* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sea Floor
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Polar ecology wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
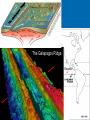
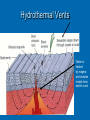
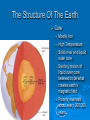
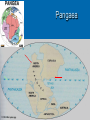
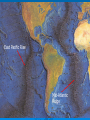
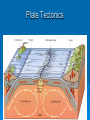
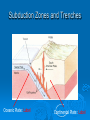
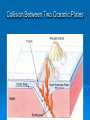
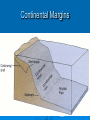
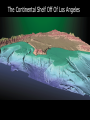
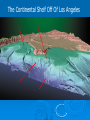
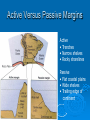
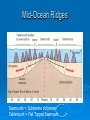
The oceans cover 71% of the earth’s surface The Four Large Ocean Basins The Arctic Ocean Shallow Low Salinity Diluted by large rivers About half covered with permanent ice Low species diversity Hallmark animals include polar bear and walrus Walruses were once common around the perimeter of the Arctic, but large-scale hunting has greatly reduced their numbers Features of Atlantic Ocean Georges and Grand Banks Great expanses of shallow water that supported cod fisheries for centuries North Sea One of most thoroughly studied marine waters on earth The Manatee (36,163 ft.) The Pacific Ocean Feb 1977 the submersible Alvin dived to a depth of 2500m over the Galapagos ridge. That is when hydrothermal vents were discovered. The Galapagos Ridge Equator The deep sea submersible Alvin Hydrothermal Vents Water is heated by magma and absorbs metals from earth’s crust Marine Iguana The Indian Ocean: Relict Species Coelacanth Stromatolites Drive from Perinet to Toamasina. Fly to Maroantsetra. Drive to Relais du Masoala Hotel. Two hour boat Ride to Ecolodge on Masoala Peninsula. Hotel Ecolodge The Four Large Ocean Basins The Ocean Basins Are Interconnected The World Ocean The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) The Southern Ocean Formed about 25 MYA when Australia and South America separated from Antarctica Isolated the Antarctic continent from warmer waters to the north and is partially responsible for the formation of Antarctica's permanent ice cover. The northern boundary is called the Antarctic Convergence or the Polar Front. The Southern Ocean Antarctic Convergence Divides warm surface waters of Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans from cold polar waters. Abundant krill Summer feeding area for baleen whales Large Scale Distribution of Antarctic Krill The Antarctic Convergence Krill are a keystone species in the Antarctic food web. Krill are crustaceans with several larval stages in their life cycle. Some of the larval stages feed on algae that grow on the lower surface of sea ice. One of the factors that determines the annual abundance of krill is the extent of sea ice in winter. Global warming may have significant impacts on krill abundance. Baleen Whales Crabeater Seals Leopard Seals Adelie Penguins Chinstrap Penguins Gentoo Penguins Krill – Euphausia superba Phytoplankton The Sun Light E Photosynthesis Food E The top predators of the Antarctic Peninsula are seabirds and seals. The Crabeater Seal is a Krill Specialist Crabeater seals are krill specialists. Their entire “terrestrial” existence is spent on ice floes, not land. Their populations may be increasing due to an increase in krill abundance associated with the decline of baleen whales. The Structure Of The Earth Core Mostly iron High Temperature Solid inner and liquid outer core Swirling motion of liquid outer core believed to be what creates earth’s magnetic field Polarity reversals about every 300,000 years The Structure Of The Earth Mantle Solid High temperature – Near the melting point of rocks It flows Iron and magnesium silicates The Structure of the Earth Crust Outermost layer Extremely thin Composition varies Continental Versus Oceanic Crust Continental Granite Low density Light Thick (20 – 50 km) Can be old (3.8by) Note: Density = Mass Volume Oceanic Basalt High density Dark Thin (5 km) Young (<200my) The Lithosphere Lithosphere = Outer layer of mantle + Crust The pates involved in plate tectonic motion are plates of the lithosphere Plates of the Lithosphere Principles of Plate Tectonics The plates of the lithosphere carry the continents like passive passengers Pangaea • 200 million years ago all the continents were combined into one landmass Pangaea The average rate of plate movement today is between 2 and 12 centimeters (1 an 5 inches) per year East Pacific Rise Mid-Atlantic Ridge Plate Tectonics Subduction Zones and Trenches Oceanic Plate: Label Continental Plate: Label Collision Between Two Oceanic Plates Island arc at trench Volcano rising from hotspot Divergent __________ Boundary Examples? Divergent Boundaries Convergent __________ Boundary Trenches and volcanoes are associated with this type of boundary Oceanic – Continental Convergence Peru – Chili Trench Andes Mountains Transform Boundaries The San Andreas Fault occurs at a transform boundary Evidence For Plate Tectonics Fit of continents Matching sequences of rocks Fossils Mid-Ocean Ridges Sediment gets (thicker/thinner?) as you move away from crest of mid-ocean ridge Rocks get (older/younger?) as you move away form the ridges Fit, Rocks, and Fossils Mesosaurus Fossils Link Africa and South America Geological Provinces of the Ocean Continental Margins Continental Shelf Gently sloping Exposed during times of low sea level Biologically richest part of ocean 8% of ocean surface area Submarine canyons Ends as shelf break The Continental Shelf Off Of Los Angeles Continental Slope Steep Edge of continent Along active margins the slope descends into submarine canyons Continental Rise Sediment deposits on ocean floor Found on passive margins (not active margins) The Continental Shelf Off Of Los Angeles Active Versus Passive Margins Active • Trenches • Narrow shelves • Rocky shorelines Passive • Flat coastal plains • Wide shelves • Trailing edge of continent Mid-Ocean Ridges Seamounts = Submarine Volcanoes Tablemount = Flat Topped Seamount Plankton Arrow worm Copepod Cyanobacteria (P/S) 10% Efficient Fish Arrow Worms The Sun 10% Efficient 10% Efficient 1-2% Efficient Copepods Herbivorous zooplankton Diatoms and Dinoflagellates 10% Efficient Plankton versus Nekton Plankton Weak swimmers Ride the ocean currents Nekton Strong swimmers Can swim against the currents Phytoplankton versus Zooplankton Photosynthetic (P/S) Nonphotosynthetic (non-P/S) Autotrophic Heterotrophic Diatoms and Dinoflagellates Copepods Brown Pelican 10% Efficient Large Carnivorous Fishes The Sun 1-2% Efficient Small carnivorous fishes Herbivorous Zooplankton 10% Efficient 10% Efficient 10% Efficient