theory of continental drift
... • Theory of Plate Tectonics: Links together the ideas of continental drift and ocean floor spreading to explain how the Earth has evolved over time. – It explains the formation, movements, collisions, and destruction of the Earth’s crust – According to the theory the Earth’s uppermost layer, called ...
... • Theory of Plate Tectonics: Links together the ideas of continental drift and ocean floor spreading to explain how the Earth has evolved over time. – It explains the formation, movements, collisions, and destruction of the Earth’s crust – According to the theory the Earth’s uppermost layer, called ...
Answers to the study guide
... a. The solid inner core spins inside the liquid outer core creating a strong magnetic field that surrounds the Earth far out into space 10. Who proposed the theory of continental drift? a. Alfred Wegener 11. What is the theory of continental drift? a. The theory is that 225 million years ago there w ...
... a. The solid inner core spins inside the liquid outer core creating a strong magnetic field that surrounds the Earth far out into space 10. Who proposed the theory of continental drift? a. Alfred Wegener 11. What is the theory of continental drift? a. The theory is that 225 million years ago there w ...
activity 1
... Some years later, geologists hypothesized that in the ............................ of the Earth there are very slow ...................................................... : the deepest material, that is very hot, ........................... , becomes cool, flows laterally and then .................. ...
... Some years later, geologists hypothesized that in the ............................ of the Earth there are very slow ...................................................... : the deepest material, that is very hot, ........................... , becomes cool, flows laterally and then .................. ...
Chapter 17- Plate Tectonics
... • Rising part of convection current spreads out as it reaches the upper mantle and causes both upward and side to side forces – Lift and split the lithosphere at divergent boundaries, Material rising from mantle ...
... • Rising part of convection current spreads out as it reaches the upper mantle and causes both upward and side to side forces – Lift and split the lithosphere at divergent boundaries, Material rising from mantle ...
Geography Exercise ppt
... The Andes Mountains are part of the “Ring of Fire.” This region of the world has a high level of geographic instability due to the collision of the Earth’s tectonic plates. ...
... The Andes Mountains are part of the “Ring of Fire.” This region of the world has a high level of geographic instability due to the collision of the Earth’s tectonic plates. ...
Early Paleozoic - This Old Earth
... In some areas evaporites accumulated to 750 meters If this occurred due to evaporation of a single body of water, the water would have to have been ~1000 kilometers deep ...
... In some areas evaporites accumulated to 750 meters If this occurred due to evaporation of a single body of water, the water would have to have been ~1000 kilometers deep ...
Inside Earth: Chapter 1
... Wegener’s theory of continental drift? • Continental drift is the hypothesis that all the continents had once been joined together in a single landmass • The continents have slowly moved apart over Earth’s surface ...
... Wegener’s theory of continental drift? • Continental drift is the hypothesis that all the continents had once been joined together in a single landmass • The continents have slowly moved apart over Earth’s surface ...
Unit 7 Test Review
... -puzzle fit of South America and Africa -same fossil remains on some or all southern land masses -similar rock structure on different continents -tropical plant fossils found in Antarctica 9. Which two continents looked like they fit together like puzzle pieces? South America and Africa 10. What cau ...
... -puzzle fit of South America and Africa -same fossil remains on some or all southern land masses -similar rock structure on different continents -tropical plant fossils found in Antarctica 9. Which two continents looked like they fit together like puzzle pieces? South America and Africa 10. What cau ...
Inside Earth: Chapter 1
... What two examples of climate change did Wegener use to support his theory of continental drift? • The Island of Spitsbergen (Artic Ocean) has evidence of tropical plants • Deep scratches in rocks were found in South Africa • These scratches support evidence of ...
... What two examples of climate change did Wegener use to support his theory of continental drift? • The Island of Spitsbergen (Artic Ocean) has evidence of tropical plants • Deep scratches in rocks were found in South Africa • These scratches support evidence of ...
Earth`s Landforms
... Scientists believe long ago Earth was one large supercontinent known as Pangaea ...
... Scientists believe long ago Earth was one large supercontinent known as Pangaea ...
Geography: Comprehensive Final Study Sheet Name the 5 oceans
... Which leader invaded Russia in 1812? Which leader invaded Russia in 1941? What was the name for the German invasion of Russia? Lenin created which communist country in 1917? What system of government takes all the property and wealth of a country and manages it manages it? Communism is based on what ...
... Which leader invaded Russia in 1812? Which leader invaded Russia in 1941? What was the name for the German invasion of Russia? Lenin created which communist country in 1917? What system of government takes all the property and wealth of a country and manages it manages it? Communism is based on what ...
2.13 Divergent Plate Boundaries
... Split down the middle by a rift valley, which extrudes lava The Bay of Fundy began as a divergent plate boundary that never completely developed into an ocean ...
... Split down the middle by a rift valley, which extrudes lava The Bay of Fundy began as a divergent plate boundary that never completely developed into an ocean ...
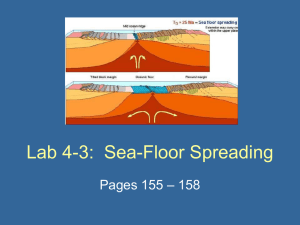
Lab 4-3: Sea-Floor Spreading
... – Ocean crust is created at a divergent boundary as plates pull apart and molten material rises from deep within the Earth. ...
... – Ocean crust is created at a divergent boundary as plates pull apart and molten material rises from deep within the Earth. ...
Lecture 2: Dynamic Earth: Plate Tectonics
... Seafloor spreading. Molten material of the mantle rises at mid-ocean ridges and spreads laterally; and the deep-ocean trenches are the sites where the ocean crust is drawn back to the mantle. ...
... Seafloor spreading. Molten material of the mantle rises at mid-ocean ridges and spreads laterally; and the deep-ocean trenches are the sites where the ocean crust is drawn back to the mantle. ...
Plate Tectonics
... convecting mantle • The upper mantle (asthenosphere) is moving do to convection currents. • This movement of the mantle causes Earth’s crust to move over time resulting in many of the landforms and geographic events that occur on Earth. ...
... convecting mantle • The upper mantle (asthenosphere) is moving do to convection currents. • This movement of the mantle causes Earth’s crust to move over time resulting in many of the landforms and geographic events that occur on Earth. ...
History in Geography
... Continental ice sheet covered parts of South America, southern Africa, India, and southern Australia about 300 million years ago Resultant glacial landforms exist in parts of the world today that are not covered by ice – like U-shaped valleys ...
... Continental ice sheet covered parts of South America, southern Africa, India, and southern Australia about 300 million years ago Resultant glacial landforms exist in parts of the world today that are not covered by ice – like U-shaped valleys ...
Science Affiliates Workshop NY Geology Powerpoint
... Taconic Orogeny Ordovician -Early Silurian ...
... Taconic Orogeny Ordovician -Early Silurian ...
Plate Tectonics Revolution: how it came about
... continental geology, leading to the "fixest" (versus "mobilist") synthesis that was the reigning theory for much of the first half of the last century. ...
... continental geology, leading to the "fixest" (versus "mobilist") synthesis that was the reigning theory for much of the first half of the last century. ...
The Late Paleozoic Era
... • When the 4000+ meter mountains are eroded away, all that remains are: • their crystalline roots, both metamorphic and intrusive igneous • Their erosion products in the clastic wedge ...
... • When the 4000+ meter mountains are eroded away, all that remains are: • their crystalline roots, both metamorphic and intrusive igneous • Their erosion products in the clastic wedge ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... Alfred Wegener's evidence for continental drift is shown on the cut-outs. Wegener used this evidence to reconstruct the positions of the continents relative to each other in the distant past. 3. Try to logically piece the continents together so that they form a giant supercontinent. ...
... Alfred Wegener's evidence for continental drift is shown on the cut-outs. Wegener used this evidence to reconstruct the positions of the continents relative to each other in the distant past. 3. Try to logically piece the continents together so that they form a giant supercontinent. ...
Week 21: Plate Tectonics
... The plume of rising magma is independent of the convection of the mantle. The lithospheric plate moves over the hot spot carrying volcanic islands away from the plume. Over time the volcanoes disconnect from the plume and become extinct. The islands farther from the hot spot are older and smaller. I ...
... The plume of rising magma is independent of the convection of the mantle. The lithospheric plate moves over the hot spot carrying volcanic islands away from the plume. Over time the volcanoes disconnect from the plume and become extinct. The islands farther from the hot spot are older and smaller. I ...
Plate Tectonics Tristan McMulen
... and the Cocos plate border the United States. We are in danger of earthquakes from the San Andreas fault and other fault lines going across the United States but, its inevitable whether it will durastically affect us. I predict that there is going to be a big landslide however that is in the very di ...
... and the Cocos plate border the United States. We are in danger of earthquakes from the San Andreas fault and other fault lines going across the United States but, its inevitable whether it will durastically affect us. I predict that there is going to be a big landslide however that is in the very di ...
1 Billion Years Ago 450 Million Years Ago 400 Million Years Ago
... standing near a soaring mountain range on a giant continent called Pangea. The rocks you see today were formed on the floor of an ancient ocean that divided that continent as plates in the Earth’s crust moved apart. Today’s Green Mountains formed as these plates eventually collided again, closing th ...
... standing near a soaring mountain range on a giant continent called Pangea. The rocks you see today were formed on the floor of an ancient ocean that divided that continent as plates in the Earth’s crust moved apart. Today’s Green Mountains formed as these plates eventually collided again, closing th ...
geology
... standing near a soaring mountain range on a giant continent called Pangea. The rocks you see today were formed on the floor of an ancient ocean that divided that continent as plates in the Earth’s crust moved apart. Today’s Green Mountains formed as these plates eventually collided again, closing th ...
... standing near a soaring mountain range on a giant continent called Pangea. The rocks you see today were formed on the floor of an ancient ocean that divided that continent as plates in the Earth’s crust moved apart. Today’s Green Mountains formed as these plates eventually collided again, closing th ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.