middle School
... • In the 1960’s scientists really started studying the sea floor • Found underwater mountain ranges • Called mid-ocean ridges • Found in every ocean • Seemed to circle the Earth like the seams of a baseball • Sea-floor Spreading • Where the ridges form • Cracks in the crust where molten rock rises, ...
... • In the 1960’s scientists really started studying the sea floor • Found underwater mountain ranges • Called mid-ocean ridges • Found in every ocean • Seemed to circle the Earth like the seams of a baseball • Sea-floor Spreading • Where the ridges form • Cracks in the crust where molten rock rises, ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Tectonic plates- large slabs of rock parts of ocean crust and continents rest on. ...
... • Tectonic plates- large slabs of rock parts of ocean crust and continents rest on. ...
plate tectonics
... PROVE HIS CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY: 1) _______________________________________________________________ 2) _______________________________________________________________ 3) _______________________________________________________________ 4) ____________________________________________________________ ...
... PROVE HIS CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY: 1) _______________________________________________________________ 2) _______________________________________________________________ 3) _______________________________________________________________ 4) ____________________________________________________________ ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.