Unit 6.3 PowerPoint File
... geologic history and that may be part of a larger piece of lithosphere, such as a continent • Continents change not only by breaking apart but also by gaining material. Most continents consist of cratons surrounded by a patchwork of terranes. • Terranes become part of a continent at convergent bound ...
... geologic history and that may be part of a larger piece of lithosphere, such as a continent • Continents change not only by breaking apart but also by gaining material. Most continents consist of cratons surrounded by a patchwork of terranes. • Terranes become part of a continent at convergent bound ...
WELCOME BACK! - Year 6 and 7 Mathematics, Science and
... The Theory of Continental Drift: Continental Drift – The continents have not always been in their present positions, but have drifted to these locations over millions of years. ...
... The Theory of Continental Drift: Continental Drift – The continents have not always been in their present positions, but have drifted to these locations over millions of years. ...
8.1 Earth has several layers
... matched rocks are found in different areas and different continents ...
... matched rocks are found in different areas and different continents ...
Alfred Wegener
... is caused by liquid mantle coming up and cooling to form new ground. This creates and ocean trenches and ridges, like the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. ...
... is caused by liquid mantle coming up and cooling to form new ground. This creates and ocean trenches and ridges, like the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. ...
11.1 OCEAN BASINS - STUDENT NOTES
... The __________ is the large, flat middle part, while the _______________________________ are the edges rising up to the land. Ocean Basins The largest changes to the ocean basin occur through the movement of ___________________, although there is also ___________ via storms, earthquakes and iceb ...
... The __________ is the large, flat middle part, while the _______________________________ are the edges rising up to the land. Ocean Basins The largest changes to the ocean basin occur through the movement of ___________________, although there is also ___________ via storms, earthquakes and iceb ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics ANSWER KEY
... 11.) Diverging plates create: mid ocean ridges such as the Mid-Atlantic ridge that runs north to south along the middle of the Atlantic Ocean between North and South America and Europe and Africa. 12.) Transform boundaries are where plates slide by one another, but because they are jagged they often ...
... 11.) Diverging plates create: mid ocean ridges such as the Mid-Atlantic ridge that runs north to south along the middle of the Atlantic Ocean between North and South America and Europe and Africa. 12.) Transform boundaries are where plates slide by one another, but because they are jagged they often ...
Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide
... formation and break up of Pangaea over 200 million years ago greatly changed Earth’s coastlines. Any such changes could make the fit of continents inexact. 29. About 200 million years ago, Wegener’s supercontinent, Pangaea, was an enormous landmass made up of all of Earth’s present continents. At th ...
... formation and break up of Pangaea over 200 million years ago greatly changed Earth’s coastlines. Any such changes could make the fit of continents inexact. 29. About 200 million years ago, Wegener’s supercontinent, Pangaea, was an enormous landmass made up of all of Earth’s present continents. At th ...
Chapter 1 Study Guide – Plate Tectonics
... What are the three main layers of the Earth and what are they made up of? a. crust – a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and ocean floor b. mantle – very hot rock that is solid c. core – made mostly of iron and nickel. It has a liquid outer core and a solid inner core ...
... What are the three main layers of the Earth and what are they made up of? a. crust – a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and ocean floor b. mantle – very hot rock that is solid c. core – made mostly of iron and nickel. It has a liquid outer core and a solid inner core ...
Sort out the cards to create a square by matching processes of the
... move and describe some evidence for this. • Skill: • Problem solving and fact-finding! ...
... move and describe some evidence for this. • Skill: • Problem solving and fact-finding! ...
Elaborating on a Preexisting Concept
... 19. If plates are moving apart two centimeters per year, that distance is so insignificant that it could never be noticed. ...
... 19. If plates are moving apart two centimeters per year, that distance is so insignificant that it could never be noticed. ...
Continental Drift Reading
... theory of continental drift. Since the mapping of the Atlantic Ocean, people had noticed that the coastlines of South America and Africa looked as though they would fit like adjacent pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. Although his formal profession was meteorology, Wegener had always been curious about the ...
... theory of continental drift. Since the mapping of the Atlantic Ocean, people had noticed that the coastlines of South America and Africa looked as though they would fit like adjacent pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. Although his formal profession was meteorology, Wegener had always been curious about the ...
No Slide Title
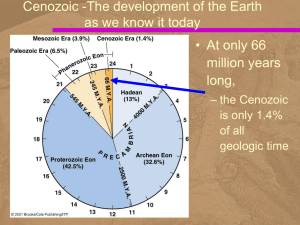
... Cenozoic -The development of the Earth as we know it today • At only 66 million years long, – the Cenozoic is only 1.4% of all geologic time ...
... Cenozoic -The development of the Earth as we know it today • At only 66 million years long, – the Cenozoic is only 1.4% of all geologic time ...
Geological Components of the ocean
... In the 1960's the unifying theory of plate tectonics was proposed ...
... In the 1960's the unifying theory of plate tectonics was proposed ...
Colliding Continents Answers
... our oceans came from many, many meteors ________________ , which contained water. meteoric bodies, meteoroids, asteroids ...
... our oceans came from many, many meteors ________________ , which contained water. meteoric bodies, meteoroids, asteroids ...
Changes Within the Earth
... 1. theory that suggests the earth is not one solid sheet of rock 2. instead, it’s broken into a number of moving plates 3. the plates vary in size and thickness 4. the earth’s oceans and continents ride atop the plates as they move in different directions 5. most earthquakes, volcanoes, & other geol ...
... 1. theory that suggests the earth is not one solid sheet of rock 2. instead, it’s broken into a number of moving plates 3. the plates vary in size and thickness 4. the earth’s oceans and continents ride atop the plates as they move in different directions 5. most earthquakes, volcanoes, & other geol ...
1: The earth is divided into continents and oceans
... And, the seismicity at the edges of the ring of fire don’t represent continents sliding over oceans; they are places where ocean floor plunges into the deep earth interior. ...
... And, the seismicity at the edges of the ring of fire don’t represent continents sliding over oceans; they are places where ocean floor plunges into the deep earth interior. ...
Study Guide
... continental drift hypothesis was his inability to provide a mechanism that was capable of moving continents around the globe. ...
... continental drift hypothesis was his inability to provide a mechanism that was capable of moving continents around the globe. ...
Name______________________ due date ______ period
... (1) The extinction of many life-forms occurred at the end of the Permian Period. (2) Only rocks of igneous origin formed in New York State during the Permian Period. (3) Permian-age rocks have been metamorphosed and cannot be identified. (4) Permian-age rocks were either eroded away or never formed ...
... (1) The extinction of many life-forms occurred at the end of the Permian Period. (2) Only rocks of igneous origin formed in New York State during the Permian Period. (3) Permian-age rocks have been metamorphosed and cannot be identified. (4) Permian-age rocks were either eroded away or never formed ...
Continental Drift PP
... • As magma in the Earth’s core circulates “magnetic or polar reversals” occur • Our current north and south flip such that the magnetic crystal line up opposite of what they would be normally. ...
... • As magma in the Earth’s core circulates “magnetic or polar reversals” occur • Our current north and south flip such that the magnetic crystal line up opposite of what they would be normally. ...
The process where the lithosphere plunges back into the interior of
... A German scientist that developed the theory of continental drift. He did not have any proof although he based his theory on the fact that the continents looked like pieces of a puzzle that fit together. ...
... A German scientist that developed the theory of continental drift. He did not have any proof although he based his theory on the fact that the continents looked like pieces of a puzzle that fit together. ...
Plate Tectonics Layered Earth Unit B Worksheet Key
... near the centers of oceans. Ocean trenches are deep sea trenches found along the edges of continents are along a chain of islands. 2. Explain the Theory of Seafloor Spreading proposed by Harry Hess. Hot magma from the Earth’s mantle rises up through the mid-ocean ridges. This magma cools and flows s ...
... near the centers of oceans. Ocean trenches are deep sea trenches found along the edges of continents are along a chain of islands. 2. Explain the Theory of Seafloor Spreading proposed by Harry Hess. Hot magma from the Earth’s mantle rises up through the mid-ocean ridges. This magma cools and flows s ...
Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics
... Geologist – person that studies rocks Thought of by Alfred Wegener in 1915. Continents "drifted" to their present positions. ...
... Geologist – person that studies rocks Thought of by Alfred Wegener in 1915. Continents "drifted" to their present positions. ...
174 CONTINENTS AND THEIR MOVEMENT B.J. Taygushanov, E.V.
... Strong evidence for the existence of Pangea, Gondwana and Laurasia were obtained by Wegener, after summarizing the paleoclimatic data. At that time it has already well known that almost all the southern continents traces of the largest ice sheet, which occurred about 280 million years ago. Glacial f ...
... Strong evidence for the existence of Pangea, Gondwana and Laurasia were obtained by Wegener, after summarizing the paleoclimatic data. At that time it has already well known that almost all the southern continents traces of the largest ice sheet, which occurred about 280 million years ago. Glacial f ...
Mesozoic Plate Tectonics
... At the end of the Paleozoic, there was one continent and one ocean. Then Pangaea began to break apart about 180 million years ago. The Panthalassa Ocean separated into the individual but interconnected oceans that we see today on Earth. Continental rifting and then seafloor spreading pushed Africa a ...
... At the end of the Paleozoic, there was one continent and one ocean. Then Pangaea began to break apart about 180 million years ago. The Panthalassa Ocean separated into the individual but interconnected oceans that we see today on Earth. Continental rifting and then seafloor spreading pushed Africa a ...
A Head
... From 1960 onwards, seismometers have been used to accurately work out where earthquakes start. Most earthquakes occur in narrow belts around the world. ...
... From 1960 onwards, seismometers have been used to accurately work out where earthquakes start. Most earthquakes occur in narrow belts around the world. ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.