The Sea Floor
... Formed about 25 MYA when Australia and South America separated from Antarctica Isolated the Antarctic continent from warmer waters to the north and is partially responsible for the formation of Antarctica's permanent ice cover. The northern boundary is called the Antarctic Convergence or the Polar F ...
... Formed about 25 MYA when Australia and South America separated from Antarctica Isolated the Antarctic continent from warmer waters to the north and is partially responsible for the formation of Antarctica's permanent ice cover. The northern boundary is called the Antarctic Convergence or the Polar F ...
5-Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... found in South America, Africa, India and Antarctica. His explanation was that the three lands were once connected into a supercontinent, which he named Gondwana. Suess believed that the oceans flooded the ...
... found in South America, Africa, India and Antarctica. His explanation was that the three lands were once connected into a supercontinent, which he named Gondwana. Suess believed that the oceans flooded the ...
Earth`s Landforms
... Where do Landforms come from? • Mountains: – Formed when plates push together, crumble and fold. Also when plates push together and one moves over the other. • Ex. Himalayas, Cascade Mts. ...
... Where do Landforms come from? • Mountains: – Formed when plates push together, crumble and fold. Also when plates push together and one moves over the other. • Ex. Himalayas, Cascade Mts. ...
Geology Introduction Assessment Give questions at beginning of
... B. The ocean basins formed in cracks that were created as the whole Earth heated after its formation C. Ocean basins form as continents move D. The ocean basins formed in cracks that were created as the whole Earth cooled after its formation 16. It is thought that there was once a single continent o ...
... B. The ocean basins formed in cracks that were created as the whole Earth heated after its formation C. Ocean basins form as continents move D. The ocean basins formed in cracks that were created as the whole Earth cooled after its formation 16. It is thought that there was once a single continent o ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth`s Crust
... the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
... the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth`s Crust
... the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
... the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
A short geologic history of the northeast United States
... deformation, metamorphism, and intrusion. The major Grenville orogenic period, ending about 950 million years ago, concluded the Precambrian. The eastern limit of the Grenville rocks is not known; it may have lain well to the east of what is now North America. The next major event seems to have been ...
... deformation, metamorphism, and intrusion. The major Grenville orogenic period, ending about 950 million years ago, concluded the Precambrian. The eastern limit of the Grenville rocks is not known; it may have lain well to the east of what is now North America. The next major event seems to have been ...
Tectonic Plates
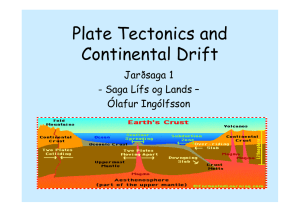
... Basic Premise of Plate Tectonics • Earth’s crust is divided into plates • Plates move relative to one another (at 1-15 cm/yr) • Deformation is concentrated at plate boundaries • There are 3 types of tectonic boundaries ...
... Basic Premise of Plate Tectonics • Earth’s crust is divided into plates • Plates move relative to one another (at 1-15 cm/yr) • Deformation is concentrated at plate boundaries • There are 3 types of tectonic boundaries ...
Backward Design Learning Plan - UNC
... continental drift. - Continental drift – hypothesis that all Earth’s continents were joined as a single landmass (Pangaea) that broke apart about 200 million years ago and slowly moved to their present positions. - Evidence for the theory of continental drift can be found in rock formations (similar ...
... continental drift. - Continental drift – hypothesis that all Earth’s continents were joined as a single landmass (Pangaea) that broke apart about 200 million years ago and slowly moved to their present positions. - Evidence for the theory of continental drift can be found in rock formations (similar ...
Reviewing Vocabulary Reviewing Key Concepts
... b. The geology of continents did not support his hypothesis. c. Fossil evidence showed that the continents were never joined. d. The climates of the continents have remained the same. ...
... b. The geology of continents did not support his hypothesis. c. Fossil evidence showed that the continents were never joined. d. The climates of the continents have remained the same. ...
No Slide Title
... • The geologic history of the North American craton may be divided into two parts – relatively stable continental interior over which epeiric seas transgressed and regressed – mobile belts where mountain building occurred ...
... • The geologic history of the North American craton may be divided into two parts – relatively stable continental interior over which epeiric seas transgressed and regressed – mobile belts where mountain building occurred ...
Mr. Altorfer - Fair Lawn Public Schools
... South America and Australia-were closer to the South Pole 250 million years ago. Wegener suggested that these continents were covered ...
... South America and Australia-were closer to the South Pole 250 million years ago. Wegener suggested that these continents were covered ...
Plate Tectonics Chapter 10
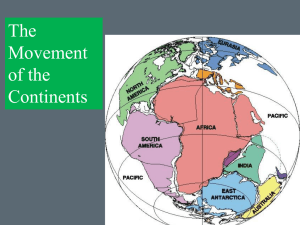
... Proposed Continental Drift Supercontinent- began breaking into smaller continents 250 million years ago Over millions of years continents drifted to present locations ...
... Proposed Continental Drift Supercontinent- began breaking into smaller continents 250 million years ago Over millions of years continents drifted to present locations ...
How Can Continents Move?
... 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift • The original supercontinent was named Pangaea by Wegener. Wegener also realized that other evidence also supported his theory. There were matching geologic features and rocks on different continents. There were matching fossils, like Mesosaurus, on differ ...
... 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift • The original supercontinent was named Pangaea by Wegener. Wegener also realized that other evidence also supported his theory. There were matching geologic features and rocks on different continents. There were matching fossils, like Mesosaurus, on differ ...
Drill
... Answer The asthenosphere is the soft putty-like solid layer of the mantle on which pieces of the lithosphere move. Those pieces are called tectonic plates. The asthenosphere carries around the tectonic plates through the process of convection. ...
... Answer The asthenosphere is the soft putty-like solid layer of the mantle on which pieces of the lithosphere move. Those pieces are called tectonic plates. The asthenosphere carries around the tectonic plates through the process of convection. ...
Slide 1
... features on opposite sides of the Atlantic ocean. 2. Match-up of glacier markings of the Southern Continents. 3. Symmetric location of alternating magnetic anomalies parallel with the mid-ocean ridge. 4. Volcanic hotspots and island chains. ...
... features on opposite sides of the Atlantic ocean. 2. Match-up of glacier markings of the Southern Continents. 3. Symmetric location of alternating magnetic anomalies parallel with the mid-ocean ridge. 4. Volcanic hotspots and island chains. ...
Plate Tectonics
... A ______________ was found in _________________ and ________________. A ______________was found on several continents. _____________ clues found on several continents indicate that these continents were covered with _______________. Rock Clues Similar ________ structures are found on different conti ...
... A ______________ was found in _________________ and ________________. A ______________was found on several continents. _____________ clues found on several continents indicate that these continents were covered with _______________. Rock Clues Similar ________ structures are found on different conti ...
mid-ocean ridges - River Mill Academy
... • Evidence of climates having at one time been the same in these puzzle piece areas. (Ex: The Karoo Desert in Africa shows marks that indicate the presence of Glaciers! Very cold in very hot?) • Resources not produced in certain biomes are mysteriously found there (Ex: coal found in the Artic when i ...
... • Evidence of climates having at one time been the same in these puzzle piece areas. (Ex: The Karoo Desert in Africa shows marks that indicate the presence of Glaciers! Very cold in very hot?) • Resources not produced in certain biomes are mysteriously found there (Ex: coal found in the Artic when i ...
Presentation
... Fossil Pattern: Fossils of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. Rocks: Rock formations and rock dating showed that these rocks and formations were the same age, thus leading scientists to believe that they were once connected into simi ...
... Fossil Pattern: Fossils of the same plant and animal species are found on continents that are on different side of the Atlantic. Rocks: Rock formations and rock dating showed that these rocks and formations were the same age, thus leading scientists to believe that they were once connected into simi ...
the geology of western north america (abridged version)
... Ocean’s basin is the successor of the original ocean which split Laurentia - our continent’s cratonic core - away from the rest of the Precambrian supercontinent Rodinia, an ocean that widened until in late Paleozoic time, it became Panthalassa, the World Ocean. Unlike the eastern side of the contin ...
... Ocean’s basin is the successor of the original ocean which split Laurentia - our continent’s cratonic core - away from the rest of the Precambrian supercontinent Rodinia, an ocean that widened until in late Paleozoic time, it became Panthalassa, the World Ocean. Unlike the eastern side of the contin ...
THE ORIGIN OF THE APPALACHIAN MOUNTAINS
... By about 550 million years ago the continents that we now know as North America, South America, Africa, and Europe - in those days they had somewhat similar shapes - were separated by the Iapetus Ocean, which very loosely might be likened to our Atlantic Ocean. These ancient continents each had thei ...
... By about 550 million years ago the continents that we now know as North America, South America, Africa, and Europe - in those days they had somewhat similar shapes - were separated by the Iapetus Ocean, which very loosely might be likened to our Atlantic Ocean. These ancient continents each had thei ...
Continental Drift Theory and Plate Tectonics
... Theory • The Shapes Match • The continents look as if they were pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle • The Plants and Animals Match • Identical fossil species along the coastal parts of Africa and South America. • Rocks Match - These broad belts match when the end of the continents are joined. ...
... Theory • The Shapes Match • The continents look as if they were pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle • The Plants and Animals Match • Identical fossil species along the coastal parts of Africa and South America. • Rocks Match - These broad belts match when the end of the continents are joined. ...
Cenozoic 1 - E. R. Greenman
... Cenozoic Plate Tectonics • The progressive fragmentation of Pangaea accounts for the present distribution of Earth's landmasses • Because the geographic locations of continents profoundly influence the atmosphere and hydrosphere, moving plates also directly affect the biosphere ...
... Cenozoic Plate Tectonics • The progressive fragmentation of Pangaea accounts for the present distribution of Earth's landmasses • Because the geographic locations of continents profoundly influence the atmosphere and hydrosphere, moving plates also directly affect the biosphere ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.