* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 7 Test Review
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Contour line wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
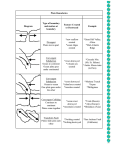
Plate Tectonics and Topography Review Review and study all of your notes and graded assignments. Study the following vocabulary: 1. Theory of plate tectonics- Theory that the Earth’s surface is made of large plates that move around, cause changes in position of the continents and oceans, and result in mountains, trenches, and volcanic rings 2. Convergent boundary- Created when tectonic plates collide with each other, producing mountain ranges, hills, etc 3. Divergent boundary- created when tectonic plates move away from each other, producing rifts, gaps, volcanic rings, etc. 4. Transform boundary- created when tectonic plates slide past each other caused by zig zags between faults 5. Mid ocean ridge- Underwater mountain ranges where the crust is spreading creating new ocean floor (divergent) 6. Trench- A deep depression of the sea floor caused by the subduction of one plate under another (convergent) 7. Ring of Fire- An area where volcanoes are concentrated on the edges of continents, along island chains or beneath the sea forming long mountain ranges- More than ½ of the world’s active volcanoes above sea level encircle the Pacific Ocean. 8. Topographic Map- maps that show the height, shape, etc., of the land in a particular area 9. Contour lines- lines that connect points that are of the same elevation on a topographic map Also, study the following questions and answers: 7. Who was the scientist who proposed the Continental Drift Theory? Alfred Wegener 8. What proofs did the scientist offer that proved his theory? -puzzle fit of South America and Africa -same fossil remains on some or all southern land masses -similar rock structure on different continents -tropical plant fossils found in Antarctica 9. Which two continents looked like they fit together like puzzle pieces? South America and Africa 10. What causes the movement of the plates? Where does this occur? Convection currents move the lithosphere and crust on top of the asthenosphere 11. Describe Pangaea and the rest of the world during its existence. Pangaea was one large land mass that was surrounded by a single large ocean 12. List each of the landforms created by a convergent boundary. Mountains on land (continental-continental), trenches (continental-oceanic), Ring of Fire/Volcanoes (continental-oceanic) 13. List each of the landforms created by a divergent boundary. Underwater mountain ranges, rift zones, underwater volcanoes (which eventually cause islands), mid-ocean ridges 14. What are the plates made up of? Crust and lithosphere 15. What do the plates move on? The asthenosphere which is the upper layer of the mantle 16. Where would newly formed crust be found? On the ocean floor next to divergent boundaries that have spread apart and added lava to make new land 17. How are islands made? They are created when a divergent boundary beneath the ocean spreads, allowing magma to flow upward to the surface, which then adds enough new land to the sea floor until it reaches the surface and continues to grow. 18. Explain the continued growth of the Himalayan Mountains. The Himalayan Mountains are caused by the Indian and Eurasian plates collision that are still moving toward each other today, causing them to continue to grow. 19. What natural disasters are created by tectonic plate movement? Volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis (caused by earthquakes) 20. On a topographic map, how do you determine a steep slope? The contour lines are closer together 21. On a topographic map, how do you determine a gently or low slope? The contour lines are farther apart 22. On a topographic map, how do you determine the flow of a river? The river flows in the opposite direction to the “V” that shows the riverRemember: rivers normally flow downhill Use the following diagram to answer the questions below. 23. Looking at the Roman Numerals, where would the newest ocean floor be found? III 24. Looking at the Roman Numerals, where would the oldest ocean floor be found? II 25. Looking at the letters in the diagram above, where would you find a convergent boundary? A and D 26. Where would you find a divergent boundary? C